|
Synthesis Report 91
2012 State Policies for Accommodations Used to Deliver Assessments Orally
Sheryl S. Lazarus, Martha L. Thurlow, and Aleksis Kincaid
August, 2013; revised January 2014
All rights reserved. Any or all portions of this document may be reproduced and distributed without prior permission, provided the source is cited as:
Lazarus, S. S., Thurlow, M. L., & Kincaid, A. (2013). 2012 state policies for accommodations used to deliver assessments orally (Synthesis Report 91). Minneapolis, MN: University of Minnesota, National Center on Educational Outcomes.
Table of Contents
Executive Summary
The National Center on Educational Outcomes (NCEO) has been tracking and analyzing states' policies on assessment accommodations since 1992. The purpose of this report is to update information on how accommodations used to deliver assessments orally (Human Reader, Text to Speech, Pre-recorded Audio) were included in state policies in 2012.
The U.S. Department of Education provided funding through Race-to-the-Top Assessment Program awards to two consortia of states--Partnership for Assessment of Readiness for College and Careers (PARCC) and Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium (Smarter Balanced)--to develop and implement next generation general assessments based on common core state standards (CCSS) that will be rolled out in 2014-15. The results of this analysis provide information about current state policies. The consortia are developing new policies, and the results of this analysis can help inform planning for the transition to them.
Key findings included:
- Most states allowed directions to be read aloud by a Human Reader on reading/English language arts (ELA) (n=36) and math assessments (n=37); some states also had policies that allowed directions to be delivered orally by Text to Speech or Pre-recorded Audio.
- For reading/ELA assessments, many states' policies only allowed the delivery of assessment items or passages orally in certain circumstances or with implications for scoring.
- Some state policies addressed who could deliver the accommodation and what test security measures needed to be in place.
- The policies of a few states indicated that Text to Speech was preferred over Human Reader due to test security issues and to help ensure standardized delivery.
- The policies of a few states also indicated how accessibility tools that were different from those in the test platform, but which were normally used for instruction, could be used.
Top of Page | Table of Contents
Overview
Both the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) of 2004 and Title I of the 2001 reauthorization of the Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA) require that all students, including students with disabilities, participate in state assessments used for accountability. Some students need accommodations to meaningfully access assessments. State policies provide information about accommodations that may be used (Thurlow, Thompson, & Lazarus, 2006; Thurlow, 2007).
This report provides a snapshot of how accommodations used to deliver assessments orally (Human Reader, Text to Speech, Pre-recorded Audio) were included in state policies in 2012. Since 1992 the National Center on Educational Outcomes (NCEO) has been tracking and analyzing state policies that address accommodations for students with disabilities, with the most recent update analyzing 2009 policies (Christensen, Braam, Scullin, & Thurlow, 2011). Each time that NCEO examined state polices, there have been significant changes (Christensen et al., 2011; Christensen, Lazarus, Crone, & Thurlow, 2008; Clapper, Morse, Lazarus, Thompson, & Thurlow, 2005; Lazarus, Thurlow, Lail, Eisenbraun, & Kato, 2006; Thurlow, House, Boys, Scott, & Ysseldyke, 2000; Thurlow, Lazarus, Thompson, & Robey, 2002; Thurlow, Scott, & Ysseldyke, 1995; Thurlow, Seyfarth, Scott, & Ysseldyke, 1997; Thurlow, Ysseldyke, & Silverstein, 1993).
The current report is distinct from previous reports. This report is the first of several reports that present the results of the most recent analyses of participation and accommodations policies. Past reports were comprehensive reports that tracked all accommodations, as well as participation policies. Over time these reports became large and cumbersome. To better meet the needs of report readers, we are publishing several smaller reports for this update--each focusing on specific accommodations, policies, or issues.
For this report, the specific research questions we sought to answer were:
- How were the three accommodations used to deliver an assessment orally (i.e., Human Reader, Text-to-Speech software, and Pre-recorded Audio) included in state policies for reading/English language arts (ELA) and math assessments in 2012?
- Have state policies for accommodations used to deliver an assessment orally changed substantially since 2009?
Similar to the 2009 report, this analysis included the 50 regular states and the District of Columbia. Throughout this report, figures are based on a total of 51 states.
This analysis did not attempt to determine the degree to which state policies complied with federal requirements under the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act (IDEA) of 2004 or Title I of the 2001 reauthorization of the Elementary and Secondary Education Act (ESEA). Instead, it is a descriptive analysis of the written policies that states have for the oral administration of assessments used for accountability.
Top of Page | Table of Contents
Process Used to Review State Policies
The procedures used for this report are similar the procedures used for previous participation and accommodation policy reports produced by NCEO (see Christensen et al., 2011 for details). Data for this report were obtained through the examination and analysis of publicly available information, including accommodations manuals or other policy documents, on state department of education websites. Accommodation guidelines for the 2012 school year were gathered from states' websites between January and April, 2012. The information from each state was coded based on information in the state policy for accommodations used to deliver directions, items, and passages orally on state reading/ELA and math assessments used for accountability purposes. Directions, items, and passages are defined as:
- Directions: The written or scripted instructions that provide a student with information about how to take, and respond to, the assessment.
- Items: The individual questions and answer choices.
- Passages: Text that provides the context for items.
The three accommodations included in this report are defined as:
- Human Reader: The use of an adult reader (e.g., teacher, aide) to deliver orally all or part of an assessment to a student.
- Text to Speech: The use of software to deliver orally part or all of an assessment to a student. This accommodation encompasses several terms that are found in state policies: "text to speech," "screen reader," and "computer reader."
- Pre-recorded Audio: The use of audio CDs and tape cassettes to deliver all or part of an assessment to a student. This includes both those provided by the State Education Agency (SEA) and those created by Local Education Agencies (LEAs).
States' policies were analyzed in terms of the restrictions placed on accommodations: Allowed (A) - if the accommodation is used, the student receives the score he or she earned, and the score applies toward accountability measures; Allowed in Certain Circumstances (AC) - the accommodation is allowed for some grade levels of the assessment but not others, or the assessment stipulates specific disability restrictions (e.g., only for a student who is blind and cannot read braille) for the use of the accommodation; Allowed with Implications for Scoring (AI) - if the accommodation is used, the resulting student score will not be considered valid, and will not count toward accountability measures (e.g., listed as a modification); Prohibited (P) - the accommodation is not allowed on state assessments; No Policy (NP) - The state did not list any policy on the specific accommodation.
If a state's policy referred to reading and did not specify a delivery method, it was assumed that the policy was referring to a human reader. When states mentioned an oral delivery accommodation for math or reading, but did not indicate whether it was for items or passages, both were coded the same. For example, if a state's policy indicated that text to speech was allowed, text to speech was coded as allowed for both items and passages.
If a state's policy specifically indicated that an accommodation was allowed for items but did not mention passages, passages would be coded as no policy. For example, if a policy stated that read aloud by a human reader was allowed for items, but said nothing about passages; human reader would be coded as allowed for items and that there was no policy for passages. Similarly, if a state mentioned an accommodation for passages but did not mention items, items would be coded as no policy.
Accommodations for oral administration were only coded when states listed them as an accommodation for students. Several states listed reading the directions aloud as a standard practice for all students; for those states, it was not considered an accommodation when coding the data.
After the information was compiled, states were sent digital forms of their state profile for review. The states were asked to indicate whether the information in their profile was: (a) accurate, or (b) inaccurate. If a state found an error in its profile, it was asked to provide documentation of publicly available information to support the requested revision before a change to the state profile was accepted. In total, 18 states responded to the request to verify information on their states' policies; of those 8 (44%) accepted the initial state profile NCEO provided, and 10 (56%) provided evidence for revisions to be made to their state profiles. For details about the documents that were used for this analysis see Appendix A.
All comparisons to 2009 state policy were based on information in Christensen et al. (2011). Longitudinal comparisons are made only for the use of a Human Reader to deliver accommodations orally because in the previous report Text to Speech and Pre-recorded Audio were part of the aggregate category of "Assistive Technology."
Top of Page | Table of Contents
Results
All states had policies that addressed oral administration accommodations for students with disabilities in reading and math. The majority of states' policies were focused on the Human Reader accommodation; fewer states had policies for Text to Speech or Pre-recorded Audio. Details and specifications are presented in Appendix B.
Accommodations for Directions
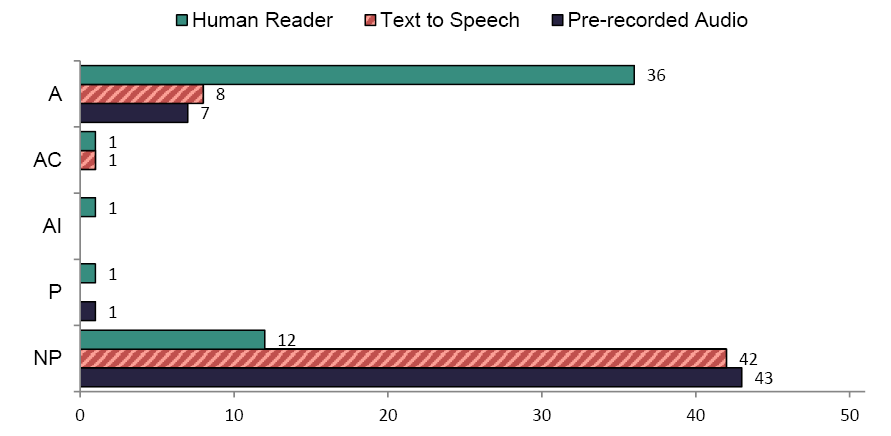
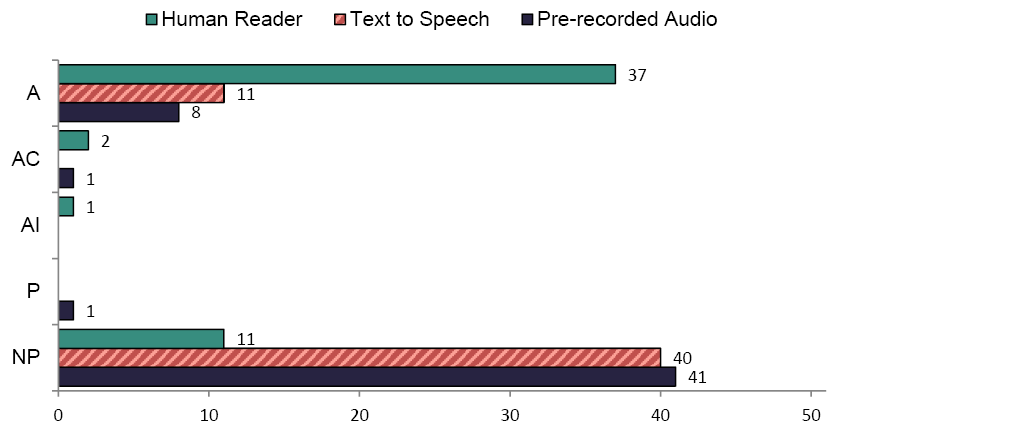
Figures 1 and 2 show states' policies on the delivery of directions orally for reading/ELA and math, respectively. The majority of states had policies on directions delivered orally by a Human Reader for reading/ELA and math, while more than 40 states had no policy on directions delivered orally by Text to Speech or Pre-recorded Audio.
As shown in Figure 1, the delivery of directions by a Human Reader was allowed in 36 states for reading/ELA; it was allowed in 37 states for math. A few states allowed this accommodation in certain circumstances (Reading/ELA: n=1; Math: n=2).
Eight states allowed the Text-to-Speech accommodation for directions on the reading/ELA assessment, and eleven states allowed it for directions on the math assessment. Text to Speech for directions was allowed in certain circumstances in one state for reading/ELA, while no states listed it as allowed in certain circumstances for math.
Seven states allowed the use of the Pre-recorded Audio accommodation for directions on the reading/ELA assessment and 8 states allowed Pre-recorded Audio for the math assessment. The majority of states had no policy on the use of Pre-recorded Audio (reading/ELA: n=43; math: n=41).
Figure 1. Oral Delivery of Directions-Reading/ELA Assessment
Note: A= Allowed, AC=Allowed in Certain Circumstances, AI = Allowed with Implications, P = Prohibited, NP = No Policy. N=51.
Figure 2. Oral Delivery of Directions-Math Assessment
Note: A= Allowed, AC=Allowed in Certain Circumstances, AI = Allowed with Implications, P = Prohibited, NP = No Policy. N=51.
Changes Since 2009
The number of states that allowed directions to be delivered orally by a Human Reader for reading/ELA increased from 30 in 2009 to 36 in 2012, and decreased from 38 to 37 in math. From 2009 to 2012 the number of states that allowed the accommodation in certain circumstances decreased from three to one for reading/ELA, and from four to two in math. In 2009, three states prohibited the use of the Human Reader for directions for reading/ELA, while in 2012 only one state prohibited it. The number of states with no policy for the Human Reader accommodation in reading/ELA decreased by one from 2009 to 2012, and increased by two in math.
Accommodations for Test Items
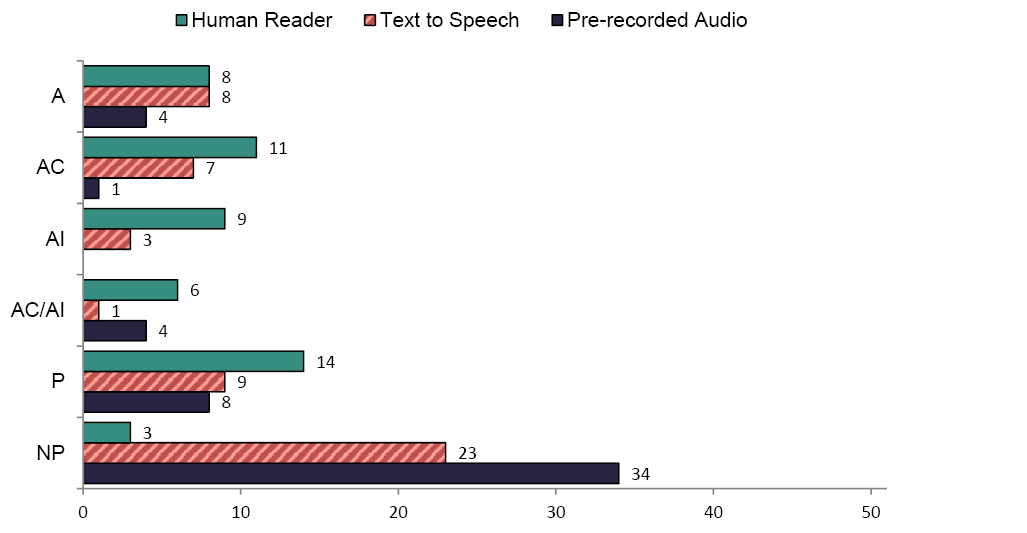
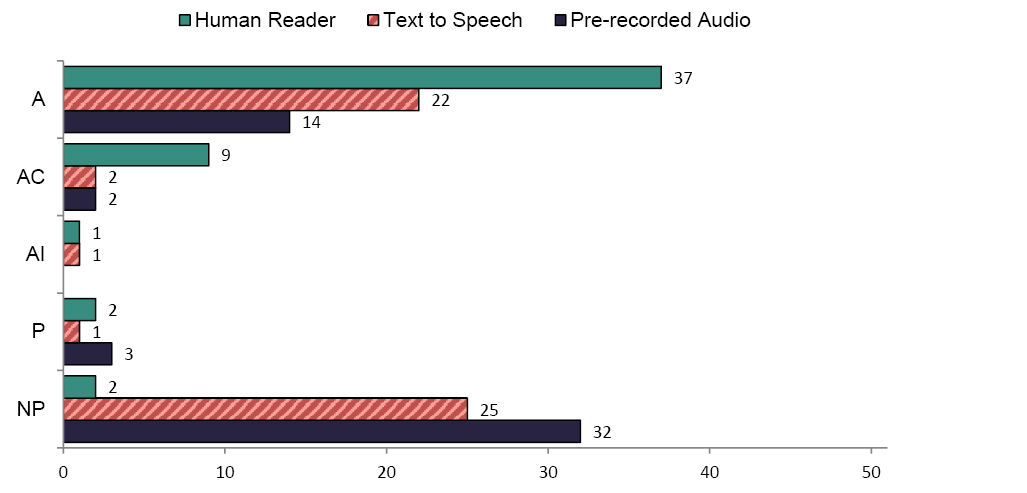
Figures 3 and 4 summarize states' policies on the oral administration of test item questions for reading and math. The majority of states had policies for delivering test items orally by a Human Reader, while about half of the states had policies on the use of Text to Speech. Two-thirds of the states had no policy on the use of Pre-recorded audio for reading/ELA and math.
Figure 3. Oral Delivery of Items-Reading/ELA Assessment
Note: A= Allowed, AC=Allowed in Certain Circumstances, AI = Allowed with Implications, P = Prohibited, NP = No Policy. N=51.
Figure 4. Oral Delivery of Items-Math Assessment
Note: A= Allowed, AC=Allowed in Certain Circumstances, AI = Allowed with Implications, P = Prohibited, NP = No Policy. N=51.
Most states had a policy for the delivery of items by a Human Reader. It was allowed in 8 states for reading/ELA, while it was allowed in 37 states in math. Some states allowed the accommodation in certain circumstances or had implications for scoring. For example, South Dakota's policy for reading/ELA indicated that the accommodation could only be used in certain circumstances:
Readers may only be provided when identified on a student's IEP or Section 504 plan to allow students with disabilities the opportunity to demonstrate their aptitude and achievement in testing situations rather than reflecting their impairment.
For reading/ELA, 14 states prohibited oral administration of questions by a Human Reader, while only 2 states prohibited the accommodation for math.
Of the states with policies for Text to Speech for the administration of questions, 8 states allowed its use in reading/ELA, while 22 states allowed its use in math. Text to Speech for questions was allowed in certain circumstances in 7 states in reading/ELA, while it was allowed in 2 states for math. Nine states prohibited the use of Text to Speech for the oral administration of items in reading/ELA, while 1 state prohibited its use in math.
Some states made a distinction between the oral administration of questions by a Human Reader and the Text-to-Speech accommodation. For example, Hawaii's policy indicated that:
TAs [Test administrators] may no longer read or reread mathematics or science test questions and answer options to any students. The text-to-speech feature will automatically be enabled for all students in TIDE [Test Information Distribution Engine]…. This will allow them to have questions or answer options read or reread to them. This procedure will ensure that all students have the test questions and response options read aloud using the same tone of voice and inflection for all words and symbols included in charts, tables, and graphs.
Several states indicated that the Human Reader accommodation should only be used if the student was unable to use the Text-to-Speech software. For example, Delaware stated:
The human reader accommodation and the TTS [Text-to-Speech] accommodation are not interchangeable and not considered to be the same accommodation. Only administer the human reader accommodation if the student is documented to receive the human reader accommodation. Students with TTS only may not receive assistance from a human reader.
Some states had identical specifications for the Human Reader accommodation and the Text-to-Speech accommodation, but required that the students have certain characteristics to use one or the other. For example, Georgia stated that the delivery of reading passages orally was:
Restricted to grades 3-8 and may be considered when both the following conditions apply: (1) The student has a specific disability that severely limits or prevents him or her from decoding text at any level of difficulty, even after varied and repeated attempts to teach the student to do so (i.e., the student is a non-reader, not simply reading below grade level); (2) The student has access to printed materials only through a reader or other electronic format during routine instruction.
Most states had no policy on the oral administration of items using Pre-recorded Audio for either reading/ELA (n=34) or math ( n=32). For those states with policies, 4 states allowed the use of Pre-recorded Audio in reading/ELA, while 14 states allowed its use in math. One state allowed the use of Pre-recorded Audio to orally administer questions in certain circumstances in reading/ELA, while 2 states allowed its use in certain circumstances in math. Some states provided detailed specifications about how Pre-recorded Audio should be administered. For example, the Maryland policy indicated that:
Audio versions of tests and other written materials need to be supplemented with a print or Braille version of the text so that a student can have access to complicated graphic material.
Several states prohibited the use of the Pre-recorded Audio accommodation to administer questions orally on the reading/ELA assessment (n=8) or the math assessment (n=3).
Changes Since 2009
The number of states that allowed a Human Reader to administer test items orally in reading/ELA (n=8) and math (n=37) remained the same from 2009 to 2012. The number of states that allowed a Human Reader to administer the assessment orally with implications for scoring increased from 2009 to 2012 in reading/ELA from 5 to 9, and in math from 0 to 1. The number of states that prohibited the Human Reader accommodation in math increased from 0 to 2 between 2009 and 2012.
Accommodations for Passages
Figures 5 and 6 summarize state policies on the delivery of passages orally. A few states did not have policies for delivering reading passages orally by a Human Reader (n=7); however, half of states had no policy for the use of Text to Speech (n=24); and more than two-thirds of states had no policy for the use of Pre-recorded Audio (n=37). In math, the same trends were reflected, with a slightly higher number of states that did not have policy for the use of a Human Reader (n=13).
Two states allowed reading passages to be orally administered by a Human Reader. For example, Kentucky's policy allowed this accommodation for reading assessments: "Reading assessments may be read to a student on the premise that the intent of reading is to measure comprehension." Twenty-eight states allowed oral administration of passages using a Human Reader for math.
Six states allowed the delivery of passages orally using a Human Reader in certain circumstances in reading/ELA, while eight states allowed the accommodation in certain circumstances in math. There were 12 states that allowed the accommodation with implications for scoring in reading/ELA, while one state allowed the accommodation with implications for scoring in math. Only 5 states allowed the administration of reading passages orally using a Human Reader in certain circumstances and with implications for scoring in reading/ELA.
Nineteen states prohibited the oral delivery of passages using a Human Reader in reading/ELA, while only one state prohibited the accommodation in math. For example, the Kansas policy for the reading assessment indicated that:
Absolutely nothing from a reading passage may be read or pronounced, including single words. If reading passages to a student on the state reading assessment is allowed on the student's plan, the student will then be counted as not participating.
Figure 5. Oral Delivery of Reading Passages-Reading/ELA Assessment
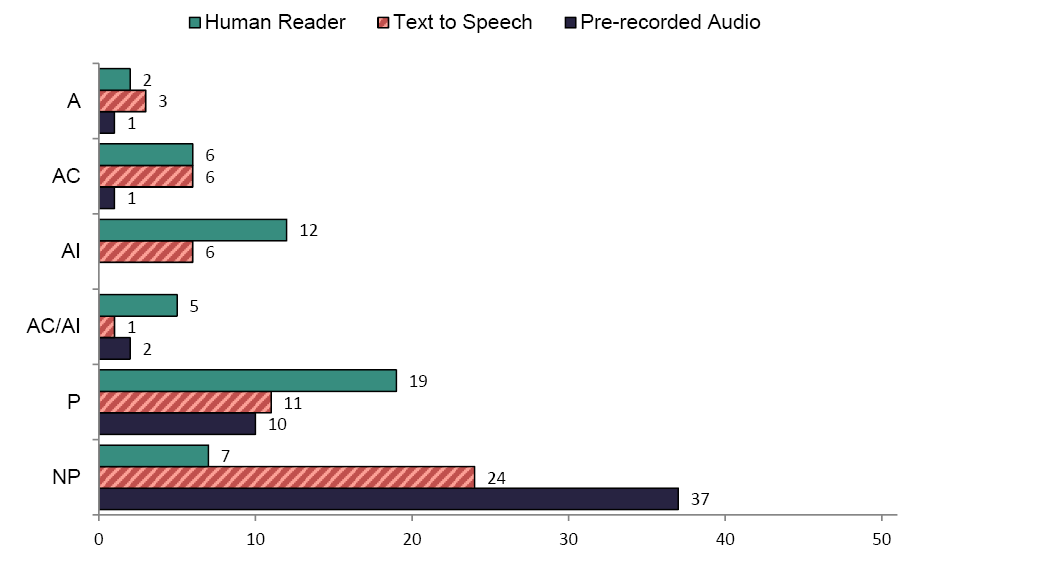
Note: A= Allowed, AC=Allowed in Certain Circumstances, AI = Allowed with Implications, P = Prohibited, NP = No Policy. N=51.
Figure 6. Oral Delivery of Reading Passages-Math Assessment
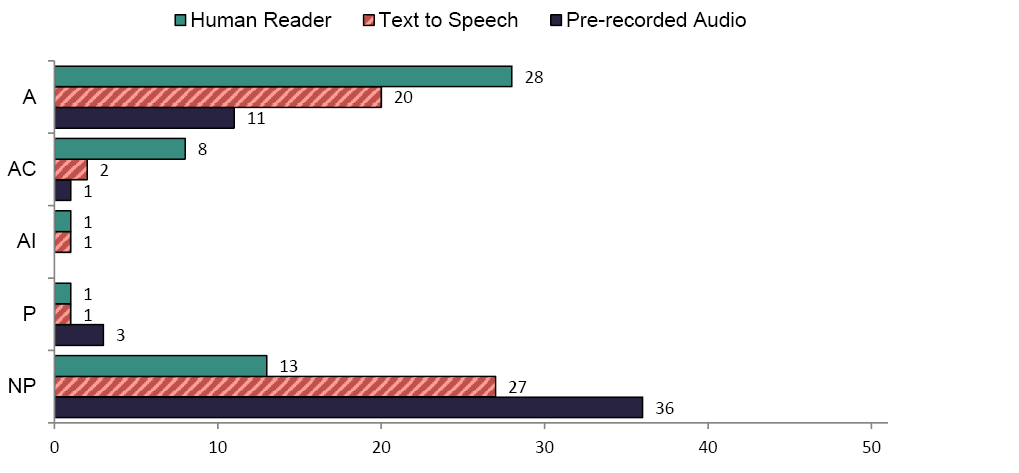
Note: A= Allowed, AC=Allowed in Certain Circumstances, AI = Allowed with Implications, P = Prohibited, NP = No Policy. N=51.
About half of the states had no policy on the administration of passages orally using Text to Speech (reading/ELA: n=24, math: n=27). Three states allowed the use of Text to Speech to orally administer passages in reading/ELA, while 20 states allowed its use for math. There were 6 states that allowed the use of Text to Speech in certain circumstances to administer passages orally in reading/ELA, and 2 states that allowed its use in certain circumstances in math. Six states allowed the use of Text to Speech with implications for scoring in reading/ELA, and one state allowed its use with implications for scoring in Math. Eleven states prohibited the use of Text to Speech to administer passages orally in Reading/ELA, while one state prohibited its use in math.
The majority of states had no policy for the administration of passages orally using Pre-recorded Audio (reading/ELA: n=37; math: n=36). For states with a policy on the use of Pre-recorded Audio to administer passages orally, one state allowed its use in reading/ELA, while 11 states allowed its use in math. There was one state that allowed its use in certain circumstances on the reading/ELA assessment, and one state that allowed its use in certain circumstances in math. Ten states prohibited the use of Pre-recorded Audio to administer passages in reading/ELA, while 3 states prohibited its use in math.
Changes Since 2009
The number of states that allowed passages to be administered orally for reading/ELA using a Human Reader remained the same (N=2) from 2009 to 2012, and increased for math from 13 to 28. From 2009 to 2012 states that allowed a Human Reader to read passages with implications for scoring increased from 7 to 12 in reading/ELA, and from 0 to 1 in math. The number of states that allowed it in certain circumstances and with implications for scoring increased from 3 to 5 in reading/ELA, and decreased from 1 to 0 in math from 2009 to 2012. The number of states that prohibited the use of a Human Reader to read passages on the reading/ELA assessment increased from 15 to 19, and remained the same for math (n=1) in 2009 and 2012. The number of states that had no policy for the administration of passages orally using Human Readers decreased in reading/ELA (from 20 to 7) and math (from 32 to 13) from 2009 to 2012.
Top of Page | Table of Contents
Summary and Conclusions
Since 2009 states' policies for accommodations that are used to deliver assessments orally for students with disabilities in reading/ELA and math have continued to evolve. Most states have policies for the use of Human Readers, and some states have policies for Text to Speech. Depending on the target of the accommodation (e.g., directions, items, or passages) and the content area (e.g., reading/ELA, math), the number of states without policies on the use of Text to Speech ranged from 23 to 42. A few states have policies for Pre-recorded Audio.
Most states allowed the use of a Human Reader to deliver directions orally on both the reading/ELA (n= 36) and math (n=37) assessment. Human Readers were allowed to deliver items orally in all circumstances and with no implications for scoring in 37 states on the math assessment, but only in 8 states on the reading/ELA assessment. The delivery of items orally by a Human Reader on the reading/ELA assessment was allowed in certain circumstances in 11 states on reading and 9 states on math assessments; it was allowed with implications for scoring in 9 states on the reading/ELA assessment and by 1 state on the math assessment.
Likewise, states' policies for Text to Speech and Pre-recorded Audio generally allowed directions to be delivered orally. Many states with policies also allowed Text to Speech and Pre-recorded Audio for items and passages. On reading/ELA assessments there was a split--some state policies allowed the delivery of items and passages orally, while others only allowed it in certain circumstances or with implications for scoring.
Regardless of the mode of delivery, many states' policies addressed the construct being assessed on the reading/ELA assessment, and made a distinction between decoding and comprehension. Because the constructs being assessed differed across grades, the policies of a few states indicated that oral delivery was allowed in certain grades (typically the higher grades), but not in others (typically the lower grades).
States are becoming more aware of test security issues. There may be more security issues when a human is used to deliver an accommodation than when technology is used to deliver the accommodation. Some state policies contain guidelines for the delivery of the assessment orally by a Human Reader that address security issues. For example, according to the New Jersey policy: "ONLY the teacher who must read the test items aloud or sign is permitted to have a test booklet assigned to him/her for this task." A few policies also addressed security issues related to Pre-recorded Audio. For example, the South Carolina policy indicated that, "Audiotapes and CDs used in statewide assessments are secure materials and must be signed out, collected, and kept in a secure location."
For those states with policies for both Human Readers and Text to Speech, some state policies indicated that the use of Text to Speech was the preferred method of delivery. Text to Speech can deliver all assessments with the same intonation to all students, decreasing the chance that a student would infer an item answer from a human reader's emphasis of an item choice. States also have better control over which parts of an assessment are delivered orally with Text to Speech because they can simply not allow the software to run for certain portions of the test. There may also be fewer security issues with Text to Speech because a Human Reader is not being used.
Some states' policies indicated who could administer the Human Reader accommodation. For example, Connecticut's policy stated, "Reader for test items (including directions) by certified staff only," while Colorado's policy indicated that this accommodation should be provided by "a trained test proctor." Some policies included guidelines designed to help ensure that the accommodation was administered appropriately and consistently. For example, the South Carolina policy indicated that:
A qualified person may be provided to read orally to students who are unable to decode text visually. Readers should use even inflection so that the student does not receive any cues by the way the information is read. It is important for readers to read test items/questions and text word for word exactly as written. Readers may not clarify, elaborate, or provide assistance to students. Readers need to be familiar with the terminology and symbols specific to the content. This is especially important for high school mathematics and science. Graphic materials may be described but should also be made available in print or tactile formats. Readers must be provided to students on an individual basis--not to a group of students. A student should have the option of asking a reader to slow down or repeat text.
Past research has provided indications that a relatively small number of students need the delivery of assessments orally to meaningfully access an assessment (see for example, Lazarus, Thurlow, Rieke, Halpin, & Dillon, 2012). Some states' policies addressed concerns that there may sometimes be a tendency to over-assign these accommodations to students for whom its use is inappropriate by explicitly indicating in their policy that the accommodation should not be over-used. For example, the Montana policy for oral delivery by a Human Reader stated:
This accommodation should be a low-incidence accommodation. Please consider the following to determine the appropriateness of this accommodation for each student. Assessment results are available to support the determination that the student's disability precludes or severely limits the student's ability to gain meaning from written language. There is documentation of remedial reading services and/or special education and supplementary aids and services. Through classroom assessment, it has been determined and documented that the student benefits from oral presentation as her/his way of learning.
Technology enhanced assessments sometimes have Text-to-Speech accessibility tools embedded in the test platform. This helps ensure consistency of delivery. These embedded tools may differ from the Text-to-Speech accessibility tools that a student uses during instruction. Sometimes the tools the student typically uses are disabled due to test security concerns, which can create accessibility issues (National Center on Educational Outcomes, 2012). To address this issue, some states' policies explicitly allowed students to use familiar Text-to-Speech software. For example, Pennsylvania's policy indicated that:
Requirements for use of screen or text reader: The student uses an electronic reader routinely during classroom instruction and assessment in this subject both before and after the test is administered; and the student is severely limited or prevented from participating in statewide tests without the use of this accommodation (i.e., student is not simply performing below grade-level expectations); and the use of an electronic reader is documented in the student's IEP or 504 plan; and PDE must approve the computer application and all program functions prior to PSSA and PSSA-M test window.
The U.S. Department of Education provided funding through Race-to-the-Top awards to two consortia of states--Partnership for Assessments of Readiness for College and Careers (PARCC) and Smarter Balanced Assessment Consortium--to work together to develop and implement next generation general assessments based on common core state standards that will be rolled out in 2014-15. The policies for accommodations used to deliver assessments orally being developed by the consortia may differ substantially from the policies currently in place in some states. States and the consortia will need to figure out how to successfully transition to the new policies. For example, teachers may need training on how to select, implement, and evaluate accommodations used to deliver an assessment orally. The evolving assessment system provides a wonderful opportunity to thoughtfully develop a plan for transitioning to new policies that will result in improved accommodations decision making.
Top of Page | Table of Contents
References
Christensen, L. L., Braam, M., Scullin, S., & Thurlow, M. L. (2011). 2009 state policies on assessment participation and accommodations for students with disabilities (Synthesis Report 83). Minneapolis, MN: University of Minnesota, National Center on Educational Outcomes.
Christensen, L. L., Lazarus, S. S., Crone, M., & Thurlow, M. L. (2008). 2007 state policies on assessment participation and accommodations for students with disabilities (Synthesis Report 69). Minneapolis, MN: University of Minnesota, National Center on Educational Outcomes.
Clapper, A. T., Morse, A. B., Lazarus, S. S., Thompson, S. J., & Thurlow, M. L. (2005). 2003 state policies on assessment participation and accommodations for students with disabilities (Synthesis Report 56). Minneapolis, MN: University of Minnesota, National Center on Educational Outcomes.
Lazarus, S. S., Thurlow, M. L., Lail, K. E., Eisenbraun, K. D., & Kato, K. (2006). 2005 state policies on assessment participation and accommodations for students with disabilities (Synthesis Report 64). Minneapolis, MN: University of Minnesota, National Center on Educational Outcomes.
Lazarus, S. S., Thurlow, M. L., Rieke, R., Halpin, D., & Dillon, T. (2012). Using cognitive labs to evaluate student experiences with the read aloud accommodation in math (Technical Report 67). Minneapolis, MN: University of Minnesota, National Center on Educational Outcomes.
National Center on Educational Outcomes. (2011). Developing common accommodations policies: Discussion points for consortia (NCEO Brief 2). Minneapolis, MN: author.
Thurlow, M. L. (2007). State policies and accommodations: Issues and implications. In C. Cahalan-Laitusis & L. Cook (Eds.), Accommodating students with disabilities on state assessments: What works? Arlington, VA: Council for Exceptional Children.
Thurlow, M., House, A., Boys, C., Scott, D., & Ysseldyke, J. (2000). State participation and accommodation policies for students with disabilities: 1999 update (Synthesis Report 33). Minneapolis, MN: University of Minnesota, National Center on Educational Outcomes.
Thurlow, M., Lazarus, S., Thompson, S., & Robey, J. (2002). 2001 state policies on assessment participation and accommodations (Synthesis Report 46.) Minneapolis, MN: University of Minnesota, National Center on Educational Outcomes.
Thurlow, M. L., Scott, D. L., & Ysseldyke, J. E. (1995). A compilation of states' guidelines for accommodations in assessments for students with disabilities (Synthesis Report 18). Minneapolis: University of Minnesota, National Center on Educational Outcomes.
Thurlow, M. L., Thompson, S. J. & Lazarus, S. S. (2006). Considerations for the administration of tests to special needs students: Accommodations, modifications, and more. In S. M. Downing & T. M. Haladyna (Eds.), Handbook of test development (pp. 653-673). Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum, Inc.
Thurlow, M. L., Ysseldyke, J. E., & Silverstein, B. (1993). Testing accommodations for students with disabilities: A review of the literature (Synthesis Report 4). Minneapolis: University of Minnesota, National Center on Educational Outcomes.
Top of Page | Table of Contents
Appendix A
State Documents Used in Analysis of Accommodation Policies
All state documents were taken from state department of education websites.
|
Alabama
|
(2010, January). Alabama Student Assessment Program and Policies for Students of Special Populations.
http://www.alsde.edu/html/sections/doc_download.asp?section=91&id=12112&sort=43
|
|
Alaska
|
(2010, February). CCSSO Accommodations Manual: How to Select, Administer, and Evaluate use of Accommodations for Instruction and Assessment of Students with Disabilities.
http://www.eed.state.ak.us/tls/assessment/accommodations/acommodationsmanual2010/
accommodationsmanual_ak.pdf
(2010, February). Professional Development Guide: Accommodations Manual.
http://www.eed.state.ak.us/tls/Assessment/accommodations/AcommodationsManual2010/ProfDevelopGuideforAccManual.pdf
(2011, June). Participation Guidelines for Alaska Students in State Assessments.
http://www.eed.state.ak.us/tls/Assessment/pdf_files/ParticipationGuidelinesWeb_2011.pdf
|
|
Arizona
|
(2011, July). Testing Accommodations: Guidelines for School Year 2011-2012.
http://www.azed.gov/standards-development-assessment/files/2011/08/testingaccommodations2011-12.pdf
|
|
Arkansas
|
(n.d.). Modifications used in the Classroom and Accommodations used on State Assessments.
http://arkansased.org/testing/pdf/assessment_accommodations.pdf
|
|
California
|
(2011, August). Testing Variations, Accommodations, and Modifications.
http://www.cde.ca.gov/ta/tg/sr/ Click on "Testing Variations, Accommodations, and Modifications"
|
|
Colorado
|
(n.d.). Colorado Accommodations Manual: Selecting and Using Accommodations for Instruction and Assessment. 2011-2012, Fifth Edition.
http://www.cde.state.co.us/cdeassess/documents/csapa/2011/2011_CO_Accom_Manual.pdf
|
|
Connecticut
|
(n.d.). Assessment Guidelines for Administering the Connecticut Mastery Test (CMT), Connecticut Academic Performance Test (CAPT), Connecticut Alternate Assessments.
http://www.csde.state.ct.us/public/cedar/assessment/agl/resources/AssessmentGuideline2011-12.pdf
(2011). CCSSO Accommodations Manual: How to Select, Administer, and Evaluate use of Accommodations for Instruction and Assessment of Students with Disabilities - Third Edition.
http://www.csde.state.ct.us/public/cedar/assessment/agl/index.htm
(2011, May).2012 Accommodations for Connecticut Mastery Test (CMT) and Connecticut Academic Performance Test (CAPT) Administration.
http://www.csde.state.ct.us/public/cedar/assessment/cmt/resources/dtc/2012%20Test%20accommodations%20update.pdf
|
|
Delaware
|
(2010, October). Accommodations and Universal Design Features: Users Guide.
http://de.portal.airast.org/resources/DCAS_Accommodations_Universal_Design_03-17-11.pdf
(2011, August). Guidelines for Inclusion of Students with Disabilities and English Language Learners.
http://www.doe.k12.de.us/aab/files/_Guidelines_for_Inclusion_8-11.pdf
|
|
District of Columbia
|
(n.d.) District of Columbia Office of the State Superintendent of Education Testing Accommodations Manual: For Students with Disabilities and English Language Learners. A Guide to Selecting, Administering and Evaluating the Use of Accommodations.
http://osse.dc.gov/publication/testing-accommodations-manual-and-policytesting-accommodations-manual
|
|
Florida
|
(2010). Guide to FCAT and FCAT 2.0 Accommodations for Students with Disabilities.
http://www.fldoe.org/ese/fcatasd.asp
(2010). Information for Parents and Teachers: Planning FCAT and FCAT 2.0 Accommodations for Students with Disabilities.
http://www.fldoe.org/ese/fcatasd.asp
|
|
Georgia
|
(2008). Accommodations Manual: A Guide to Selecting, Administering, and Evaluating the Use of Test Administration Accommodations for Students with Disabilities.
http://www.doe.k12.ga.us/ci_exceptional.aspx
|
|
Hawaii
|
(n.d.). Student Assessment Section [Online] http://sas.sao.k12.hi.us/STATE/SAO/SASWebsite.nsf/
10d1a575953d0e908a256c340001adab/ecc807af618cedd20a2579f900698a31?OpenDocument
|
|
Idaho
|
(n.d.). Accommodations for Instruction and Assessment:- IEP Team Guidelines.
http://www.sde.idaho.gov/site/assessment/ISAT/testAdmin.htm
(2011). Test Administration Manual for Accommodated Materials: Spring 2011.
http://www.sde.idaho.gov/site/assessment/ISAT/testCoordinators.htm
|
|
Illinois
|
(n.d.) Illinois State Board of Education Assessment Accommodations - Students with Disabilities: IEP and 504 Guidance for 2011-2012.
http://www.isbe.state.il.us/assessment/isat.htm
(2010, September). State-Approved Accommodations for IEP/504/LEP [Chart].
http://www.isbe.state.il.us/assessment/isat.htm
|
|
Indiana
|
(n.d). 2011-2012 ISTEP+ Program Manual: Policies and Procedures for Indiana's Assessment System.
http://www.doe.in.gov/achievement/assessment
|
|
Iowa
|
(2006, July). Iowa Guidelines for the Use of Accommodations during Instruction and District Wide Assessments for Students with Disabilities (adapted from the CCSSO Accommodations Manual). http://www.iowa.gov/educate/index.php?option=com_content&task=view&id=596&Itemid=1578
|
|
Kansas
|
(2011, November). Accommodations Manual: How to Select, Administer, and Evaluate Accommodations For Instruction and Assessment.
http://www.ksde.org/Default.aspx?tabid=2372
(n.d). KSDE Training Document for: 2012 - Read-Aloud Accommodation/KCA Audio Voice.
http://www.ksde.org/LinkClick.aspx?fileticket=O0J67H7UKNA%3D&tabid=420&
|
|
Kentucky
|
(n.d). Inclusion of Special Populations in the State-Required Assessment and Accountability Programs: February 2004.
http://www.education.ky.gov/NR/rdonlyres/434456A0-02B0-4911-AFF7-2225760B646F/0/InclusionsDocument.pdf
(2011, February) Kentucky Standard Accommodations. No link available.
|
|
Louisiana
|
LEAP and GEE Special Populations and Accommodations.
http://www.louisianaschools.net/lde/uploads/18146.pdf
(2007, February). Louisiana Statewide Assessments, Accommodations and Assistive Technology.
http://www.louisianaschools.net/lde/uploads/10255.pdf
|
|
Maine
|
(2010, August) New England Common Assessment Program: Accommodations Guide.
http://www.maine.gov/education/lsalt/paap/materialstools/documents/NECAPAccommodationsGuideFinal.pdf
|
|
Maryland
|
(2008, February). Maryland Accommodations Manual.
http://www.marylandpublicschools.org/NR/rdonlyres/840EFBB6-CD7D-404E-8A77-E978F6D508AA/
16337/MDAccommodationsManual_21108.pdf
|
|
Massachusetts
|
(n.d.). 2011-2012 Update: Requirements for the Participation of Students with Disabilities in MCAS Including Test Accommodations and Alternate Assessment.
http://www.doe.mass.edu/mcas/participation/sped.pdf
|
|
Michigan
|
(2011, September). Assessment Accommodation Summary Table.
http://www.michigan.gov/documents/mde/Updated_Revised_Accommodation_Summary_Table_080211_359704_7.pdf
(2011). Michigan Statewide Assessment Selection Guidance.
http://www.michigan.gov/documents/mde/Michigan_Statewide_Assessment_Selection_Guidelines_360226_7.pdf
|
|
Minnesota
|
(2011, December). Procedures Manual for the Minnesota Assessments 2011-2012. No link available.
|
|
Mississippi
|
(2011, August). Mississippi Testing Accommodations Manual.
http://www.mde.k12.ms.us/docs/public-notice/mississippi_testing_accommodations_manual_revision
_06-20-2011_final.pdf?sfvrsn=1
|
|
Missouri
|
(2011). Examiner's Manual: Grade 5 Communication Arts, Mathematics, and Science Assessments.
http://dese.mo.gov/divimprove/assess/documents/asmt-gl-em05-2011.pdf
Missouri Accommodations Manual.
http://dese.mo.gov/divimprove/assess/tech/accommodationsmanualpowerpoint.pdf
|
|
Montana
|
(n.d). 2011 OPI List of Approved Accommodations.
http://opi.mt.gov/Pdf/Assessment/CRT/TA/11ApprovedAccommodations.pdf
(n.d). CRT Accommodation Manual: Spring 2011.
http://opi.mt.gov/pdf/Assessment/CRT/TA/11AccommodationManual.pdf
|
|
Nebraska
|
(n.d). Nebraska State Accountability (NeSA) Approved Accommodations.
http://www.education.ne.gov/Assessment/NeSA_Accommodations.htm
|
|
Nevada
|
(n.d). Accommodations Form for Students Participating in Special Education Programs: Nevada Proficiency Examination Program (NPEP). Effective for the 2012-2013 School Year Only.
http://nde.doe.nv.gov/Assessment_NPEP_Resources.htm
(n.d). IEP Accommodations Form: Nevada Proficiency Examination Program. Effective for the 2007-2008 School Year Only.
http://nde.doe.nv.gov/Assessment_NPEP_Resources.htm
|
|
New Hampshire
|
(2010, August). New England Common Assessment Program. Accommodations Guide: NH Edition.
http://www.measuredprogress.org/documents/10157/40685/NECAP_AccommodationsGuide.pdf
|
|
New Jersey
|
(n.d.). Accommodations and Modifications of Test Administration Procedures for Statewide Assessments.
http://www.state.nj.us/education/specialed/accom900.htm
|
|
New Mexico
|
(2011, August). Student Assessment Accommodations Manual.
http://www.ped.state.nm.us/AssessmentAccountability/AssessmentEvaluation/dl11/Accommodations%20
Manual%20%209.1.11.pdf
|
|
New York
|
(2006, May). Test Access and Accommodations for Students with Disabilities: Policy and Tools to Guide Decision-Making and Implementation.
http://www.p12.nysed.gov/specialed/publications/policy/testaccess/manual506.pdf
|
|
North Carolina
|
(2011, August). Testing Students with Disabilities: North Carolina Testing Program.
http://www.ncpublicschools.org/docs/accountability/policyoperations/tswd/tswd1112.pdf
|
|
North Dakota
|
(2011). North Dakota State Assessment Test Coordinator's Manual: Fall 2011. Grades 3-8 and 11.
http://www.dpi.state.nd.us/testing/assess/manual.pdf
|
|
Ohio
|
(2011, February). Accommodations Manual: Selection, Use, and Evaluation of Accommodations that Support Instruction and Assessment of Children with Disabilities.
http://www.edresourcesohio.org/files/Accommodations%20Manual%20February%202011.pdf
|
|
Oklahoma
|
(2010, September). Oklahoma Accommodations Manual for Instruction and Assessment: How to Select, Administer, and Evaluate the Use of Accommodations for Instruction and Assessment of Students with Disabilities.
http://sde.state.ok.us/Curriculum/SpecEd/pdf/Assessment/AccommGuideMan.pdf
|
|
Oregon
|
(2011, July). Accommodations Manual 2011-2012: How to Select, Administer, and Evaluate Accommodations for Oregon's Statewide Assessment.
http://www.ode.state.or.us/search/page/?id=487
|
|
Pennsylvania
|
(2010, January). PSSA and PSSA-M Accommodation Guidelines for Students with IEPs and Students with 504 Plans.
http://www.portal.state.pa.us/portal/server.pt
|
|
Rhode Island
|
(n.d.). New England Common Assessment Program: Accommodations Guide.
http://www.ride.ri.gov/assessment/DOCS/NECAP/Test_Admin/NECAP_Accommodations_Guide.pdf
|
|
South Carolina
|
(2009). Accommodations Manual: A Guide to Selecting, Administering, and Evaluating the Use of Test Administration Accommodations for Students with Disabilities.
http://ed.sc.gov/agency/programs-services/172/documents/AccomManualJan11.pdf
|
|
South Dakota
|
(2012). 2012 Test Coordinator Handbook.
http://doe.sd.gov/oats/documents/dTCH_2012.pdf
|
|
Tennessee
|
(n.d.). TCAP Allowable Accommodations Chart 2011-2012.
http://www.tn.gov/education/assessment/doc/Allow_Accomm_Chart_10_11.pdf
|
|
Texas
|
(2011, October). Accommodations for Students with Disabilities Taking STARR, STARR Spanish, STARR Modified, STARR L, or TELPAS [PowerPoint].
http://www.tea.state.tx.us/student.assessment/accommodations/staar-telpas/
|
|
Utah
|
(2011, July). Assessment Participation and Accommodations Policy.
http://www.schools.utah.gov/sars/DOCS/assessment/Special_Needs_Accommodations_Policy-pdf.aspx
|
|
Vermont
|
(2010, August). New England Common Assessment Program Accommodations Guide.
http://education.vermont.gov/new/pdfdoc/pgm_assessment/necap/educ_necap_accommodations_guide.pdf
|
|
Virginia
|
(2011, November). Procedures for Participation of Students with Disabilities in Virginia's Accountability System: Including Participation Criteria and Testing Accommodations. A Guide for Educators and Parents.
http://www.doe.virginia.gov/testing/participation/participation_va_accountability_system.pdf
|
|
Washington
|
(2011, October). Washington State Accommodations Guidelines for Statewide Assessments.
http://www.k12.wa.us/Assessment/AlternativeAssessment/pubdocs/AccommodationManual.pdf
|
|
West Virginia
|
(n.d.). West Virginia Guidelines for Participation in State Assessments.
http://wvde.state.wv.us/oaa/pdf/Accommodations%20Study%20Report%20120809.pdf
|
|
Wisconsin
|
(2011) Allowable Test Practices for All Students - Updated 2011.
http://dpi.wi.gov/oea/pdf/allowtestpr.pdf
(2011) The Assessment Accommodations Matrix for Students with Disabilities - Updated 2011.
http://dpi.wi.gov/oea/pdf/accomswd.pdf
|
|
Wyoming
|
(2006, January). Wyoming Accommodations Manual for Instruction and Assessment: How to Select, Administer, and Evaluate use of Accommodations for Instruction and Assessment of Students with Disabilities.
http://edu.wyoming.gov/Programs/statewide_assessment_system/paws/paws_accommodations.aspx
(2011, September). Wyoming Statewide Assessment System: PAWS 2012 Standard Accommodations.
http://edu.wyoming.gov/Programs/statewide_assessment_system/paws/paws_accommodations.aspx
|
Top of Page | Table of Contents
Appendix B
Accommodation Guidelines by State
Table B1. Oral Delivery Accommodations
|
State
|
Human Reader
|
Text-to Speech
|
Pre-recorded Audio
|
|
Directions
|
Items
|
Passages
|
Directions
|
Items
|
Passages
|
Directions
|
Items
|
Passages
|
|
Read
|
Math
|
Read
|
Math
|
Read
|
Math
|
Read
|
Math
|
Read
|
Math
|
Read
|
Math
|
Read
|
Math
|
Read
|
Math
|
Read
|
Math
|
|
Alabama
|
|
|
P*
|
A
|
P*
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Alaska
|
A
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AC*
|
|
AC*
|
|
AC*
|
|
Arizona
|
A
|
A
|
P*
|
A
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Arkansas
|
P
|
A
|
P
|
A*
|
P
|
A*
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
California
|
|
|
AC/AI*
|
A
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AC/AI*
|
A
|
|
|
|
Colorado
|
A
|
A
|
P
|
AC*
|
P
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Connecticut
|
|
|
P
|
AC*
|
P
|
AC*
|
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Delaware
|
AC*
|
AC*
|
AC*
|
AC*
|
AI*
|
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
AI*
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
District of Columbia
|
|
|
AI*
|
A
|
AI*
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Florida
|
A
|
A
|
AC*
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Georgia
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
AC*
|
|
|
|
A
|
A
|
AC*
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hawaii
|
|
|
|
P*
|
|
|
|
|
AC*
|
A
|
AC*
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Idaho
|
A
|
A
|
AI*
|
P*
|
AI*
|
P*
|
|
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
|
|
P
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
|
Illinois
|
A
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
P
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
P
|
|
|
Indiana
|
A
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
P
|
|
|
|
P
|
A
|
P
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Iowa
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
|
Kansas
|
|
|
A
|
A
|
AI*
|
A
|
|
|
A
|
A
|
|
A
|
|
|
P
|
P
|
|
|
|
Kentucky
|
A
|
|
A
|
|
A*
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A*
|
A*
|
|
|
|
|
|
Louisiana
|
A
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
P
|
|
|
|
P
|
|
P
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maine
|
A
|
A
|
AI*
|
AC*
|
AI*
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maryland
|
A
|
A
|
AC/AI*
|
A
|
AC/AI*
|
|
|
|
AC/AI*
|
A*
|
|
|
|
|
AC/AI*
|
A
|
AC/AI*
|
|
|
Massachusetts
|
A
|
|
AC*
|
A
|
|
|
|
|
AC*
|
A
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Michigan
|
A
|
A
|
AI*
|
A
|
|
|
|
|
AI*
|
|
|
|
|
|
P
|
A*
|
|
|
|
Minnesota
|
|
|
|
A*
|
|
|
|
|
|
A*
|
|
|
|
|
|
A
|
|
|
|
Mississippi
|
A
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
|
|
A
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
P
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Missouri
|
|
|
AC/AI*
|
A
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Montana
|
|
|
AC*
|
A
|
AI*
|
|
|
|
|
|
AC/AI*
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
New Hampshire
|
A
|
A
|
AI*
|
AC*
|
AI*
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
New Jersey
|
AI*
|
AI*
|
AI*
|
AI*
|
P
|
AI*
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
New Mexico
|
A
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
P
|
|
|
|
P
|
AC*
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
New York
|
A
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
P
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
North Carolina
|
A
|
A
|
AI*
|
A
|
AI*
|
|
|
|
AI*
|
A
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
North Dakota
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
AI*
|
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ohio
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
P
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
P*
|
|
|
Oklahoma
|
A
|
A
|
|
A
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oregon
|
A
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pennsylvania
|
A
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
|
|
A
|
A
|
P
|
AC*
|
|
|
A
|
A
|
P
|
AC*
|
|
|
|
Rhode Island
|
A
|
A
|
AI*
|
AC*
|
AI*
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
South Carolina
|
|
|
AC/AI*
|
A
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AC/AI*
|
A
|
|
|
|
South Dakota
|
A
|
A
|
AC*
|
AC*
|
P
|
A
|
|
|
A
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
|
|
A
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
|
Tennessee
|
A
|
A
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Texas
|
|
|
AC*
|
A
|
P
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Utah
|
A
|
A
|
AC*
|
A
|
AC*
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
A*
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vermont
|
A
|
A
|
AI*
|
AC*
|
AI*
|
|
|
|
P*
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Virginia
|
A
|
A
|
AC/AI*
|
A
|
AC/AI*
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AC/AI*
|
AC*
|
AC/AI*
|
|
|
Washington
|
A
|
A
|
AC*
|
A
|
AC*
|
|
|
|
AC*
|
A
|
AC*
|
|
|
|
AC*
|
|
AC*
|
|
|
West Virginia
|
A
|
A
|
|
A
|
|
A
|
AC*
|
A
|
AC*
|
A
|
AC*
|
A
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wisconsin
|
A
|
A
|
AC*
|
A*
|
AC*
|
A*
|
|
|
P
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
A
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
P
|
A
|
|
Wyoming
|
|
A
|
|
A
|
|
|
|
A
|
|
A
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total
|
A:36
AC:1
AI:1
P:1
|
A:36
AC:1
AI:1
|
A:6
AC:10
AI:9
AC/AI:5
P:15
|
A:36
AC:10
AI:1
P:2
|
A:2
AC:4
AI:11
AC/AI:2
P:16
|
A:10
AC:1
AI:1
P:1
|
A:7
AC:1
|
A:11
|
A:7
AC:5
AI:2
AC/AI:1
P:10
|
A:21
AC:3
|
A:3
AC:4
AI:1
AC/AI:1
P:8
|
A:10
|
A:6
|
A:7
AC:1
|
A:3
AC:2
AC/AI:4
P:6
|
A:11
AC:4
P:1
|
A:1
AC:1
AC/AI:2
P:6
|
A:4
AC:1
|
A = Allowed, AC = Allowed in Certain Circumstances, AI = Allowed with Implications for Scoring, P = Prohibited
See Table B.2 for specifications.
Table B.2. Specifications and Descriptions of "Certain Circumstances" and "implications for Scoring" for Oral Delivery Accommodations
Alabama |
Human Reader - Reading Items: No reading accommodation allowed for Reading Comprehension.
Human Reader - Math Items: Mathematics procedures subtest read aloud by test administrator. Mathematics Problem Solving subtest read aloud by test administrator.
Human Reader - Reading Passages: No reading accommodation allowed for Reading Comprehension.
Human Reader - Math Passages: Mathematics procedures subtest read aloud by test administrator. Mathematics Problem Solving subtest read aloud by test administrator. |
Alaska |
Pre-recorded Audio - Math Directions: Using test contractor audio version of Grade 10 SBA-HSGQE or HSGQE Retest mathematics tests if available.
Pre-recorded Audio - Math Items: Using test contractor audio version of Grade 10 SBA-HSGQE or HSGQE Retest mathematics tests if available.
Pre-recorded Audio - Math Passages: Using test contractor audio version of Grade 10 SBA-HSGQE or HSGQE Retest mathematics tests if available. |
Arkansas |
Pre-recorded Audio - Math Directions: Audiocassettes are not currently available.
Pre-recorded Audio - Math Items: Audiocassettes are not currently available.
Pre-recorded Audio - Math Passages: Audiocassettes are not currently available. |
California |
Human Reader - Reading Items: Listed as modification. Test questions and answer options read aloud to student. For the STAR Program (CST and STS only) and CELDT, eligible students shall be permitted to take the tests with modifications if specified in the eligible student’s IEP or Section 504 plan.
Pre-recorded Audio - Reading Items: Listed as modification. Test questions and answer options read aloud to student using audio CD presentation. For the STAR Program (CST and STS only) and CELDT, eligible students shall be permitted to take the tests with modifications if specified in the eligible student’s IEP or Section 504 plan. |
Colorado |
Human Reader - Math Items: A trained test proctor may be provided to read the entire test orally to students who are unable to decode text visually. Test proctors should be provided to students on an individual basis. A student should have the option of asking a reader to slow down or repeat text....Scripts are in separate books for Mathematics. Accommodation appropriate for: students with visual impairments, students with communication-processing impairments, students with reading processing impairments (i.e., dyslexia).
Human Reader - Math Passages: A trained test proctor may be provided to read the entire test orally to students who are unable to decode text visually. Test proctors should be provided to students on an individual basis. A student should have the option of asking a reader to slow down or repeat text....Scripts are in separate books for Mathematics. Accommodation appropriate for: students with visual impairments, students with communication-processing impairments, students with reading processing impairments (i.e., dyslexia). |
Connecticut |
Human Reader - Math Directions: Students receiving the test reader for test items accommodation will also receive the test directions read accommodation for the corresponding content area sub-test.
Human Reader - Math Items: Reader for test items (including directions) by certified staff only. This accommodation is only for students unable to use the Text Reader function on the MIST application or whose disability precludes them from being assessed using the MIST application.
Human Reader - Math Passages: Reader for test items (including directions) by certified staff only. This accommodation is only for students unable to use the Text Reader function on the MIST application or whose disability precludes them from being assessed using the MIST application. |
Delaware |
Human Reader - Reading Directions: The human reader accommodation and the TTS [Text-to-Speech] accommodation are not interchangeable and not considered to be the same accommodation. Only administer the human reader accommodation if the student is documented to receive the human reader accommodation. Students with TTS only may not receive assistance from a human reader.
Human Reader - Math Directions: The human reader accommodation and the TTS [Text-to-Speech] accommodation are not interchangeable and not considered to be the same accommodation. Only administer the human reader accommodation if the student is documented to receive the human reader accommodation.
Human Reader - Reading Items: The human reader accommodation and the TTS [Text-to-speech] accommodation are not interchangeable and not considered to be the same accommodation. Only administer the human reader accommodation if the student is documented to receive the human reader accommodation. Students with TTS only may not receive assistance from a human reader.
Human Reader - Math Items: The human reader accommodation and the TTS [Text-to-Speech] accommodation are not interchangeable and not considered to be the same accommodation. Only administer the human reader accommodation if the student is documented to receive the human reader accommodation.
Human Reader - Reading Passages: Reading aloud the reading passages is a non-standard accommodation. Students who receive this accommodation will count as non-participants in calculations of participation and will be excluded from calculations of proficiency rates in Adequate Yearly Progress.
Text to Speech - Reading Passages: Presenting the reading passages or texts for the reading test via text-to-speech Software. Student chooses which parts of the test he/she would like the computer to read. The entire text may be read if the student wishes. These accommodations are non-standard. Students will count as non-participants in AYP calculations and will be excluded from AYP proficiency calculations. |
District of Columbia |
Human Reader - Reading Passages: Assisted reading of comprehension passages when used as an assessment accommodation, it will be considered a modification of the test.
Human Reader - Reading Items: Reading of entire comprehension test when used as an assessment accommodation, it will be considered a modification of the test. |
Florida |
Human Reader - Reading Items: Listed under unique accommodations. Auditory presentation of reading items for students with both visual and tactile disabilities who are not able to physically access print, large print, or braille materials.
Text to Speech - Reading Items: Listed under unique accommodations. Auditory presentation of reading items for students with both visual and tactile disabilities who are not able to physically access print, large print, or braille materials. |
Georgia |
Human Reader - Reading Passages: Restricted to grades 3-8 and may be considered when both the following conditions apply: (1) The student has a specific disability that severely limits or prevents him or her from decoding text at any level of difficulty, even after varied and repeated attempts to teach the student to do so (i.e. the student is a non-reader, not simply reading below grade level); (2) The student has access to printed materials only through a reader or other electronic format during routine instruction.
Text to Speech - Reading Passages: Restricted to grades 3-8 and may be considered when both the following conditions apply: (1) The student has a specific disability that severely limits or prevents him or her from decoding text at any level of difficulty, even after varied and repeated attempts to teach the student to do so (i.e. the student is a non-reader, not simply reading below grade level); (2) The student has access to printed materials only through a reader or other electronic format during routine instruction. |
Hawaii |
Human Reader - Math Items: TAs may no longer read or reread mathematics test questions and answer options to any students. The text-to-speech feature will automatically be enabled for all students in TIDE…. This will allow them to have questions or answer options read or reread to them. This procedure will ensure that all students have the test questions and response options read aloud using the same tone of voice and inflection for all words and symbols included in charts, tables, and graphs.
Text to Speech - Reading Items: Using the text-to-speech feature for the reading passages, test questions, and answer options in the Reading Assessment. Students using this accommodation must meet two criteria: The student is a non-reader who will never be able to read any sentences at any grade level throughout his or her life. The student accesses all printed materials for every subject via an audio format all of the time during classroom instruction.
Text to Speech - Reading Passages: Using the text-to-speech feature for the reading passages, test questions, and answer options in the Reading Assessment. Students using this accommodation must meet two criteria: The student is a non-reader who will never be able to read any sentences at any grade level throughout his or her life. The student accesses all printed materials for every subject via an audio format all of the time during classroom instruction. |
Idaho |
Human Reader - Reading Items: If adaptations are used, the student is deemed not proficient and will not be counted towards participation. Examples of adaptations: reading a Reading test to a student
Human Reader - Math Items: No human readers will be allowed. If a student using paper, large print, or Braille needs a language usage, mathematics, or science test read to him/her, an audio CD must be used [emphasis in original].
Human Reader - Reading Passages: If adaptations are used, the student is deemed not proficient and will not be counted towards participation. Examples of adaptations: reading a Reading test to a student
Human Reader - Math Passages: No human readers will be allowed. If a student using paper, large print, or Braille needs a language usage, mathematics, or science test read to him/her, an audio CD must be used. |
Indiana |
Human Reader - Reading Items: Cannot be used for reading comprehension portion of test.
Text to Speech - Reading Items: Cannot be used for reading comprehension portion of test. |
Kansas |
Human Reader - Reading Passages: Absolutely nothing from a reading passage may be read or pronounced, including single words. If reading passages to a student on the state reading assessment is allowed on the student’s plan, the student will then be counted as not participating.
Text to Speech - Reading Passages: Absolutely nothing from a reading passage may be read or pronounced, including single words. If reading passages to a student on the state reading assessment is allowed on the student’s plan, the student will then be counted as not participating. |
Kentucky |
Human Reader - Reading Items: Reading assessments may be read to a student on the premise that the intent of reading is to measure comprehension.
Human Reader - Reading Passages: Reading assessments may be read to a student on the premise that the intent of reading is to measure comprehension.
Pre-recorded Audio - Reading Directions: During the state-required Assessment, a student with a disability or limited English proficiency may use special equipment, including assistive or adaptive technology...such as: Audiotaped directions.
Pre-recorded Audio - Math Directions: During the state-required Assessment, a student with a disability or limited English proficiency may use special equipment, including assistive or adaptive technology...such as: Audiotaped directions. |
Louisiana |
Human Reader - Reading Items: Students receiving this accommodation must have been provided it in classroom assessment. These students should have the tests read aloud with the exception of the Reading and Responding session of the English Language Arts test (Phase 2), which cannot be read aloud.
Human Reader - Reading Passages: Students receiving this accommodation must have been provided it in classroom assessment. These students should have the tests read aloud with the exception of the Reading and Responding session of the English Language Arts test (Phase 2), which cannot be read aloud.
Text to Speech - Reading Items: An electronic reader may not be used during the Reading and Responding session of the English Language Arts test.
Text to Speech - Reading Passages: An electronic reader may not be used during the Reading and Responding session of the English Language Arts test. |
Maine |
Human Reader - Reading Items: Reading any portion of the Reading Test to students is considered a modification (M2) and invalidates all test sessions that have been read.
Human Reader -Math Items: On the Mathematics Test, the symbols or numbers written as numerals may not be read aloud. All symbols and numerals in mathematics items and multiple-choice answers are to be pointed to only.
Human Reader - Reading Passages: Reading any portion of the Reading Test to students is considered a modification (M2) and invalidates all test sessions that have been read.
Human Reader -Math Passages: On the Mathematics Test, the symbols or numbers written as numerals may not be read aloud. All symbols and numerals in mathematics items and multiple-choice answers are to be pointed to only. |
Maryland |
Human Reader - Reading Items: Use of the verbatim reading accommodation is permitted on all assessments as a standard accommodation, with the exception of: (1) the Maryland School Assessment in Reading, grade 3 ONLY, which assesses a student’s ability to decode printed language. Students in grade 3 receiving this accommodation on the assessment will receive a score based on standards 2 and 3 (comprehension of informational and literary Reading material) but will not receive a score for standard 1, general Reading processes; and (2) the Maryland Functional Reading Test.
Human Reader - Math Items: Graphic materials may be described, but should also be made available in print or tactile formats.
Human Reader - Reading Passages: Use of the verbatim reading accommodation is permitted on all assessments as a standard accommodation, with the exception of: (1) the Maryland School Assessment in Reading, grade 3 ONLY, which assesses a student’s ability to decode printed language. Students in grade 3 receiving this accommodation on the assessment will receive a score based on standards 2 and 3 (comprehension of informational and literary Reading material) but will not receive a score for standard 1, general Reading processes; and (2) the Maryland Functional Reading Test.
Human Reader - Math Passages: Graphic materials may be described, but should also be made available in print or tactile formats.
Text to Speech - Reading Items: Use of the verbatim reading accommodation is permitted on all assessments as a standard accommodation, with the exception of: (1) the Maryland School Assessment in Reading, grade 3 ONLY, which assesses a student’s ability to decode printed language. Students in grade 3 receiving this accommodation on the assessment will receive a score based on standards 2 and 3 (comprehension of informational and literary Reading material) but will not receive a score for standard 1, general Reading processes; and (2) the Maryland Functional Reading Test.
Text to Speech - Math Items: Mathematics formulas are sometimes displayed on screen as graphics that cannot be read by a screen reader.
Text to Speech - Reading Passages: Use of the verbatim reading accommodation is permitted on all assessments as a standard accommodation, with the exception of: (1) the Maryland School Assessment in Reading, grade 3 ONLY, which assesses a student’s ability to decode printed language. Students in grade 3 receiving this accommodation on the assessment will receive a score based on standards 2 and 3 (comprehension of informational and literary Reading material) but will not receive a score for standard 1, general Reading processes; and (2) the Maryland Functional Reading Test.
Text to Speech - Math Passages: Mathematics formulas are sometimes displayed on screen as graphics that cannot be read by a screen reader.
Pre-recorded Audio - Reading Items: Written tests and instructional materials are prerecorded on an audio cassette or compact disk that a student accesses by listening.... Audio versions of tests and other written materials need to be supplemented with a print or Braille version of the text so that a student can have access to complicated graphic material. Use of the verbatim reading accommodation is permitted on all assessments as a standard accommodation, with the exception of: (1) the Maryland School Assessment in Reading, grade 3 ONLY, which assesses a student’s ability to decode printed language. Students in grade 3 receiving this accommodation on the assessment will receive a score based on standards 2 and 3 (comprehension of informational and literary Reading material) but will not receive a score for standard 1, general Reading processes; and (2) the Maryland Functional Reading Test.
Pre-recorded Audio - Reading Passages: Written tests and instructional materials are prerecorded on an audio cassette or compact disk that a student accesses by listening.... Audio versions of tests and other written materials need to be supplemented with a print or Braille version of the text so that a student can have access to complicated graphic material. Use of the verbatim reading accommodation is permitted on all assessments as a standard accommodation, with the exception of: (1) the Maryland School Assessment in Reading, grade 3 ONLY, which assesses a student’s ability to decode printed language. Students in grade 3 receiving this accommodation on the assessment will receive a score based on standards 2 and 3 (comprehension of informational and literary Reading material) but will not receive a score for standard 1, general Reading processes; and (2) the Maryland Functional Reading Test. |
Massachusetts
|
Human Reader - Reading Directions: The test administrator clarifies general administration instructions.
Human Reader - Math Directions: The test administrator clarifies general administration instructions.
Human Reader - Reading Items: No portion of the ELA Reading Comprehension test may be read aloud unless accommodation 26 [Test Administrator Reads Aloud the ELA Reading Comprehension Test] is listed in the student’s IEP. Criteria required for use: 1. The student has a specific disability that severely limits or prevents him or her from decoding text, even after varied and repeated attempts to teach the student to do so. The student must be a virtual non-reader (i.e., at the beginning stages of learning to decode), not simply reading below grade level. AND 2. The student has access to printed materials only through a reader and/or is provided with spoken text on audiotape, CD, video, or other electronic format during routine instruction, except while the student is actually being taught to decode.
Human Reader - Reading Passages: No portion of the ELA Reading Comprehension test may be read aloud unless accommodation 26 [Test Administrator Reads Aloud the ELA Reading Comprehension Test] is listed in the student’s IEP. The student has a specific disability that severely limits or prevents him or her from decoding text, even after varied and repeated attempts to teach the student to do so. The student must be a virtual non-reader (i.e., at the beginning stages of learning to decode), not simply reading below grade level. The student has access to printed materials only through a reader and/or is provided with spoken text on audiotape, CD, video, or other electronic format during routine instruction, except while the student is actually being taught to decode
Text to Speech - Reading Items: Listed under nonstandard accommodations. Electronic text reader for the ELA Reading Comprehension test: The student uses an electronic text reader (i.e., Kurzweil 3000) for the ELA Reading Comprehension test.
Text to Speech - Reading Passages: The student has a specific documented disability that severely limits or prevents him or her from decoding text, even after varied and repeated attempts to teach the student to do so. The student must be a virtual non-reader (i.e., at the beginning stages of learning to decode), not simply reading below grade level. The student has access to printed materials only through an electronic text reader and is provided this accommodation during routine instruction, except while the student is actually being taught to decode. |
Michigan |
Human Reader - Reading Items: Listed as a nonstandard accommodation. A student assessed using a nonstandard assessment accommodation will not count as being assessed when calculating NCLB participation rates.
Human Reader - Reading Passages: Listed as a nonstandard Accommodation. A student assessed using a nonstandard assessment accommodation will not count as being assessed when calculating NCLB participation rates.
Text to Speech - Reading Items: Listed as Nonstandard Accommodation. Nonstandard assessment accommodations will not count as being assessed when calculating NCLB participation rates.
Text to Speech - Reading Passages: Listed as Nonstandard Accommodation. Nonstandard assessment accommodations will not count as being assessed when calculating NCLB participation rates. |
Minnesota |
Human Reader - Math Items: Only a small number of students typically need the script; the default should be the regular text-to-speech available in the online form.
Human Reader - Math Passages: Only a small number of students typically need the script; the default should be the regular text-to-speech available in the online form.
Text to Speech - Math Items: The accommodated text-to-speech differs from the regular text-to-speech because it reads not only all the questions and answer choices but also all the labels, graphs and charts….Only a small number of students typically need the accommodated text-to-speech; the default should be the regular text-to-speech.
Text to Speech - Math Passages: The accommodated text-to-speech differs from the regular text-to-speech because it reads not only all the questions and answer choices but also all the labels, graphs and charts….Only a small number of students typically need the accommodated text-to-speech; the default should be the regular text-to-speech |
Mississippi |
Human Reader - Reading Items: Not allowed for items in the reading sections of the MCT2 (MCT2 - Reading) or the SATP (English II Multiple Choice - Vocabulary/Reading).
Human Reader - Text to Speech: Not allowed for items in the reading sections of the MCT2 (MCT2 - Reading) or the SATP (English II Multiple Choice - Vocabulary/Reading). |
Missouri |
Human Reader - Reading Items: Oral reading, oral reading in native language, or signing during the Communication Arts Assessment will result in the LOSS (Lowest Obtainable Scale Score). Oral reading of assessment to Blind/Partial Sight students does not invalidate the score.
Human Reader - Reading Passages: Oral reading of assessment to Blind/Partial Sight students [test not invalidated]. Oral reading, oral reading in native language, or signing during the Communication Arts Assessment will result in the LOSS (Lowest Obtainable Scale Score). Oral reading of assessment to Blind/Partial Sight students does not invalidate the score. |
Montana |
Human Reader - Reading Items: This accommodation should be a low-incidence accommodation. Please consider the following to determine the appropriateness of this accommodation for each student. Assessment results are available to support the determination that the student’s disability precludes or severely limits the student’s ability to gain meaning from written language. There is documentation of remedial reading services and/or special education and supplementary aids and services. Through classroom assessment, it has been determined and documented that the student benefits from oral presentation as her/his way of learning.
Human Reader - Reading Passages: Nonstandard Accommodation. Reading aloud the reading passages to a student for reading passages. A student for whom this type of nonstandard accommodation might be used would be a student with a learning disability in reading who, without the text being read, could not participate in this portion of the test.
Text to Speech - Reading Passages: Nonstandard Accommodation. Student uses text-reader software for reading passages. A student for whom this type of nonstandard accommodation might be used would be a student with a learning disability in reading who, without the text being read, could not participate in this portion of the test. |
Nebraska |
Pre-recorded Audio - Directions: To be used in conjunction with the paper/pencil test.
Pre-recorded - Directions: To be used in conjunction with the paper/pencil test.
Pre-recorded Audio - Reading Items: To be used in conjunction with the paper/pencil test.
Pre-recorded - Audio Math Items: To be used in conjunction with the paper/pencil test.
Pre-recorded - Audio Math Passages: To be used in conjunction with the paper/pencil test. |
Nevada |
Human Reader - Math Items: Verbalizing, explaining, signing, or defining mathematical or scientific symbols (including numerals) is prohibited. Paraphrasing or explaining any part of the test is prohibited.
Human Reader - Math Passages: Verbalizing, explaining, signing, or defining mathematical or scientific symbols (including numerals) is prohibited. Paraphrasing or explaining any part of the test is prohibited. |
New
Hampshire |
Human Reader - Reading Items: Note that reading any portion of the Reading Test to students is considered a modification (M2) and invalidates all test sessions that have been read.
Human Reader - Math Items: On the Mathematics Test, the symbols or numbers written as numerals may not be read aloud. All symbols and numerals in mathematics items and multiple-choice answers are to be pointed to only.
Human Reader - Reading Passages: Note that reading any portion of the Reading Test to students is considered a modification (M2) and invalidates all test sessions that have been read.
Human Reader - Math Passages: On the Mathematics Test, the symbols or numbers written as numerals may not be read aloud. All symbols and numerals in mathematics items and multiple-choice answers are to be pointed to only. |
New Jersey |
Human Reader - Reading Directions: Listed under test procedure modifications.
Human Reader - Math Directions: Listed under test procedure modifications.
Human Reader - Reading Items: Listed under test procedure modifications. ONLY the teacher who must read the test items aloud or sign is permitted to have a test booklet assigned to him/her for this task.
Human Reader - Math Items: Listed under test procedure modifications. ONLY the teacher who must read the test items aloud or sign is permitted to have a test booklet assigned to him/her for this task.
Human Reader - Math Passages: Listed under test procedure modifications. ONLY the teacher who must read the test items aloud or sign is permitted to have a test booklet assigned to him/her for this task. |
New Mexico |
Text to Speech - Math Items: Assistive technology devices. Students with visual and hearing impairments may use assistive technology devices. Use of assistive technology restricted to: (1) Closed circuit TV, (2) Low vision devices, such as magnifiers, (3), Amplification equipment, such as FM systems, (4) Kurzweil, (5) Projector. Assistive technology voice output must be disabled during the reading assessments.
Text to Speech - Math Passages: Assistive technology devices. Students with visual and hearing impairments may use assistive technology devices. Use of assistive technology restricted to: (1) Closed circuit TV, (2) Low vision devices, such as magnifiers, (3), Amplification equipment, such as FM systems, (4) Kurzweil, (5) Projector. Assistive technology voice output must be disabled during the reading assessments. |
New York |
Human Reader - Reading Items: This testing accommodation is not permitted for use on certain sections of the State Grades 3-8 ELA tests because these sections measure a student’s reading skills (decoding and comprehension). For some tests intended to measure reading skills, reading the test to students becomes a modification resulting in invalid scores.
Human Reader - Reading Passages: This testing accommodation is not permitted for use on certain sections of the State Grades 3-8 ELA tests because these sections measure a student’s reading skills (decoding and comprehension). For some tests intended to measure reading skills, reading the test to students becomes a modification resulting in invalid scores. |
North Carolina |
Human Reader - Reading Items: Use of this accommodation during the administration of a state test that measures reading comprehension invalidates the results from the test.
Human Reader - Reading Passages: Reading aloud the selections/passages, sample questions, test questions, and answer choices from North Carolina tests that measure reading comprehension invalidates the results from those tests.
Text to Speech - Reading Items: Computer reads test aloud - student controlled. Use of this accommodation during the administration of a state test that measures reading comprehension invalidates the results from the test.
Text to Speech - Reading Passages: Computer reads test aloud - student controlled. Use of this accommodation during the administration of a state test that measures reading comprehension invalidates the results from the test. |
North Dakota |
Human Reader - Reading Passages: Reading aloud to a student the reading passage within the Reading and Language Arts content area test is identified as a modification and will invalidate a student’s NDSA or NDAA 2 test score. |
Ohio |
Pre-recorded - Audio Reading Passages: Represents standardized read-aloud accommodation for directions, questions, and answer choices aloud. (Reading test passages are NOT read aloud on CD.) |
Oklahoma |
Human Reader - Math Items: Teacher reading items must read over the student’s shoulder not from a separate test booklet. |
Oregon |
Human Reader - Directions: Introductions to reading passages are not considered part of the directions and may not be read. Any information in the body of an item is considered part of that item and may not be read as directions. |
Pennsylvania |
Text to Speech - Math Items: Requirements for use of screen or text reader: The student uses an electronic reader routinely during classroom instruction and assessment in this subject (both before and after the test is administered; and the student is severely limited or prevented from participating in statewide tests without the use of this accommodation (i.e. student is not simply performing below grade-level expectations); and the use of an electronic reader is documented in the student’s IEP or 504 plan; and PDE must approve the computer application and all program functions prior to PSSA and PSSA-M test window.
Text to Speech - Math Passages: The student uses an electronic reader routinely during classroom instruction and assessment in this subject (both before and after the test is administered; and the student is severely limited or prevented from participating in statewide tests without the use of this accommodation (i.e. student is not simply performing below grade-level expectations); and the use of an electronic application and all program functions prior to PSSA and PSSA-M test window.
Pre-recorded Audio - Math Items: Requirements for use of audio version CD: The student uses an audio version routinely during classroom instruction and assessment in this subject (both before and after the test is administered; and the student is severely limited or prevented from participating in statewide tests without the use of this accommodation (i.e. student is not simply performing below grade-level expectations); and the use of an audio version is documented in the student’s IEP or 504 plan; and PDE must approve the use of the audio version CD prior to test window. |
Rhode Island |
Human Reader - Reading Items: Modification. The read aloud accommodation (P3) is not allowed for the Reading test. If it is used, all reading items in the sessions that are read aloud will be scored as incorrect.
Human Reader - Math Items: On the Mathematics Test, the symbols or numbers written as numerals may not be read aloud. All symbols and numerals in mathematics items and multiple-choice answers are to be pointed to only.
Human Reader - Reading Passages: Note that reading any portion of the Reading Test to students is considered a modification (M2) and invalidates all test sessions that have been read.
Human Reader - Math Passages: On the Mathematics Test, the symbols or numbers written as numerals may not be read aloud. All symbols and numerals in mathematics items and multiple-choice answers are to be pointed to only. |
South Carolina |
Human Reader - Reading Items: A qualified person may be provided to read orally to students who are unable to decode text visually. Readers should use even inflection so that the student does not receive any cues by the way the information is read. It is important for readers to read test items/questions and text word for word exactly as written. Readers may not clarify, elaborate, or provide assistance to students. Readers need to be familiar with the terminology and symbols specific to the content. Graphic materials may be described but should also be made available in print or tactile formats. Readers must be provided to students on an individual basis--not to a group of students. A student should have the option of asking a reader to slow down or repeat text. This cannot occur when a person is reading to an entire group of students. *NOTE: Non-standard on the ELA test of the PASS in third and fourth grades only.
Human Reader - Math Items: A qualified person may be provided to read orally to students who are unable to decode text visually. Readers should use even inflection so that the student does not receive any cues by the way the information is read. It is important for readers to read test items/questions and text word for word exactly as written. Readers may not clarify, elaborate, or provide assistance to students. Readers need to be familiar with the terminology and symbols specific to the content. This is especially important for high school mathematics and science. Graphic materials may be described but should also be made available in print or tactile formats. Readers must be provided to students on an individual basis--not to a group of students. A student should have the option of asking a reader to slow down or repeat text. This cannot occur when a person is reading to an entire group of students.
Human Reader - Reading Passages: A qualified person may be provided to read orally to students who are unable to decode text visually. Readers should use even inflection so that the student does not receive any cues by the way the information is read. It is important for readers to read test items/questions and text word for word exactly as written. Readers may not clarify, elaborate, or provide assistance to students. Readers need to be familiar with the terminology and symbols specific to the content. Graphic materials may be described but should also be made available in print or tactile formats. Readers must be provided to students on an individual basis--not to a group of students. A student should have the option of asking a reader to slow down or repeat text. This cannot occur when a person is reading to an entire group of students. *NOTE: Non-standard on the ELA test of the PASS in third and fourth grades only.
Human Reader - Math Passages: A qualified person may be provided to read orally to students who are unable to decode text visually. Readers should use even inflection so that the student does not receive any cues by the way the information is read. It is important for readers to read test items/questions and text word for word exactly as written. Readers may not clarify, elaborate, or provide assistance to students. Readers need to be familiar with the terminology and symbols specific to the content. This is especially important for high school mathematics and science. Graphic materials may be described but should also be made available in print or tactile formats. Readers must be provided to students on an individual basis--not to a group of students. A student should have the option of asking a reader to slow down or repeat text. This cannot occur when a person is reading to an entire group of students.
Pre-recorded Audio - Reading Items: Written tests are prerecorded on an audio cassette or compact disk (CD) that a student accesses by listening. Audio versions of tests need to be supplemented with a print or Braille version of the text so a student can have access to complicated graphic material. Spot check audio formats before use to make certain everything is working properly. Copyright issues may need to be addressed. Audiotapes and CDs used in statewide assessments are secure materials and must be signed out, collected, and kept in a secure location. *NOTE: Non-standard on the ELA test of the PASS in third and fourth grades only.
Pre-recorded Audio - Math Items: Written tests are prerecorded on an audio cassette or compact disk (CD) that a student accesses by listening. Audio versions of tests need to be supplemented with a print or Braille version of the text so a student can have access to complicated graphic material. Spot check audio formats before use to make certain everything is working properly. Copyright issues may need to be addressed. Audiotapes and CDs used in statewide assessments are secure materials and must be signed out, collected, and kept in a secure location. *NOTE: Non-standard on the ELA test of the PASS in third and fourth grades only.
Pre-recorded Audio - Reading Passages: Written tests are prerecorded on an audio cassette or compact disk (CD) that a student accesses by listening. Audio versions of tests need to be supplemented with a print or Braille version of the text so a student can have access to complicated graphic material. Spot check audio formats before use to make certain everything is working properly. Copyright issues may need to be addressed. Audiotapes and CDs used in statewide assessments are secure materials and must be signed out, collected, and kept in a secure location. *NOTE: Non-standard on the ELA test of the PASS in third and fourth grades only.
Pre-recorded Audio - Math Passages: Written tests are prerecorded on an audio cassette or compact disk (CD) that a student accesses by listening. Audio versions of tests need to be supplemented with a print or Braille version of the text so a student can have access to complicated graphic material. Spot check audio formats before use to make certain everything is working properly. Copyright issues may need to be addressed. Audiotapes and CDs used in statewide assessments are secure materials and must be signed out, collected, and kept in a secure location. *NOTE: Non-standard on the ELA test of the PASS in third and fourth grades only. |
South Dakota |
Human Reader - Reading Items: Reading the Reading Comprehension test questions aloud is permissible. Readers may only be provided when identified on a student’s IEP or Section 504 plan to allow students with disabilities the opportunity to demonstrate their aptitude and achievement in testing situations rather than reflecting their impairment.
Human Reader - Math Items: Readers may only be provided when identified on a student’s IEP or Section 504 plan to allow students with disabilities the opportunity to demonstrate their aptitude and achievement in testing situations rather than reflecting their impairment. For example, allowing a student with dyslexia to have word problems read to him or her during the mathematics subtest is an appropriate accommodation for this student because math skills, not reading, are being assessed.
Human Reader - Math Passages: Readers may only be provided when identified on a student’s IEP or Section 504 plan to allow students with disabilities the opportunity to demonstrate their aptitude and achievement in testing situations rather than reflecting their impairment. For example, allowing a student with dyslexia to have word problems read to him or her during the mathematics subtest is an appropriate accommodation for this student because math skills, not reading, are being assessed. |
Texas |
Human Reader - Reading Items: Oral Administration. Gr. 3-8 reading test questions and answer choices only; NEVER the reading selections. |
Utah |
Human Reader - Reading Items: Computer based CRTs: Screen reader should be used to provide this accommodation on all CRTs. If a student is unable to interact with the screen reader, appropriate documentation must be included in the student’s IEP, ELL plan or 504 plan.
Human Reader - Math Items: Computer based CRTs: Screen reader should be used to provide this accommodation on all CRTs. If a student is unable to interact with the screen reader, appropriate documentation must be included in the student’s IEP, ELL plan or 504 plan.
Human Reader - Reading Passages: CRT: Screen reader should be used to provide this accommodation on all CRTs. If a student is unable to interact with the screen reader, appropriate documentation must be included in the student’s IEP, ELL plan or 504 plan.
Human Reader - Math Passages: CRT: Screen reader should be used to provide this accommodation on all CRTs. If a student is unable to interact with the screen reader, appropriate documentation must be included in the student’s IEP, ELL plan or 504 plan. |
Vermont |
Human Reader - Reading Items: Modifications. The read aloud accommodation (P3) is not allowed for the Reading test. If it is used, all reading items in the sessions that are read aloud will be scored as incorrect.
Human Reader - Math Items: On the Mathematics Test, the symbols or numbers written as numerals may not be read aloud. All symbols and numerals in mathematics items and multiple-choice answers are to be pointed to only.
Human Reader - Reading Passages: Note that reading any portion of the Reading Test to students is considered a modification (M2) and invalidates all test sessions that have been read.
Human Reader - Math Passages: On the Mathematics Test, the symbols or numbers written as numerals may not be read aloud. All symbols and numerals in mathematics items and multiple-choice answers are to be pointed to only. |
Virginia |
Human Reader - Reading Items: All read-aloud administrations must be recorded or proctored. The read-aloud accommodation on the statewide Reading assessments is allowed only for students with a visual impairment, including blindness, and those students with a specific disability that severely limits or prevents them from decoding text at any level of difficulty as determined by a diagnostic tool or instrument that was administered by a qualified professional. Students with disabilities who are simply having difficulty reading text and/or are reading below grade-level are not allowed the read-aloud accommodation on the statewide Reading assessments. If the read-aloud accommodation for the reading test is provided for students with disabilities who have not been determined as eligible by the school division according to the criteria stated above, the read-aloud will be considered a non-standard accommodation and the student will be considered a non-participant in the calculation of Adequate Yearly Progress (AYP).
Human Reader - Math Items: All read-aloud administrations must be recorded or proctored.
Human Reader - Reading Passages: All read-aloud administrations must be recorded or proctored. The read-aloud accommodation on the statewide Reading assessments is allowed only for students with a visual impairment, including blindness, and those students with a specific disability that severely limits or prevents them from decoding text at any level of difficulty as determined by a diagnostic tool or instrument that was administered by a qualified professional. Students with disabilities who are simply having difficulty reading text and/or are reading below grade-level are not allowed the read-aloud accommodation on the statewide Reading assessments. If the read-aloud accommodation for the reading test is provided for students with disabilities who have not been determined as eligible by the school division according to the criteria stated above, the read-aloud will be considered a non-standard accommodation and the student will be considered a non-participant in the calculation of Adequate Yearly Progress (AYP).
Human Reader - Math Passages: All read-aloud administrations must be recorded or proctored.
Pre-recorded Audio - Reading Items: The audio accommodation on the statewide Reading assessments is allowed only for students with a visual impairment, including blindness, and those students with a specific disability that severely limits or prevents them from decoding text at any level of difficulty as determined by a diagnostic tool or instrument that was administered by a qualified professional. Students with disabilities who are simply having difficulty reading text and/or are reading below grade-level are not allowed the audio accommodation on the statewide Reading assessments. If the audio accommodation for the reading test is used for students with disabilities who have not been determined as eligible by the school division according to the criteria stated above, the audio will be considered a non-standard accommodation and the student will be considered a non-participant in the calculation of Adequate Yearly Progress (AYP). |
Washington |
Human Reader - Reading Items: Human readers are not allowed for the reading assessment in grades 3-8 or on any reading section or level of the WELPA.
Human Reader - Reading Passages: Human readers are not allowed for the reading assessment in grades 3-8 or on any reading section or level of the WELPA.
Text to Speech - Reading Items: Text-to-speech software/technology may not be used for the reading assessment in grades 3-8.
Text to Speech - Reading Passages: Text-to-speech software/technology may not be used for the reading assessment in grades 3-8.
Pre-recorded Audio - Reading Items: Read aloud CDs are available for high school students taking the reading HSPE and WAAS-DAPE at both the MS (middle school) and ES (elementary school) levels. These CDs should be used in place of a human reader.
Pre-recorded Audio - Reading Passages: Read aloud CDs are available for high school students taking the reading HSPE and WAAS-DAPE at both the MS (middle school) and ES (elementary school) levels. These CDs should be used in place of a human reader. |
West Virginia |
Text to Speech - Reading Directions: Use a text-talk converter to present directions, stimulus material, questions, and answer choices verbatim for a blind or partially-sighted student when that is the student’s typical mode of accessing written material.
Text to Speech - Reading Items: Use a text-talk converter to present directions, stimulus material, questions, and answer choices verbatim for a blind or partially-sighted student when that is the student’s typical mode of accessing written material.
Text to Speech - Reading Passages: Use a text-talk converter to present directions, stimulus material, questions, and answer choices verbatim for a blind or partially-sighted student when that is the student’s typical mode of accessing written material. |
Wisconsin |
Human Reader - Reading Items: Read the Reading test ONLY in the following scenarios as described in Form I-7-B: For a student with visual impairments who is not yet proficient in contracted Braille, the WKCE Reading test passages and questions may be read aloud.
Human Reader - Reading Passages: Read the Reading test ONLY in the following scenarios as described in Form I-7-B: For a student with visual impairments who is not yet proficient in contracted Braille, the WKCE Reading test passages and questions may be read aloud. |
Wyoming |
Human Reader - Math Directions: Teachers reads directions verbatim looking over the student’s shoulder, not from a separate book or computer screen.
Human Reader - Math Items: Teachers reads questions verbatim looking over the student’s shoulder, not from a separate book or computer screen.
Text to Speech - Reading Items: Listed as a nonstandard accommodation.
Text to Speech - Math Items: Listed as a nonstandard accommodation.
Text to Speech - Reading Passages: Listed as a nonstandard accommodation.
Text to Speech - Math Passages: Listed as a nonstandard accommodation. |
Top of page |

 Note: A= Allowed, AC=Allowed in Certain Circumstances, AI = Allowed with Implications, P = Prohibited, NP = No Policy. N=51.
Note: A= Allowed, AC=Allowed in Certain Circumstances, AI = Allowed with Implications, P = Prohibited, NP = No Policy. N=51.
 Note: A= Allowed, AC=Allowed in Certain Circumstances, AI = Allowed with Implications, P = Prohibited, NP = No Policy. N=51.
Note: A= Allowed, AC=Allowed in Certain Circumstances, AI = Allowed with Implications, P = Prohibited, NP = No Policy. N=51.

 Note: A= Allowed, AC=Allowed in Certain Circumstances, AI = Allowed with Implications, P = Prohibited, NP = No Policy. N=51.
Note: A= Allowed, AC=Allowed in Certain Circumstances, AI = Allowed with Implications, P = Prohibited, NP = No Policy. N=51.
