Appendix B
Participation and
Accommodation Guidelines by State
Table B.1: Additional Testing
Options
|
State
|
Selective
Participation
|
Combination
Participation
|
Out-of-Level
Assessments
|
Locally
Selected Assessments
|
Testing with
Modifications or Non-standard
Accommodations
|
Testing
Using Unique Aggregated
Accommodations
|
|
Alabama
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Alaska
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Arizona
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Arkansas
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
California
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Colorado
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Connecticut
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Delaware
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
District of
Columbia
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Florida
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Georgia
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Hawaii
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Idaho
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Illinois
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indiana
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Iowa
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Kansas
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Kentucky
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Louisiana
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maine
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maryland
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Massachusetts
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Michigan
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Minnesota
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mississippi
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Missouri
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Montana
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Nebraska
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Nevada
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
New Hampshire
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
New Jersey
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
New Mexico
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
New York
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
North Carolina
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
North Dakota
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ohio
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oklahoma
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oregon
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Pennsylvania
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rhode Island
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
South Carolina
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
South Dakota
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Tennessee
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Texas
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Utah
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Vermont
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
Virginia
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Washington
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
West Virginia
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wisconsin
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wyoming
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total
|
2
|
16
|
5
|
1
|
21
|
3
|
Table B.2: Specifications of
Additional Testing Options
|
Alabama
|
Testing with
modifications or non-standard
accommodations - Some
accommodations are listed as
non-standard and result in only
raw scores being reported.
|
|
Colorado
|
Testing with
modifications or non-standard
accommodations - Any
requests that are determined to
affect the integrity, validity,
reliability, or comparability of
the assessments results, or are
identified as a modification
will not be approved. If a
request is not approved: the
student may test without the
accommodation but if it is used
they will receive a "no score."
Combination
Participation -
Participation in both CSAP and
CSAPA by content area is
allowed.
|
|
Delaware
|
Selective
Participation - ELL students
with disabilities may receive
exemptions for the reading and
writing tests.
|
|
Florida
|
Combination
Participation - Students may
need certain accommodations on
some subtests, but not on
others; for example, a student
may need extra time and testing
in a small group situation to
complete extended response
questions, but can take a test
with multiple-choice questions
without accommodations.
|
|
Georgia
|
Testing using
unique aggregated accommodations
- Conditional and non-standard
accommodations: more expansive
accommodations that should be
used sparingly but do not affect
the reporting of scores.
|
|
Idaho
|
Combination
Participation - If the IEP
team determines that the student
meets the criteria for
participation in the alternate
assessment and the student is
working on content standards
within the general education
curriculum, the student may
participate in relevant portions
of the regular assessments and
participate in appropriate areas
in the alternate assessment.
|
|
Indiana
|
Combination
Participation - It may be
determined by a case conference
committee that a student would
benefit from participation in
both ISTEP+ and ISTAR (alternate
assessment). In this case, ISTAR
is considered a supplemental
assessment to ISTEP+, not an
alternate to ISTEP+.
|
|
Iowa
|
Combination
Participation - Some
students with that
classification will take part in
the general assessment (probably
with accommodations) and some
students with disabilities who
have other level classifications
may take part in the alternate
assessment although this would
be rare.
|
|
Massachusetts
|
Testing using
unique aggregated accommodations
- A non-standard accommodation
is defined as an accommodation
which changes the way an MCAS
test is presented or the way a
student responds to test
questions which may alter a
portion of what the test is
intended to measure. Performance
level results for students with
disabilities −whether
they take the standard tests
with standard or nonstandard
accommodations, or without
accommodations, or participate
through the MCAS-Alt, are
aggregated in MCAS reports with
the results for students who
took the tests without
accommodations. Scaled scores
for tests taken with either
standard or nonstandard
accommodations are also
aggregated in MCAS reports with
scores of tests taken without
accommodations.
|
|
Michigan
|
Testing with
modifications or non-standard
accommodations -
Non-standard accommodations
change the construct that the
assessment is measuring
rendering scores that are not
valid; students who use
nonstandard assessment
accommodations will not count as
being assessed for the
calculation of the NCLB
participation rates for both the
school and district.
|
|
Montana
|
Testing using
unique aggregated accommodations
- Nonstandard accommodations.
Use makes test invalid and is
not included as a part of AYP.
|
|
Oregon
|
Testing with
modifications or non-standard
accommodations -
Modifications. Any change away
from a standard administration
that is not listed in the
Accommodations Tables is
considered a modification. A
modification is any practice or
procedure that compromises the
intent of the assessment through
a change in the learning
expectations, construct,
grade-level standard, or
measured outcome of the
assessment that is not
authorized explicitly by the
Oregon Accommodations Panel and
listed on the stateís
Accommodations Table A. . . .
Assessments taken under any
modified condition are counted
as non-participants in all state
accountability measures and
reports.
|
|
South Dakota
|
Out-of-Level
Assessments - This feature
allows an instructor to enter a
student at the grade level that
he/she would like the student to
start on either the Math or
Reading test.
|
|
Vermont
|
Out-of-Level
Assessments - The adapted
assessment option is based on
out-of-level administrations of
the general statewide
assessments.
Locally Selected Assessments
- The studentís team may select
modified assessments or prepare
a portfolio of work samples that
will be submitted to the
Departmentís Alternate
Assessment Program for review
and scoring. A studentís support
team can also select two content
areas from the Lifeskills
Portfolio format to assess using
the portfolio method.
Testing with modifications or
non-standard accommodations
- IEP teams do have the
authority to use unapproved
accommodations on the assessment
for a student; however, these
tests will be considered
non-comparable to the general
assessment and scored as invalid
in the school accountability
index.
|
|
Virginia
|
Testing with
modifications or non-standard
accommodations - A student
who has passed a Standard of
learning assessment utilizing
any accommodation, including a
non-standard accommodation, has
passed for all purposes,
including earning verified
credit.
|
|
Washington
|
Out-of-Level
Assessments - Students take
the WASL, with or without
accommodations, at a grade level
that best matches their
abilities.
|
Table B.3: Circumstances in
Which Students are Not Included in any
Form of Statewide Assessment
|
State
|
Exclusion
Prohibited
|
Parent
Exemption
|
Emotional
Distress
|
Medical
Condition/Illness
|
Student
Refusal
|
Disruptive
Behavior
|
Absence
|
Other
|
|
Alabama
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Alaska
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Arizona
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Arkansas
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
California
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Colorado
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Connecticut
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Delaware
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
District of
Columbia
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Florida
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Georgia
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hawaii
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Idaho
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Illinois
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indiana
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Iowa
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Kansas
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Kentucky
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Louisiana
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maine
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Maryland
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Massachusetts
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Michigan
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Minnesota
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mississippi
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Missouri
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Montana
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Nebraska
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nevada
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
New Hampshire
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
New Jersey
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
New Mexico
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
New York
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
North Carolina
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
North Dakota
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ohio
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oklahoma
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oregon
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pennsylvania
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rhode Island
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
South Carolina
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
South Dakota
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tennessee
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Texas
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Utah
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Vermont
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Virginia
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Washington
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
West Virginia
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wisconsin
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wyoming
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total
|
30
|
6
|
4
|
16
|
0
|
2
|
2
|
12
|
Table B.4: Specifications and
Descriptions of ďOtherĒ Circumstances in
Which Students Are Not Included in any
Form of Statewide Assessment
|
California
|
Parent Exemption
Ė Understanding 2009 STAR
Program Tests and California
Code of Regulations (CCR),
Section 852.
Medical Condition/Illness
- CCR Section 850(n) defines a
significant medical emergency
that would preclude
participation.
|
|
Connecticut
|
Medical
Condition/Illness - Students
should be tested unless there
are medical constraints or a
medical emergency.
|
|
Delaware
|
Absence Ė
May be exempt due to excessive
absenteeism.
Other - ELL students with
disabilities may be exempt due
to: lack of formal education,
interrupted education, or
transient student.
|
|
Hawaii
|
Parent Exemption
- A student who is exempted from
participating in the Hawaii
State Reading and Mathematics
Assessments at the written
request of the studentís parents
counts for participation
purposes. The principal must
forward the parentís written
request to the Systems
Accountability Office, Student
Assessment Section, where it
will be reviewed and approved or
disapproved.
Emotional Distress - A
studentís current physical,
mental, and/or emotional needs
do not prevent the student from
taking the assessment at the
most appropriate site during the
testing window.
Medical Condition/Illness
- A student who has a
significant medical emergency
must have a physicianís signed
report that describes the
medical emergency that causes
the student to be deemed
medically unable to participate
in the Hawaii State Reading and
Mathematics Assessments.
Disruptive Behavior - If
a student becomes disruptive
during a session, the student
must be removed from the testing
room immediately and the
situation documented on the
Irregularity Report Form. The
student may not retake or make
up that session.
Other - A
student who is receiving
services at an out-of-state
residential program that is
approved by the studentís
Individualized Education Program
(IEP) or Modification Plan (MP)
team, a hearings officer, or a
judge cannot be tested because
the Department of Education will
not allow its secure test
materials to be released to a
site outside the state. A
student who meets the
requirements of Regulation 4140,
Exceptions to Compulsory School
Attendance, will not be tested
if the student withdraws from
the Hawaii public school and
public charter school system
before the first day of the
official testing window. A
student who is dismissed, as
opposed to suspended, from
school will not be tested.
|
|
Indiana
|
Other -
Students in nonpublic schools
that are not accredited,
including home schooled
students, may not participate in
ISTEP+ testing in their
nonpublic school.
|
|
Kansas
|
Medical
Condition/Illness -
Catastrophic illness or accident
has caused a student to be
seriously disabled by accident
or illness. Student does not
need to be tested.
Absence Ė If a student is
absent due to a medical
condition/illness or suspension,
the student does not need to be
tested.
Other Ė Students in the
following situations do not need
to be tested: Long term
suspension, dropped out of
school, is home schooled, is 19
years or older, or is in jail or
special center in an adult
facility. ELL criteria for
recent arrival to US allows
student not to take certain
assessments.
|
|
Kentucky
|
Emotional
Distress Ė Exemption may be
granted if participation in the
state required assessment would
jeopardize a studentís mental or
emotional well being and a
school or district has submitted
a request.
|
|
Maine
|
Emotional
Distress - Special
Consideration may be available
when a studentís long-term or
emergency condition, physical or
mental, prevents the studentís
participation in the MEA even
with accommodations or through
PAAP (terminal illness,
injuries, extraordinary medical
treatment for either a physical
or psychiatric condition).
Medical Condition/Illness
- Special Consideration may be
available when a studentís
long-term or emergency
condition, physical or mental,
prevents the studentís
participation in the MEA even
with accommodations or through
PAAP (terminal illness,
injuries, extraordinary medical
treatment for either a physical
or psychiatric condition).
Disruptive Behavior -
Special Consideration may be
available when a studentís
long-term or emergency
condition, physical or mental,
prevents the studentís
participation in the MEA even
with accommodations or through
PAAP (terminal illness,
injuries, extraordinary medical
treatment for either a physical
or psychiatric condition).
|
|
Maryland
|
Emotional
Distress - The student has
demonstrated by past performance
that he/she cannot function in a
testing situation (for example,
the student exhibits intense or
extreme anxiety behaviors during
testing).
Medical Condition/Illness
- Students may be exempted from
the MSA when they cannot take
the assessment during the entire
testing window, including the
make-up dates, because of a
significant medical emergency.
Other - The student has
had a recent traumatic
experience, which has made
him/her unable to cope with the
testing situation.
|
|
Massachusetts
|
Other -
Schools have the option of
assessing LEP students who first
enrolled in a U.S. school after
March 1, 2008, in the English
Language Arts test.
|
|
Minnesota
|
Parent Exemption
- Parental refusal.
|
|
Mississippi
|
Medical
Condition/Illness -
Non-Participation Due to
Significant Medical Emergency.
|
|
Missouri
|
Other -
Students whose IEP teams have
determined that MAP-A is the
appropriate assessment, and
English Language Learner
students who have been in the
United States 12 months or fewer
at the time of administration of
MAP assessments may be exempted
from taking only the
Communication Arts test. All
other content areas must be
assessed.
|
|
Montana
|
Other - For
their first year in the US, LEP
students are required to
participate only in the
mathematics and science tests,
they are excluded from the
reading assessment. Students not
enrolled in an accredited
Montana school, a private
non-accredited school, or
enrolled part-time taking a
mathematics, reading, or science
course may participate (but are
not required to participate).
|
|
New
Hampshire
|
Other -
First year LEP students;
Enrolled after test window
opens, withdrew during test
window, placed out-of-state by
district and participate in
receiving stateís assessment and
accountability system; home
schooled.
|
|
Oklahoma
|
Medical
Condition/Illness - In the
event that an unforeseen medical
emergency absolutely prevents
the student from being available
for testing during the stateís
testing window, emergency
exemption permission must be
obtained from the Office of
Accountability and Assessments.
|
|
Oregon
|
Parent Exemption
- Oregon Administrative Rule
581-022-0612.
|
|
Pennsylvania
|
Parent Exemption
- A student may be excused from
the assessment if a parent
believes the test conflicts with
religious beliefs.
|
|
South Carolina
|
Medical
Condition/Illness -
Homebound students for whom the
district has documentation
indicating that the student is
not physically and/or
emotionally able to take the
tests.
Other - Expelled students
(unless the student has an IEP).
|
|
Utah
|
Emotional
Distress - Any student may
be excused from participation in
statewide assessments in the
event of a medical emergency
where a student is suffering
extreme distress, such as a
medical or psychological crisis.
Medical Condition/Illness
Ė See note above.
Other - ELL students
enrolled on or after April 15th
of the current school year and
who are new to the United States
(first year of enrollment in any
U.S. school) are exempt from all
state tests.
|
|
Vermont
|
Medical
Condition/Illness - Student
must have a written statement
from a medical doctor indicating
the student cannot participate
in the assessment for the entire
test administration window.
Other - Students who are
experiencing a family emergency
or student crisis, students who
enroll in the school after the
testing window, students who are
expelled or suspended for the
entire test administration
window.
|
|
West Virginia
|
Medical
Condition/Illness - Special
participation rate exemptions
for medically, physically, or
mentally fragile students are
based on a studentís physical or
mental condition and may be
available for students suffering
from a terminal illness or
injuries or receiving
extraordinary short-term medical
treatment for either a physical
or psychiatric condition.
|
|
Wisconsin
|
Medical
Condition/Illness -
Significant medical emergency.
|
Table B.5: Participation
Policy Variables That Can be Used to
Make Decisions About How Students with
Disabilities Participate in Statewide
Assessment
|
State
|
IEP
Deter-
mined
|
Nature or
Category of
Disability
|
Instructional
Relevance/
Instruction Goals
|
Past
Performance
|
Non-pursuit of
a Standard Diploma
|
Degree
of Adap-
tations Needed
|
Content/
Purpose/
Nature of Assessment
|
Current
Performance/ Level of
Functioning
|
Level of
Independence
|
Student Needs
and Charac-teristics
|
Other
|
|
Alabama
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Alaska
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Arizona
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Arkansas
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
California
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Colorado
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Connecticut
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Delaware
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
District
of Columbia
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
Florida
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Georgia
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hawaii
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Idaho
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Illinois
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Indiana
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Iowa
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
Kansas
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Kentucky
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Louisiana
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Maine
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maryland
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
Massachusetts
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Michigan
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Minnesota
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Mississippi
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Missouri
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Montana
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Nebraska
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Nevada
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
New Hampshire
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
New Jersey
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
New Mexico
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
New York
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
North
Carolina
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
North
Dakota
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Ohio
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Oklahoma
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Oregon
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Pennsylvania
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rhode
Island
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
South
Carolina
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
South
Dakota
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Tennessee
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
Texas
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Utah
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Vermont
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Virginia
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Washington
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
West
Virginia
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Wisconsin
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Wyoming
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Total
|
51
|
23
|
39
|
15
|
4
|
16
|
7
|
33
|
24
|
28
|
8
|
Table B.6: Specifications and
Descriptions of ďOtherĒ Participation
Policy Variables That Can Be Used to
Make Decisions About How Students with
Disabilities Participate in Statewide
Assessment
|
Alaska
|
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
- Objectives written for the
student in the designated
content area(s) are less complex
than the grade level
expectations, making the regular
assessment, even with
accommodations, inappropriate
for this student.
Degree of Adaptations Needed
- The modifications needed by
the student to participate in
the regular assessment would
compromise validity of the test.
Student Needs
and Characteristics -
Cognitive ability and adaptive
skill. The student requires
extensive, frequent,
individualized instruction in
multiple settings to acquire,
maintain, generalize and
demonstrate performance of
skills. The student demonstrates
cognitive ability and adaptive
behavior that require
substantial adjustments to the
general curriculum.
|
|
Arizona
|
Nature or
Category of Disability -
Empirical evidence of a
significant cognitive
disability.
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
- The goals and objectives in
the studentís IEP focus on
enrolled grade-level Alternate
Arizona Academic Standards, from
eligibility determination form
for alternate assessments.
Current Performance/Level of
Functioning - Student has a
significant cognitive disability
that prevents the acquisition of
the Arizona Academic Standards.
Level of Independence -
It is extremely difficult for
the student to acquire,
maintain, generalize, and apply
academic skills across
environments even with
extensive/intensive, pervasive,
frequent, and individualized
instruction in multiple
settings.
|
|
Arkansas
|
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
- Studentís course of study is
primarily functional and
life-skills oriented.
Past Performance - Based
on current and historical data.
Other - Decisions were
made at the IEP meeting
preceding the next school yearís
administration of any statewide
assessment.
|
|
California
|
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
- Learning objectives and
expected outcomes focus on the
functional applications of the
general curriculum.
Degree of Adaptations Needed
- Student requires substantial
adjustments to the general
curriculum. The student cannot
address the performance level
assessed in the statewide
assessment, even with
accommodations or modifications.
Current Performance/Level of
Functioning -Demonstrates
academic/cognitive ability and
adaptive behavior that require
substantial adjustments to the
general curriculum.
|
|
Colorado
|
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
- In order to determine
eligibility of students who take
the CSAPA, the teacher must look
at the studentís use of expanded
benchmarks.
Past Performance - Review
previous evidence of student
participation and results in the
CSAP and CELA.
Content/Purpose/Nature of
Assessment - Decisions about
which assessment the student
will participate must be made
annually and for each content
area.
Current Performance/Level of
Functioning - Consider the
capacity of the student to
demonstrate and communicated as
needed for the tasks required by
each test administered at the
studentís grade level.
Student Needs and
Characteristics -
Accommodations must be based
upon individual student needs.
|
|
Connecticut
|
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
- Does the studentís IEP include
goals that are based on the
academic content standards for
the grade in which the student
is enrolled?
Degree of Adaptations Needed
- Did student receive classroom
accommodations that have also
been used during state/district
assessment? Does the student
receive classroom modifications?
Current Performance/Level of
Functioning - Does the
studentís disability cause
substantial academic
difficulties? Does the
disability of the student
preclude him/her from achieving
grade-level proficiency at the
same rate as his/her
non-disabled peers?
Other - Is the studentís
difficulty with regular
curriculum demands primarily due
to his/her disability and
not/due to excessive absences
unrelated to the disability, or
social, environmental, or
economic factors?
|
|
Delaware
|
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
- The student requires
extensively modified instruction
focusing on a less complex
application of skills in order
to access the Delaware Content
Standards.
Past Performance -
Longitudinal data across
multiple settings in the areas
of academics, communication,
cognition, social competence,
recreation or leisure, domestic
community living, and vocational
skills.
Degree of Adaptations Needed
- Extensive modifications are
required in order to access the
general curriculum.
Current Performance/Level of
Functioning - Current
performance data across multiple
settings in the areas of
academics, communication,
cognition, social competence,
recreation or leisure, domestic
community living, and vocational
skills.
Level of Independence -
Student requires extensive
direct instruction and/or
extensive supports to accomplish
the application, and transfer of
skills to school, home, work,
and community environments.
Other -
Behavioral observations in
multiple settings. Adaptive
behavior. Continuous assessment
of progress on IEP goals and
objectives.
|
|
Florida
|
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
- IEP teams should ask the
question: is the student
participating in a modified or
functional curriculum based on
competencies in the Sunshine
State Standards for Special
Diploma for all academic areas?
Current
Performance/Level of Functioning
- Demonstrated low cognitive
ability. Student unable to
master the grade-level Sunshine
State Standards, even with
appropriate and allowable
course-accommodations.
Level of Independence -
Need for extensive, direct
instruction in the application
of skills in domestic, community
and vocational activities.
|
|
Georgia
|
Nature or
Category of Disability -
Does the student have
significant intellectual
disabilities or a combination of
intellectual disabilities with
motor, sensory, or emotional
behavior disabilities?
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
- Does the student require
instruction focused on
application of state standards
through relevant life skills?
Degree of Adaptations Needed
- Does the student require
substantial adaptations and
support to access the general
education curriculum?
|
|
Hawaii
|
Nature or
Category of Disability - The
student demonstrates significant
cognitive disabilities that may
be combined with limited
adaptive skills, physical or
behavioral limitations, and
requires a highly specialized
educational program with
intensive modifications and
accommodations for access to the
general academic curriculum.
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
- The studentís daily
instruction focuses on the
academic content standards
through Alternate Performance
Indicators that link to the
grade-level benchmarks. The
Alternate Performance Indicators
are at a lower level of
complexity and are designed to
serve as access or entry points
to the grade-level benchmarks.
Level of Independence -
The student requires intensive
direct instruction in multiple
settings to accomplish the
acquisition, application, and
transfer of knowledge and
skills.
Other - A studentís
current physical, mental, or
emotional needs do not prevent
the student from taking the
assessment at the most
appropriate site during the
testing window.
|
|
Idaho
|
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
- The studentís course of study
is primarily functional-skill
and living-skill oriented.
Current Performance/Level of
Functioning - The studentís
demonstrated cognitive ability
and adaptive behavior prevent
completion of the general
academic curriculum even with
program modifications.
Level of Independence -
The student is unable to
acquire, maintain, or generalize
skills (in multiple settings)
and demonstrate performance of
those skills without intensive
frequent individualized
instruction.
|
|
Illinois
|
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
- The points at which the
student accesses the general
education curriculum more
closely reflect alternate
performance indicators than
age/grade-appropriate
benchmarks.
Level of
Independence - When compared
to other students with
disabilities, the student
requires more frequent, more
intensive instruction given in
small incremental steps in order
to apply and transfer skills
across settings.
|
|
Indiana
|
Other - If
student has intent to graduate
from high school page, (rights
of student to pursue high school
diploma).
|
|
Iowa
|
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
- Has the grade level content
been significantly changed in
terms of delivery?
Degree of Adaptations Needed
- Need for very intensive,
highly specialized instruction.
Current Performance/Level of
Functioning - The student is
generally unable, even with
accommodations, to demonstrate
knowledge and skills on
district-wide assessments used
for the majority of students.
Level of
Independence - The student
requires very intensive, highly
specialized instruction in order
to acquire knowledge, make
generalizations, or demonstrate
skills across natural
environments (home, school,
community, or workplace).
Student Needs and
Characteristics - The
student has characteristics of a
severe disability, including
significant deficits in language
and communication and adaptive
behaviors.
|
|
Louisiana
|
Past Performance
- The student scored at the
unsatisfactory level in English
language arts and/or mathematics
on the previous yearís
LEAP/iLEAP/GEE or participated
in LAA 1 or LAA 2.
Current Performance/Level of
Functioning - The studentís
IEP reflects a functioning grade
level in English language arts
(including reading) or
mathematics at least three grade
levels below the actual grade
level in which he or she is
enrolled.
Student Needs and
Characteristics - The
decision for LAA2 is an IEP team
decision based on the needs of
the student.
|
|
Maine
|
Nature or
Category of Disability -
Must be in special education and
have an identified significant
or profound disability.
|
|
Maryland
|
IEP Determined
- A student who would have been
eligible for the Mod-MSA would
be identified based on his/her
individual evaluation
information and the
instructional and service
information on his/her IEP.
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
- The student requires explicit
and ongoing instruction in
functional skills.
Past Performance
- There must be sufficient
objective evidence demonstrating
that the student is not likely
to achieve grade-level
proficiency within the school
year covered by his/her IEP.
Degree of Adaptations Needed
- The student requires and
receives modified academic
achievement standards aligned
with the Maryland Academic
Content Standards for the
studentís grade level during
instruction and assessments. The
student requires extensive and
substantial modification of the
general education curriculum.
Current Performance/Level of
Functioning - The student
has had consecutive years of
individualized intensive
instruction in Reading,
Mathematics, or Science
consistent with his/her IEP, and
although progress toward
grade-level standards was made,
he/she is not yet making
progress at grade level. The
student demonstrates that he/she
cannot attain proficiency on the
actual grade-level MSA, even
with the provision of
accommodations based on
documented multiple valid and
objective measures of studentís
progress.
Level of Independence -
The student requires extensive
support to perform and
participate meaningfully and
productively in daily activities
in school, home, community, and
work environments.
Student Needs and
Characteristics - The
student requires extensive
support to perform and
participate meaningfully and
productively in daily activities
in school, home, community, and
work environments.
|
|
Massachusetts
|
IEP Determined
- During its annual meeting, a
studentís IEP or 504 team must
determine how the student will
participate in MCAS for each
subject scheduled for
assessment.
Nature or Category of
Disability - Working on
learning standards that have
been substantially modified due
to the nature and severity of
his or her disability.
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
- Student is receiving
intensive, individualized
instruction in order to acquire,
generalize, and demonstrate
knowledge and skills.
Current Performance/Level of
Functioning - The student is
generally unable to demonstrate
knowledge and skills on a
paper-and-pencil test, even with
accommodations.
Level of Independence -
IEP teams should consider
whether the student is receiving
intensive, individualized
instruction in order to acquire,
generalize, and demonstrate
knowledge and skills.
|
|
Minnesota
|
Student Needs
and Characteristics - IEP
team is responsible for making
annual assessment and
accommodation decisions, which
must be based on individual need
in accordance with state and
federal guidelines.
|
|
Mississippi
|
IEP Determined
- Federal and state regulations
require the IEP team to make the
decision as the most appropriate
method of participation for a
student with disabilities in
each applicable component of the
testing program.
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
- How does the student access
the general education
curriculum?
Degree of Adaptations Needed
- What accommodation or support
is required by the student to
perform or participate
meaningfully and productively in
the general education
curriculum?
Content/Purpose/Nature of
Assessment - The IEP team
should make this decision (about
participation) separately for
each subject as a student may be
accessing the curriculum
differently depending on the
content.
Student Needs and
Characteristics - How does
the student access the general
education curriculum?
|
|
Missouri
|
IEP Determined
- All decisions regarding how a
student with a disability will
participate in the Missouri
Assessment Program are made by
the studentís IEP team and
documented in the IEP.
Nature or Category of
Disability - The student has
a demonstrated significant
cognitive disability and
adaptive behavioral skills.
Therefore, the student has
difficulty acquiring new skills,
and skills must be taught in
very small steps.
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
- The studentís educational
program centers on the
application of essential skills
to the Missouri Show-Me
Standards.
Past Performance - The
student does not keep pace with
peers, even with the majority of
students in special education,
with respect to the total number
of skills acquired.
Degree of Adaptations Needed
- Therefore, the student has
difficulty acquiring new skills,
and skills must be taught in
very small steps.
|
|
Nebraska
|
IEP Determined
- To assure students with
disabilities are engaged in
standards-based instruction and
assessments, every IEP team
member must be knowledgeable
about the state and district
academic content standards and
assessments.
Current Performance/Level of
Functioning - The studentís
demonstrated cognitive ability
and adaptive behavior prevent
completion of the general
academic curriculum, even with
appropriately designed and
implemented modifications and
accommodations.
Level of Independence -
The student requires intensive,
frequent and individualized
instruction in order to acquire,
maintain, and demonstrate
performance of those skills.
|
|
Nevada
|
IEP Determined
- The IEP committee has the
authority to determine how a
student will participate in the
statewide assessment program.
|
|
New Hampshire
|
Degree of
Adaptations Needed - Highly
Specialized Instruction and
Ample Supports listed as a
characteristic of students and
lists the nature of these (e.g.,
deliberate instruction to apply
skills across multiple settings;
specially designed prompting
procedures).
Current Performance/Level of
Functioning - Very low
levels of academic achievement
listed as a characteristic of
students appropriately served
under alternate assessment.
|
|
New Jersey
|
Nature or
Category of Disability - Is
the nature of the studentís
cognitive disability severe?
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
- Is the studentís cognitive
disability so severe that the
student is not receiving
instruction in any of the
knowledge and skills measured by
the general statewide
assessment?
Current Performance/Level of
Functioning - Is the
studentís cognitive disability
so severe that the student
cannot complete any of the types
of questions on the assessment
in the content area, even with
accommodations and
modifications?
|
|
New Mexico
|
IEP Determined
- The Individualized Education
Plan team determines how the
student will participate.
Student Needs and
Characteristics - This
(participation) decision is made
after carefully considering the
studentís unique needs and the
specific test(s) the student is
required to take.
|
|
New York
|
Nature or
Category of Disability -
Student has a severe cognitive
disability.
|
|
Oklahoma
|
IEP Determined
- Oklahoma law has mandated that
test accommodations be provided
for the testing of students with
disabilities. The accommodation
must be (1) specified in the IEP
or Section 504 Plan, and (2)
selected from the accommodations
specified in Appendix II.
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
- Criteria checklist for
assessing students with
disabilities on state
assessments.
Past Performance -
Previous performance on state
assessments. Criteria checklist
for assessing students with
disabilities on state
assessments.
Degree of Adaptations Needed
- Criteria checklist for
assessing students with
disabilities on state
assessments.
Current Performance/Level of
Functioning - The studentís
progress, to date, in response
to appropriate instruction.
Criteria checklist for assessing
students with disabilities on
state assessments.
Level of Independence -
Criteria checklist for assessing
students with disabilities on
state assessments.
Student Needs and
Characteristics - Criteria
checklist for assessing students
with disabilities on state
assessments.
Other - Other assessments
that document academic
achievement. Criteria checklist
for assessing students with
disabilities on state
assessments.
|
|
Oregon
|
Nature or
Category of Disability -
Performs significantly impacted
by the disability. How the
studentís disability affects
involvement and progress in the
general education curriculum.
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
- Instruction is primarily from
a specialized curriculum or from
general curriculum must be
significantly reduced in
breadth, depth, and complexity.
Past Performance -
Previous relevant experiences.
As appropriate, the studentís
performance on State or
district-wide assessments.
Current
Performance/Level of Functioning
- Performs well below grade
level. Is significantly below
grade level in reading. Student
has academic difficulties that
are generalized (to all subject
areas) and are significant. Is
the student able to interact
with instructional material in a
way that provides meaningful
feedback? Results of the initial
or most recent evaluation.
Level of Independence -
Benefits from specialized
individualized supports. Relies
on individual and significant
supports to access reduced
content materials.
Student Needs and
Characteristics - How is his
attention? The academic,
developmental, and functional
needs of the child.
Other - What assessment
did he take last year? What
types of behaviors should be
considered?
|
|
Pennsylvania
|
Nature or
Category of Disability - To
participate in PASA, students
must . . . have significant
cognitive disabilities.
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
- To participate in PASA,
students must . . . require
substantial modifications of
general education curriculum.
Non-pursuit of a Standard
Diploma - To participate in
PASA, students must . . .
require intensive instruction to
learn and require extensive
adaptation and support to
perform and meaningfully
participate in the activities.
Degree of Adaptations Needed
- To participate in PASA,
students must...require
intensive instruction to learn.
|
|
Rhode Island
|
IEP Determined
- Criteria for participation in
RIAA.
Nature or Category of
Disability - Student has a
disability that significantly
impacts cognitive function and
adaptive behavior.
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
- Criteria for participation in
RIAA.
Level of Independence -
The student is unable to apply
academic skills in home, school
and community without intensive,
frequent and individualized
instruction in multiple
settings.
|
|
South Carolina
|
Level of
Independence - The student
has current adaptive skills
requiring extensive direct
instruction and practice in
multiple settings to accomplish
the application and transfer of
skills necessary for application
in school, work, home, and
community environments.
Student Needs
and Characteristics -
Student is unable to apply or
use academic skills across
natural settings when instructed
solely or primarily through
classroom instruction.
|
|
South Dakota
|
Current
Performance/Level of Functioning
- The studentís cognitive
abilities are 2 standard
deviations or more below the
mean.
Level of
Independence - Student
primarily requires direct and
extensive instruction to
acquire, maintain, generalize
and transfer skills done in
naturally occurring settings of
the studentís life.
|
|
Tennessee
|
Non-pursuit of a
Standard Diploma - The
student is unable to complete a
state approved high school
diploma program, even with
extended learning opportunities
or accommodations.
Level of Independence -
The student requires intensive,
frequent individualized
instruction in a variety of
settings including school,
community, home, or the
workplace to acquire, maintain,
and generalize functional
academics and life skills.
Student Needs and
Characteristics - The
decision for TCAP-Alt
participation is based on the
needs of the student.
|
|
Texas
|
Student Needs
and Characteristics -
Accommodations must be selected
on the basis of an individual
studentís needs.
|
|
Utah
|
IEP Determined
- The IEP team must determine
how the student will participate
in U-PASS.
Current Performance/Level of
Functioning - Student
demonstrates cognitive ability
and adaptive skill levels that
prevent completion of the
general academic core curricula
even with instructional
accommodations.
Level of Independence -
Student requires extensive
individualized instruction in
multiple settings to transfer
and generalize skills.
|
|
Virginia
|
Nature or
Category of Disability - As
a result of a disability,
student is unable to demonstrate
knowledge and skills on a
multiple-choice test, even with
accommodations.
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
- Student must demonstrate
impairments that prevent the
completion of curriculum based
on the Standards of Learning
even with program and assessment
accommodations.
Non-pursuit of a Standard
Diploma - Is working toward
educational goals other than
those prescribed for a Modified
Standard, Standard, or Advanced
Studies diploma.
Content/Purpose/Nature of
Assessment - As a result of
a disability, is unable to
demonstrate knowledge and skills
on a multiple-choice test, even
with accommodations.
Level of Independence -
Requires intensive, frequent,
and individualized instruction
in a variety of settings to show
interaction and achievement.
|
|
Washington
|
Student Needs
and Characteristics - The
IEP team, which includes a
studentís parents or guardians,
decides which testing tool to
use based on the studentís needs
in each content area.
|
|
West Virginia
|
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
Ė A student shall not
participate in alternate
assessment unless he/she is
instructed by the extended
standards.
|
|
Wisconsin
|
IEP Determined
- IEP teams determine with
parent as equal participant.
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
- Studentís curriculum and daily
instruction.
|
|
Wyoming
|
Nature or
Category of Disability - The
student demonstrates a
significant cognitive disability
which results in performance
that is substantially below
grade-level achievement
expectations even with the use
of accommodations and
modifications.
Instructional
Relevance/Instruction Goals
- Students must participate in
the regular PAWS if they receive
any instruction on the standards
assessed, regardless of where
the instruction takes place.
Student Needs and
Characteristics - Learning
characteristics.
|
Table B.7: Participation
Policy Variables that Cannot Be Used to
Make Decisions About How Students with
Disabilities Participate in Statewide
Assessment
|
State
|
Receiving
Special Education Services
|
Presence or
Category of
Disability
|
Instructional
Program/Program Setting
|
Achievement
Level
|
Excessive
Absences
|
Percent Time
Receiving Special Education
Services
|
Cultural,
Social, Linguistic, or
Environmental Factors
|
Low
Expectations for the Student/
Anticipated
Low Scores
|
Other
|
|
Alabama
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Alaska
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Arizona
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Arkansas
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
California
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Colorado
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Connecticut
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Delaware
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
District
of Columbia
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Florida
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Georgia
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hawaii
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Idaho
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Illinois
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
Indiana
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Iowa
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Kansas
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Kentucky
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Louisiana
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Maine
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maryland
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Massachusetts
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Michigan
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Minnesota
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Mississippi
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Missouri
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Montana
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nebraska
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nevada
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
New Hampshire
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
New Jersey
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
New Mexico
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
New York
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
North Carolina
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
North Dakota
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ohio
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
Oklahoma
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Oregon
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pennsylvania
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rhode Island
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
South Carolina
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
South Dakota
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tennessee
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
Texas
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Utah
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vermont
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Virginia
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Washington
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
West Virginia
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wisconsin
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wyoming
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Total
|
9
|
23
|
14
|
11
|
16
|
8
|
18
|
14
|
18
|
Table B.8: Specifications and
Descriptions of ďOtherĒ Participation
Policy Variables That Cannot Be Used to
Make Decisions About How Students with
Disabilities Participate in Statewide
Assessment
|
Alaska
|
Receiving
Special Education Services -
The decision to participate in
the Alternate Assessment is not
primarily based on a specific
eligibility determination.
Presence or Category of
Disability -
Deafness/blindness, visual,
auditory, or motor disabilities,
not primarily based on a
specific eligibility
determination, not based
primarily on the studentís
visual, auditory, physical, or
emotional behavioral
disabilities.
Instructional Program/Program
Setting - The decision to
participate in Alternate
Assessment is not based on the
fact that the studentís
instructional reading level is
below the grade level of the
regular assessment to be
administered.
Low Expectations for the
Student/Anticipated Low Scores
- Not based on the fact that the
student is expected to perform
poorly on the regular
assessment.
Other - Make sure
decision is not being made for
program administration reasons.
The decision to administer the
alternate assessment is not
based on the fact that the
student is expected to
experience duress under testing
conditions or that there is a
high probability that the
student will demonstrate
disruptive behaviors during the
regular assessment.
|
|
Arizona
|
Other -
Students with learning
disabilities who have overall
intellectual or adaptive
behavior abilities within the
average range are not students
with a significant cognitive
disability.
|
|
Arkansas
|
Other -
Disruptive behavior, student IQ,
impact of scores on
school/district performance
scores.
|
|
California
|
Presence or
Category of Disability - Not
based on deafness/blindness,
visual, auditory, and/or motor
disabilities. Not primarily
based on a specific categorical
label.
Other - Not an
administrative decision.
|
|
Colorado
|
Achievement
Level - Student reading
level.
Other - Ongoing
disruptive behavior.
|
|
Connecticut
|
Other -
Studentís placement in a
self-contained or regional
program. Considerations of
obtaining a certificate of
mastery- for decisions about
retakes-option for students in
general.
|
|
Delaware
|
Receiving
Special Education Services -
Existence of an IEP.
Instructional Program/Program
Setting - Educational
placement.
Achievement Level -
Studentís reading level.
Cultural, Social, Linguistic,
or Environmental Factors -
English Language Learner status,
socio-economic or cultural
differences.
Other -
Disruptive behavior.
|
|
District of
Columbia
|
Other -
Where the student is likely to
score highest.
|
|
Idaho
|
Cultural,
Social, Linguistic, or
Environmental Factors -
Socioeconomic or cultural
differences.
Other - Lack of
instruction.
|
|
Illinois
|
Presence or
Category of Disability - The
student has emotional,
behavioral, visual, auditory, or
physical challenges.
Cultural, Social, Linguistic,
or Environmental Factors -
Social, cultural, or economic
differences.
Low Expectations for the
Student/Anticipated Low Scores
- The student may not perform
well on the regular assessment,
which may affect the AYP status
of the studentís home school or
district.
|
|
Indiana
|
Other -
Emotional, behavioral, or
physical challenges; concern for
local AYP calculations. Also,
must not exempt students from
testing based on limited English
proficiency, but LEP students
who have been enrolled in U.S.
schools for one year or more
will participate fully in the
ISTEP+ assessment program. Those
in their first year must take
math and science ISTEP+, but
have an option to take ELA or
LAS Links for language.
|
|
Iowa
|
Other -
English language learner status,
disruptive behavior, student
reading level, performance tied
solely to a level, label, or cut
score.
|
|
Kansas
|
Other - Any
specific categorical label.
|
|
Louisiana
|
Instructional
Program/Program Setting -
Studentís reading level.
Cultural, Social, Linguistic,
or Environmental Factors -
Includes English proficiency.
Other - Disruptive
behavior, studentís placement,
administrative decision.
|
|
Minnesota
|
Other -
Concern for AYP calculations.
|
|
Missouri
|
Excessive
Absences - The studentís
inability to participate in the
MAP subject-area assessments is
not primarily the result of
excessive absences; visual or
auditory disabilities; or
social, cultural, language, or
economic differences.
Cultural, Social, Linguistic,
or Environmental Factors -
The studentís inability to
participate in the MAP
subject-area assessments is not
primarily the result of
excessive absences; visual or
auditory disabilities; or
social, cultural, language, or
economic differences.
|
|
Oklahoma
|
Presence or
Category of Disability - A
particular disability category.
Instructional Program/Program
Setting - Location of
service delivery.
Achievement Level - The
fact that the academic
achievement of the student is
significantly below his/her same
age peers.
|
|
Pennsylvania
|
Receiving
Special Education Services -
Participation decisions may not
be based upon the studentís
disability or class placement.
Presence or Category of
Disability - Participation
decisions may not be based upon
the studentís disability or
class placement.
Instructional Program/Program
Setting - Participation
decisions may not be based upon
the studentís disability or
class placement.
|
|
Rhode Island
|
Achievement
Level - The decision to
administer the RIAA is not based
solely on the fact that the
studentís instructional reading
level is below grade level
expectations.
Other - The decision to
administer the RIAA is not based
on the fact that the student is
expected to experience distress
under testing conditions.
|
|
South
Carolina
|
Other -
Administrative convenience.
|
|
Tennessee
|
Presence or
Category of Disability - The
following conditions are not the
primary reason the student is
not participating in the general
TCAP: sensory impairments,
emotional-behavioral
impairments, specific learning
disabilities, specific learning
disabilities, language
impairment, other health
impairment, developmental
disability (i.e., Autism,
Aspergerís Syndrome,
Developmental Delay), limited
English proficiency.
Excessive Absences - p.1
of TCAP accommodations
instructions.
Cultural, Social, Linguistic,
or Environmental Factors -
Social, cultural, and economic
differences.
Low Expectations
for the Student/Anticipated Low
Scores - The decision for
TCAP-Alt participation is not
based upon anticipated impact on
system and/or school performance
scores.
|
|
Virginia
|
Achievement
Level - Student is reading
or is performing below grade
level. Student has not mastered
all of the curricula that are
covered on grades 3 through 8
SOL assessments.
Low Expectations for the
Student/Anticipated Low Scores
- Belief that the student may
fail the test.
Other - Belief that the
student does not need this
assessment to be promoted to the
next grade or to graduate with
an advanced studies diploma, a
standard diploma, a modified
standard diploma, a special
diploma, or a certificate.
Belief that the experience will
be too stressful for the
student. The studentís behavior
prohibits taking the test with a
group.
|
|
Wyoming
|
Other -
Developmental level or mental
age of the student
|
Table B.9: Additional Student
Groups Eligible for Accommodations
|
State
|
504
Students
|
All Students
May Use Without Qualification
|
All Students
May Use With Qualifications
|
ELL/IEP
|
Students
Receiving Title I Services
|
English
Language Learners
|
Other
|
|
Alabama
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Alaska
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Arizona
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Arkansas
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
California
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Colorado
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Connecticut
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Delaware
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
District of
Columbia
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Florida
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Georgia
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Hawaii
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Idaho
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Illinois
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Indiana
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Iowa
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Kansas
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Kentucky
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Louisiana
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Maine
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Maryland
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Massachusetts
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Michigan
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Minnesota
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Mississippi
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Missouri
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Montana
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Nebraska
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Nevada
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
New Hampshire
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
New Jersey
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
New Mexico
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
New York
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
North Carolina
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
North Dakota
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Ohio
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Oklahoma
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Oregon
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Pennsylvania
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Rhode Island
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
South Carolina
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
South Dakota
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Tennessee
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Texas
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Utah
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Vermont
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Virginia
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Washington
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
West Virginia
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Wisconsin
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Wyoming
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Total
|
42
|
1
|
14
|
48
|
0
|
42
|
16
|
Table B.10: Specifications
and Descriptions of ďOtherĒ Additional
Student Groups Eligible for
Accommodations
|
Arizona
|
All Students May
Use With Qualifications -
Universal accommodations are
available to all students as
deemed needed by the teacher.
English Language Learners
- English language learners may
also be considered for standard
accommodations. Note: Standard
accommodations are reserved for
students with IEPs or a 504
plan.
Other - A student with an
injury, such as a broken hand or
arm.
|
|
Arkansas
|
English Language
Learners - Modifications
used in the classroom and
accommodations used on state
assessments.
|
|
California
|
All Students May
Use With Qualifications -
All students may use some test
variations, and others may only
be used if regularly used in the
classroom.
|
|
Colorado
|
All Students May
Use With Qualifications -
All students who need an
accommodation are afforded one.
The stipulation is that the need
for that student must be made on
an individual basis and
documented in a formal plan.
Other - Students who
suffer from unforeseeable
circumstances less than two
months prior to the start of
testing, such as a broken arm or
a car accident.
|
|
Hawaii
|
ELL/IEP - If
a student is receiving
IDEA-eligible and ELL services,
the studentís IDEA eligibility
must be considered first in the
determination of the
participation criteria for the
Hawaii State Reading and
Mathematics Assessments.
English Language Learners
- Grade 5 Hawaiian Language
Immersion Program students.
Other - If a student
breaks an arm, hand, or finger
on the writing hand during
testing and needs the scribe
accommodation, a school may
submit an Additional
Accommodation Request Form even
though the student is not in a
population that is identified to
use it, and it will be reviewed
for approval. In this situation,
the form may be submitted after
March 13, 2009.
|
|
Idaho
|
ELL/IEP -
[strict criteria] Inferred from
the LEP policy.
English Language Learners
- LEP students
|
|
Indiana
|
ELL/IEP -
LEP students may be entitled to
the assessment accommodations
specified in their
Individualized Education
Programs (IEPs), Section 504
plans, or Individualized
Learning Plans (ILPs).
English Language Learners
- Only LEP students who place as
not proficient or approaching
proficient on the Placement Test
may be considered for the
accommodations approved for
Proficiency levels 1-4 on LAS
Links.
Other - Students with a
temporary disability, such as a
broken arm; Homebound students.
|
|
Kansas
|
All Students May
Use Without Qualification -
All accommodations in this
manual allowable for general
education student. (Calculator
on non calculator section not
allowable for any student.)
Other - Students with a
pre-intervention plan (student
improvement plan).
|
|
Kentucky
|
English Language
Learners - Students with
limited English proficiency.
Other - Students with
temporary medical conditions
(e.g. broken hand).
|
|
Maine
|
All Students May
Use With Qualifications -
Students who may be considered
for accommodations include, but
are not limited to, those who
are ill or incapacitated in some
way, who have limited English
proficiency, who have an
identified disability under
IDEIA, who are identified as
having disabilities under
Section 504, or for whom
classroom accommodations are
necessary on a daily basis to
measure academic achievement.
English Language Learners
- ELLs or LEP
Other - Students who are
ill or incapacitated in some
way; students for whom classroom
accommodations are necessary on
a daily basis to measure
academic achievement.
|
|
Maryland
|
504 Students
- Students with temporary or
long-term disabilities and
Section 504 students: general
education students or students
with a 504 Plan who have a
temporary or long-term disabling
condition that interferes with
test performance should be
offered testing accommodations
to compensate for their
disabling condition.
Accommodations must be justified
and documented in each studentís
record.
ELL/IEP - ELL:
appropriate accommodations
identified by the ELL committee
are permitted for students who
meet the criteria for an ELL
program. Accommodations must be
justified and documented in each
studentís record.
English Language Learners
- ELL: appropriate
accommodations identified by the
ELL committee are permitted for
students who meet the criteria
for an ELL program.
Accommodations must be justified
and documented in each studentís
record."
Other - Reclassified
English Language Learners:
Reclassified ELLs are those
students who were formerly
receiving English for Speakers
of other Languages services
(ESOL), but who are no longer
receiving those services, and
whose progress is being tracked
for two years after their exit
from the ESOL program.
|
|
Michigan
|
Other -
Students who have a rapid onset
of a medical disability (e.g.
student broke arm a few days
prior to assessment).
|
|
Mississippi
|
Other -
Students with a temporary
physical disability.
|
|
Montana
|
All Students May
Use With Qualifications -
Standard accommodations are
available to all students, based
on individual need, as
determined by the studentís
educational team.
|
|
Nevada
|
English Language
Learners - Students with
Limited English Proficiency
(LEP).
|
|
New Hampshire
|
All Students May
Use With Qualifications -
Standard accommodations
available to all students on the
basis of individual need
regardless of disability status.
|
|
New York
|
Other -
Students who incur disabilities
shortly (30 days or less) before
administration of a state or
district wide test and who are
authorized by the principal to
receive certain testing
accommodations.
|
|
Ohio
|
Other -
Broken arm exception: If the
student suffers an injury prior
to or during a test
administration that prevents the
person from physically writing
responses, a scribing
accommodation may be provided.
|
|
Oregon
|
All Students May
Use With Qualifications - In
the state of Oregon, any student
is eligible to use a
state-approved accommodation;
however, the decision to use the
state-approved accommodations
should always be made on an
individual student basis, not to
a group of students or to an
entire class without an
investigation of individual
student need.
|
|
Pennsylvania
|
All Students May
Use With Qualifications -
Certain accommodations allowed
for all students. These
accommodations must be ongoing
and documented in the student
record file. All students may
use extended time, preferential
seating, separate setting,
hospital/home testing, small
grouping, keyboarding, special
paper, reading windows, recorded
directions, recorded verbatim
sections of mathematics, student
marks in test booklet, dictation
for mathematics and reading
(illegible writing, broken arm),
reading aloud for all directions
and mathematics test, marking
answer at student direction,
student use of stickers or
highlighters, simplified
directions.
|
|
Rhode Island
|
All Students May
Use With Qualifications -
All students eligible to utilize
appropriate assessment
accommodations from Table of
Standard Test Accommodations
when participating in the NECAP
assessment. Any accommodations
utilized for the assessment of
individual students must be: (1)
the result of a decision made
prior to the test by the IEP,
Section 504, or school team that
includes, whenever possible, the
studentís parent(s) or
guardian(s), (2) based on the
individual studentís needs, (3)
consistent with those
accommodations used during the
studentís regular classroom
instruction, including
test-taking, and if applicable,
the studentís IEP or 504 plan,
and (4) documented at the
appropriate local level.
|
|
Tennessee
|
All Students May
Use With Qualifications -
All students may use allowable
accommodations as needed.
Special accommodations may be
used if the student meets
required conditions. Conditions
are documented in the IEP or 504
Service Plan and verified
according to the studentís
specific impairment or through
individualized assessment
showing the severity of the
disability. Notice: In rare
cases, additional accommodations
may be needed for students who
are not receiving services under
Special Education or Section 504
(e.g., a short term medical
problem). For these students,
the Unique Adaptive
Accommodations Request Form
should be submitted to the
Department of Education for
review and approval.
|
|
Texas
|
All Students May
Use With Qualifications -
General education students with
special needs.
ELL/IEP - Students who
are LEP-exempt and need
linguistic accommodations.
English Language Learners
- Students who are LEP-exempt
and need linguistic
accommodations.
|
|
Utah
|
Other -
Students with a temporary
disability (e.g. broken dominant
hand or medication problem).
|
|
Vermont
|
All Students May
Use With Qualifications -
Accommodations available to all
students on the basis of need,
regardless of disability status.
Other - Students with
educational support team plans
(EST/157).
|
|
West Virginia
|
ELL/IEP -
[strict criteria] Students who
are both disabled and limited
English proficient are
considered for accommodations
available to both groups.
|
|
Wisconsin
|
All Students May
Use With Qualifications -
Specific accommodations may be
used with specific groups of
students (all, students with
disabilities, ELLs).
|
Table B.11: Accommodation
Policy Variables That Can be Used to
Guide the Decision Making Process for
Using Accommodations During Statewide
Assessment
|
State
|
Used for
Classroom and Instruction
|
Length of Time
Accommodation Used
|
Maintains
Validity of the Test and
Resulting Scores
|
Individual
Student Needs/Characteristics
|
Purpose/Nature
of the Assessment
|
Other
|
|
Alabama
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Alaska
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Arizona
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Arkansas
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
California
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Colorado
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Connecticut
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Delaware
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
District of
Columbia
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Florida
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
Georgia
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
Hawaii
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Idaho
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Illinois
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Indiana
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Iowa
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Kansas
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Kentucky
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Louisiana
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Maine
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Maryland
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Massachusetts
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Michigan
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Minnesota
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Mississippi
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Missouri
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Montana
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Nebraska
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Nevada
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
New Hampshire
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
New Jersey
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
New Mexico
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
New York
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
North Carolina
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
North Dakota
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Ohio
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Oklahoma
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Oregon
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pennsylvania
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Rhode Island
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
South Carolina
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
South Dakota
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Tennessee
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Texas
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Utah
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Vermont
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Virginia
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Washington
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
West Virginia
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Wisconsin
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Wyoming
|
Y
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Total
|
45
|
8
|
25
|
37
|
8
|
19
|
Table B.12: Specifications
and Descriptions of ďOtherĒ
Accommodation Policy Variables That Can
Be Used to Guide the Decision Making
Process for Using Accommodations During
Statewide Assessment
|
Alaska
|
Used for
Classroom and Instruction -
What specialized instruction
does the student need to achieve
grade-level content standards?"
Length of Time Accommodation
Has Been Used - What
accommodations are regularly
used by the student during
instruction and assessments?
Maintains the Validity of the
Test and Resulting Scores -
Does the adaptation give the
student an unfair advantage over
a student who has the same
proficiency level, and who is
not eligible to use the
adaptation?
Individual Student
Needs/Characteristics - What
are the studentís learning
strengths and areas of further
improvement? How does the
studentís learning needs affect
the achievement of grade-level
content standards? What
accommodations will increase the
studentís access to instruction
and assessment by addressing the
studentís learning needs and
reducing the effect of the
studentís disability?
Other - What are the
results for assignments and
assessments when accommodations
were used and not used? What was
the studentís perception of how
well an accommodation worked?
Are there effective combinations
of accommodations? Would use of
the adaptation cause a breach of
test security or make it
impossible to score the test?
|
|
Arizona
|
Used for
Classroom and Instruction -
Students should receive the same
accommodations for classroom
instruction, classroom
assessments, district
assessment, and state
assessments. No accommodations
should be provided during
assessments that are not also
provided during instruction.
However, not all accommodations
appropriate for instruction are
appropriate for use during a
standardized state assessment.
Individual Student
Needs/Characteristics -
There should be a direct
connection between a studentís
disability or need and the
accommodation(s) provided to the
student during educational
activities, including
assessment.
|
|
Colorado
|
Length of Time
Accommodation Has Been Used
- For state assessment purposes
the accommodation must be in use
at least 90 days prior to the
administration of the
assessment.
Individual Student
Needs/Characteristics - What
are the studentís learning
strengths and areas of further
improvement? How does the
studentís learning needs affect
the achievement of grade-level
content standards? What
specialized instruction does the
student need to achieve
grade-level content standards?
What accommodations will
increase the studentís access to
instruction and assessment?
Other - What
are the results for assignments
and assessments when
accommodations were used and not
used? What are the perceptions
of the student, parents,
teachers, and specialists about
how the accommodation worked?
|
|
Connecticut
|
Individual
Student Needs/Characteristics
- Is it necessary for the child;
also, in addition to specific
characteristics of student,
consider whether the student is
sufficiently skilled to use the
accommodation.
Other - IEP or 504 plan
calls for the same or similar
accommodation in class work.
(There were two statements
geared at use in instruction).
|
|
Delaware
|
Purpose/Nature
of the Assessment -
Accommodations may differ for a
single student depending on the
content of the test.
|
|
Florida
|
Purpose/Nature
of the Assessment - IEP
teams should ask the question:
what does the student need to
know and be able to do to take
the test.
|
|
Georgia
|
Length of Time
Accommodation Has Been Used
- Previous experience and
usefulness with the recommended
accommodation.
|
|
Hawaii
|
Used for
Classroom and Instruction -
currently provided during
classroom instruction.
Individual Student
Needs/Characteristics - The
studentís ELL needs should also
be considered by the IEP team
members when they are
determining the appropriate
accommodations; and based on a
studentís identified learning
needs.
Other - Table 5 lists
accommodations that may be
provided during the
administration of the Hawaii
State Reading and Mathematics
Assessments. Agreed on by the
ELL staff members and classroom
teachers who provide services
for the student, stated in the
studentís Individualized
Education Program (IEP), or
Modification Plan (MP), and
agreed on by all members of the
IEP or MP team, if an ELL
student is also receiving
IDEA-eligible or Section 504
services.
|
|
Illinois
|
Individual
Student Needs/Characteristics
- Accommodations should be
selected with care on an
individual student basis,
considering studentís mode of
communication, level of
instruction, learning style,
etc.
Other - Studentís present
levels of performance in
relation to the districtís
general education curriculum.
|
|
Indiana
|
Used for
Classroom and Instruction -
Assessment accommodations should
be a subset of classroom
accommodations. Accommodations
approved and implemented for
classroom assessments, such as
using a calculator or scribe,
may be appropriate for use
during ISTEP+ and GQE testing.
Maintains the Validity of the
Test and Resulting Scores -
. . . individualized
determination of necessary
accommodations and the effects
of those on test results. The
effect of assessment
accommodations may have a
different impact upon the
general validity of assessment
depending, along with other
things, upon whether the test is
referenced to national norms or
to specific educational
criteria. Since the purpose of
accommodation is to achieve
parity and not to provide an
unfair advantage or disadvantage
to a particular student, the
Indiana Department of Education
is studying the impact of
accommodations on test results
in order to minimize any
unintended effects.
Other - Consult the
charts in this section and
collaborate with [groups named],
to determine which, if any,
accommodations are appropriate
for individual students; uses
the accommodation in testing
situations that occur through
the studentís educational
program.
|
|
Iowa
|
Length of Time
Accommodation Has Been Used
- A new accommodation is not to
be introduced solely for the use
during district wide assessment.
|
|
Kansas
|
Other - How
accommodation increases access
to instruction and assessment.
Student performance with or
without the accommodation in the
past; how the student and other
persons involved perceived the
accommodation to work, if
combination of accommodations
were effective.
|
|
Kentucky
|
Other -
Evaluation information and the
IEP (studentís present level of
performance etc.).
|
|
Louisiana
|
Other -
Documented on IEP or 504/IAP.
Special populations and
accommodations. LEP
accommodations determined by
classroom teacher and ESL
teacher or other individual
providing language services.
|
|
Maine
|
Maintains the
Validity of the Test and
Resulting Scores - All
accommodations used must not
change what is being measured.
|
|
Maryland
|
Used for
Classroom and Instruction -
The accommodations provided to a
student must be the same for
classroom instruction, classroom
assessments, and district and
State assessments.
Individual Student
Needs/Characteristics -
Accommodations must be based
upon individual student needs
and not upon a category of
disability, level of
instruction, amount of time
spent in general classroom, or
program setting.
|
|
Massachusetts
|
Used for
Classroom and Instruction -
Uses the accommodation
routinely.
Individual Student
Needs/Characteristics -
Requires the accommodation in
order to participate in
statewide testing.
Other - A student who
does not have a documented
disability is not eligible to
receive accommodations on MCAS
tests.
|
|
Michigan
|
Individual
Student Needs/Characteristics
- All decisions about which
accommodations a student needs
must 1) be made by the studentís
EIP team, 2) be documented in
the studentís IEP, and 3)
reflect what the student
routinely uses or how he or she
routinely responds during
instruction.
|
|
Minnesota
|
Used for
Classroom and Instruction -
Accommodations provided to a
student during state assessments
must also be provided during
classroom instruction, classroom
assessments, and district
assessments.
Individual Student
Needs/Characteristics - IEP
team is responsible for making
annual assessment and
accommodation decisions, which
must be based on individual need
in accordance with state and
federal guidelines.
|
|
Mississippi
|
Used for
Classroom and Instruction -
Integrate assessment
accommodations into classroom
instruction.
Maintains the Validity of the
Test and Resulting Scores -
Does the accommodation interfere
with what the test is designed
to measure?
Individual Student
Needs/Characteristics - Base
accommodations on student need.
Purpose/Nature of the
Assessment - Understand the
purpose of the assessment.
Select only those accommodations
that do not interfere with the
intent of the test.
Other - Make sure the
student and his or her family
are comfortable with it.
|
|
Missouri
|
Individual
Student Needs/Characteristics
- What are the studentís
learning strengths and needs?
What specialized instruction
(e.g., learning strategies,
organizational skills, reading
skills) does the student need to
achieve grade level content?
What accommodations will
increase the studentís access to
instruction and assessment by
reducing the effects of the
disability?
Other - How do the
studentís learning needs affect
the achievement of grade level
content?
|
|
Montana
|
Used for
Classroom and Instruction -
. . . must be something that is
routinely used with the student
in classroom instruction and
assessment for a period of two
to three months prior to
testing.
Individual Student
Needs/Characteristics -
Standard accommodations are
available to all students, based
on individual need, as
determined by the studentís
educational team.
|
|
Nebraska
|
Used for
Classroom and Instruction -
What accommodations are
regularly used by the student
during instruction and
assessments? An accommodation
may not be used solely during
assessments.
Individual Student
Needs/Characteristics - What
are the studentís strengths and
areas of further improvement?
How does the studentís learning
needs affect the achievement of
grade-level content standards?
|
|
New Jersey
|
Used for
Classroom and Instruction -
Accommodations used during
statewide testing should be
consistent with instructional
and assessment procedures used
in the classroom.
|
|
New Mexico
|
Used for
Classroom and Instruction -
What accommodations are used by
the student in the classroom and
on tests?
Individual Student
Needs/Characteristics -
Accommodations selected for
assessment must have
instructional relevance and be
connected to a specific skill
deficit.
Other - What are the
results of classroom assignments
and tests when accommodations
are use and not used? What is
the studentís perception of how
well the accommodation worked?
|
|
New York
|
Length of Time
Accommodation Has Been Used
- Accommodations should not be
introduced for the first time
during a state or district wide
assessment.
|
|
North
Carolina
|
Other - IEP
teams and section 504 committees
should be respectful of the
studentís cultural and ethnic
background when an accommodation
is being discussed.
|
|
North Dakota
|
Other -
Studentís current level of
functioning, language
functioning, and relevant
background factors.
|
|
Oregon
|
Used for
Classroom and Instruction -
Never use an assessment
accommodation or modification if
the student does not use the
same one on a daily basis.
|
|
Pennsylvania
|
Length of Time
Accommodation Has Been Used
- It is not recommended to
introduce new accommodations to
students for the first time when
they are taking the PSSA.
|
|
Rhode Island
|
Purpose/Nature
of the Assessment - Are
there unique circumstances
created by the NECAP assessment
that might require
accommodations for this student?
|
|
South Dakota
|
Length of Time
Accommodation Has Been Used
- Accommodations should be in
place at least 5 weeks prior to
test administration.
Individual Student
Needs/Characteristics - How
does the studentís learning
needs affect the achievement of
grade-level content standards?
What is the studentís learning
strengths and areas for further
improvement?
|
|
Tennessee
|
Maintains the
Validity of the Test and
Resulting Scores -
Accommodations should not
subvert the purpose of the test.
|
|
Texas
|
Used for
Classroom and Instruction -
Should be routinely used in
instruction and testing.
Maintains the Validity of the
Test and Resulting Scores -
Are there procedures in place to
ensure that test administration
procedures are not compromised
by the provision of
accommodations?
Individual Student
Needs/Characteristics -
Accommodations must be selected
on the basis of an individual
studentís needs.
Other - Policies ensuring
ethical testing practices, test
security.
|
|
Utah
|
Used for
Classroom and Instruction -
The student must be provided
with the selected accommodations
during instructional periods
that necessitate their use. An
accommodation may not be used
solely during assessments.
Maintains the Validity of the
Test and Resulting Scores -
When selecting accommodations
for state assessments with a
student, it is important to look
at state policies and procedures
to determine whether use of an
accommodation results in
consequences on a state
test.(e.g., lowering or not
counting a studentís score).
Individual Student
Needs/Characteristics -
Teams should ask the questions:
What are the studentís learning
strengths and areas for further
improvement? How does the
studentís learning needs affect
the achievement of core
standards? How do you make
accommodations decisions based
on individualized needs?
Other - Teachers and
other team members can play a
key role in working with
students to advocate for
themselves in the context of
selecting, using, and evaluating
accommodations.
|
|
Vermont
|
Purpose/Nature
of the Assessment - Are
there unique circumstances
created by the NECAP assessment
that might require
accommodations for this student?
|
|
Washington
|
Individual
Student Needs/Characteristics
- How do the studentís learning
needs affect the achievement of
grade-level content standards?
Other - What specialized
instruction does the student
need to achieve grade-level
content standards?
|
|
West Virginia
|
Maintains the
Validity of the Test and
Resulting Scores - Prohibit
modifications that change what
the test measures and assure
modifications are NOT written
into the IEP or Section 504
plan.
|
|
Wisconsin
|
Used for
Classroom and Instruction -
Must be consistent with the
studentís day-to-day
instruction.
Maintains the Validity of the
Test and Resulting Scores -
Allows us to measure the
academic content the student has
learned without interference
from the disability.
Other - Must be
documented on current IEP.
|
|
Wyoming
|
Individual
Student Needs/Characteristics
- What specialized instruction
does the student need to achieve
grade-level content standards?
What are the students learning
strengths and areas of further
improvement?
|
Table B.13: Accommodations
Policy Variables That Cannot be Used to
Guide the Decision Making Process for
Using Accommodations During Statewide
Assessment
|
State
|
Nature/Category of Disability
|
Instructional
Program/ Program
Setting
|
Percent
Time/Amount of Services Received
|
Parent
Request
|
Administrative
Convenience
|
Other
|
|
Alabama
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Alaska
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Arizona
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Arkansas
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
California
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Colorado
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Connecticut
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Delaware
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
District of
Columbia
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Florida
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Georgia
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Hawaii
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Idaho
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Illinois
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Indiana
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Iowa
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Kansas
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Kentucky
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Louisiana
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maine
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maryland
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Massachusetts
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Michigan
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Minnesota
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mississippi
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Missouri
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Montana
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nebraska
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Nevada
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
New Hampshire
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
New Jersey
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
New Mexico
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
New York
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
North Carolina
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
North Dakota
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Ohio
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oklahoma
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oregon
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pennsylvania
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rhode Island
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
South Carolina
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
South Dakota
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tennessee
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Texas
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Utah
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Vermont
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Virginia
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Washington
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
West Virginia
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wisconsin
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wyoming
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
Total
|
10
|
3
|
1
|
0
|
12
|
3
|
Table B.14: Specifications
and Descriptions of ďOtherĒ
Accommodation Policy Variables That
Cannot Be Used to Guide the Decision
Making Process for Using Accommodations
During Statewide Assessment
|
Colorado
|
Nature/Category
of Disability -
Accommodations must be based
upon individual student needs .
. . not a category of disability
or specific to a program.
Instructional Program/
Program Setting -
Accommodations must be based
upon individual student needs .
. . not a category of disability
or specific to a program.
|
|
Florida
|
Nature/Category
of Disability - The
selection of accommodations must
not be based solely on
exceptionality.
Instructional Program/
Program Setting - The
selection of accommodations must
not be based solely on
educational placement.
Other - The selection of
accommodations must not be based
solely on grade level.
|
|
Kansas
|
Other - Doís
and Doníts (donít assume same
accommodations across content
areas, donít assume
accommodations stay the same
year to year, donít check more
accommodations to be Ďsafeí,
donít assume all instructional
accommodations are appropriate
for assessment, and donít give
unrelated accommodations to
students thinking it will give
an advantage).
|
|
Maine
|
Instructional
Program/ Program Setting -
Recommended accommodations
should be consistent with
accommodations already being
employed in the studentís
instructional program.
|
|
Maryland
|
Nature/Category
of Disability -
Accommodations must be based
upon individual student needs
and not upon a category of
disability, level of
instruction, amount of time
spent in general classroom, or
program setting.
Instructional Program/
Program Setting -
Accommodations must be based
upon individual student needs
and not upon a category of
disability, level of
instruction, amount of time
spent in general classroom, or
program setting.
Percent Time/Amount of
Services Received -
Accommodations must be based
upon individual student needs
and not upon a category of
disability, level of
instruction, amount of time
spent in general classroom, or
program setting.
|
|
Nebraska
|
Administrative
Convenience - Donít make
accommodations decisions based
on whatever is easiest to do
(e.g., preferential seating).
|
|
New Mexico
|
Administrative
Convenience - Donít make
accommodations decisions based
on whatever is easiest to do.
|
|
North Dakota
|
Administrative
Convenience - Donít make
accommodations decisions based
on whatever is easiest to do.
Other - Donít make
decisions about instructional
and assessment accommodations
alone.
|
|
Utah
|
Administrative
Convenience - Donít make
accommodations decisions based
on whatever is easiest to do
(e.g., preferential seating).
|
|
Wyoming
|
Administrative
Convenience - Donít make
accommodations decisions based
on whatever is easiest to do.
|
Table B.15: Guidance for
Using Accommodations That are Not on the
ďApprovedĒ List
|
State
|
Seek Approval
from State Board or
Department of
Education
|
Committee
Review
|
Required
Contact
|
Non-approved
Accommodations May Not be Used
|
Other
|
|
Alabama
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Alaska
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Arizona
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Arkansas
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
California
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Colorado
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Connecticut
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Delaware
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
District of
Columbia
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Florida
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Georgia
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Hawaii
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Idaho
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Illinois
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
Indiana
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Iowa
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Kansas
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Kentucky
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Louisiana
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maine
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maryland
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Massachusetts
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Michigan
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Minnesota
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mississippi
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Missouri
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Montana
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nebraska
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nevada
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
New Hampshire
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
New Jersey
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
New Mexico
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
New York
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
North Carolina
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
North Dakota
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ohio
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oklahoma
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oregon
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Pennsylvania
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rhode Island
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
South Carolina
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
South Dakota
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tennessee
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Texas
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Utah
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vermont
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Virginia
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Washington
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
West Virginia
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wisconsin
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Wyoming
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total
|
29
|
5
|
5
|
1
|
1
|
Table B.16: Specifications
and Descriptions of ďOtherĒ Guidance for
Using Accommodations That Are Not on the
ďApprovedĒ List
|
Alabama
|
Seek Approval
from State Board or Department
of Education - Checklists
indicate with SDE approval only.
|
|
California
|
Seek Approval
from State Board or Department
of Education - For unlisted
accommodations or modifications,
check with the California
Department of Education.
|
|
Colorado
|
Committee Review
- The district assessment
coordinator and special
education director must submit a
request to the Unit of Student
Assessment.
|
|
Connecticut
|
Seek Approval
from State Board or Department
of Education - In
exceptional circumstances, there
may be a student whose
disabilities are such that the
allowable accommodations listed
here will be insufficient to
provide access to the standard
CMT/CAPT. In these cases, prior
to the testing window the
district test coordinator must
contact the student assessment
office for guidance. The
district test coordinator will
be provided with information
regarding the Special
Accommodations Petition Process.
These special accommodations
petitions must be submitted to
the State Department of
Education in writing, prior to
testing, with the necessary
documentation to support any
request for the use of an
accommodation other than those
listed here.
Required Contact - In
exceptional circumstances, there
may be a student whose
disabilities are such that the
allowable accommodations listed
here will be insufficient to
provide access to the standard
CMT/CAPT. In these cases, prior
to the testing window the
district test coordinator must
contact the student assessment
office for guidance. The
district test coordinator will
be provided with information
regarding the Special
Accommodations Petition Process.
These special accommodations
petitions must be submitted to
the State Department of
Education in writing, prior to
testing, with the necessary
documentation to support any
request for the use of an
accommodation other than those
listed here.
|
|
Florida
|
Seek Approval
from State Board or Department
of Education - Each unique
accommodation must be approved
by the Commissioner of Education
prior to its use.
|
|
Georgia
|
Committee Review
- Assessment Research and
Development Division of the GA
department of education.
|
|
Hawaii
|
Seek Approval
from State Board or Department
of Education - Requires
Student Assessment Office review
at department of education. If a
student is currently receiving a
documented accommodation that is
not included on the Hawaii State
Reading and Mathematics
Assessments Accommodations List,
the school must submit an
Additional Accommodation Request
Form to the Student Assessment
Section no later than March 13,
2009. The request form will be
reviewed before this documented
accommodation is approved or
disapproved for use by the
student during the Hawaii State
Reading and Mathematics
Assessments.
|
|
Idaho
|
Seek Approval
from State Board or Department
of Education - Email the
testing coordinator at the Idaho
State department of education.
|
|
Illinois
|
Other - Any
accommodations that were not
addressed in the preceding
sections may be implemented if
they do not invalidate the
assessment and are appropriate
methods for increasing access
for the student with
disabilities to demonstrate
ability and knowledge. Use of
any accommodation during testing
should be familiar to the
student because the
accommodation has been utilized
in the studentís instructional
programming.
|
|
Kansas
|
Seek Approval
from State Board or Department
of Education - To use an
accommodation other than one
listed, contact your district
test coordinator who will send
the request to Cherie Randall at
KSDE.
Required Contact - To use
an accommodation other than one
listed, contact your district
test coordinator who will send
the request to Cherie Randall at
KSDE.
|
|
Maine
|
Seek Approval
from State Board or Department
of Education - Contact Susan
Smith, MEA Coordinator at
susan.smith@maine.gov
|
|
Maryland
|
Seek Approval
from State Board or Department
of Education - The Local
Accountability Coordinator must
submit to MSDE, for approval, an
accommodation beyond those
listed in the document.
|
|
Minnesota
|
Seek Approval
from State Board or Department
of Education - Email
mde.testing@state.mn.us
|
|
Mississippi
|
Seek Approval
from State Board or Department
of Education - In rare
instances, students may require
special consideration for an
accommodation not provided for
in the allowable accommodations
approved by the Office of
Student Assessment. In such
cases, the local school district
superintendent or district test
coordinator may make a petition
for special consideration to the
Office of Student Assessment.
|
|
Montana
|
Seek Approval
from State Board or Department
of Education - Seek approval
from OPI state assessment
director and/or the OPI
bilingual specialist.
|
|
Nevada
|
Seek Approval
from State Board or Department
of Education - . . . the
district test director must
submit a written request for the
accommodation to the test
security coordinator at the
Nevada Department of Education,
Office of Assessment, Program
Accountability, and Curriculum,
no later than one month prior to
the scheduled test date.
|
|
New Jersey
|
Required Contact
- Office of Assessment.
|
|
New Mexico
|
Non-approved
accommodations may not be used
- If the requested accommodation
is determined to affect the
validity of comparability of
assessment results or is
identified as a modification
that is not approved through the
PED, the student may test:
without accommodations or with
allowable accommodations.
|
|
Ohio
|
Seek Approval
from State Board or Department
of Education - Contact the
Office of Exceptional Children
at 614.466.2650.
|
|
Oregon
|
Committee Review
- Requests are reviewed by an
Accommodations Panel. Decision
process for adaptations to
become accommodations.
|
|
Pennsylvania
|
Seek Approval
from State Board or Department
of Education - Contact the
Pennsylvania Department of
Educationís Bureau of Assessment
and Accountability if you have
questions at (717) 787-4234 or
(717) 705-2343.
|
|
South
Carolina
|
Seek Approval
from State Board or Department
of Education - The IEP or
504 team may request a certain
accommodation (modification)
through the district test
coordinator (DTC) to be approved
by the state.
|
|
South Dakota
|
Seek Approval
from State Board or Department
of Education - Approval from
Department of Education.
|
|
Tennessee
|
Seek Approval
from State Board or Department
of Education - Submit a
Unique Adaptive Accommodations
Request Form to the Department
of Education.
|
|
Texas
|
Seek Approval
from State Board or Department
of Education - Online
accommodations request form.
|
|
Vermont
|
Seek Approval
from State Board or Department
of Education - Contact the
State Department of Education
staff to discuss and receive
approval for any accommodation
not listed on the Table of
Standard Test Accommodations.
|
|
Virginia
|
Required Contact
- Questions about any
accommodations not listed above
should be directed to the
Division Director of Testing who
will consult with Department of
Education staff if needed.
|
|
Washington
|
Seek Approval
from State Board or Department
of Education - For an
accommodation not listed above,
District Coordinators submit an
Exceptional Accommodation form
for approval before the
state-mandated testing dates.
Separate testing location: home
based, hospital or other
(available for all students
submitting a Medical Exemption
request).
|
|
West Virginia
|
Seek Approval
from State Board or Department
of Education - A request for
a student to use an assessment
accommodation that does not
appear in this document must be
received by the Office of
Assessment and Accountability
(Attention: Vaughn Rhudy) no
later than the 3rd Friday in
February.
|
|
Wisconsin
|
Seek Approval
from State Board or Department
of Education - Any
accommodation not on this list
must be submitted to DPI for
approval, as it may represent a
modification which changes the
skill or construct being
measured.
Committee Review - Submit
request to:
http://dpi.wi.gov/oca/dacforms.html.
|
|
Wyoming
|
Seek Approval
from State Board or Department
of Education - If there are
any questions regarding the
[accommodations] list, please
contact Charlene Turner at the
Standards and Assessment Unit,
Wyoming Department of Education.
307.777.7322 or
cturne@educ.state.wy.us.
|
Table B.17: Guidelines for
the Administration of Accommodations
Involving a Third Party
|
State
|
No Guidelines
|
Scribe
|
Reader
|
Sign Language
Interpreter
|
|
Alabama
|
|
|
|
|
|
Alaska
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Arizona
|
|
|
|
|
|
Arkansas
|
|
|
|
|
|
California
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Colorado
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Connecticut
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Delaware
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
District of Columbia
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Florida
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
Georgia
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Hawaii
|
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Idaho
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Illinois
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
Indiana
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Iowa
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Kansas
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Kentucky
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Louisiana
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Maine
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Maryland
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Massachusetts
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Michigan
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Minnesota
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
Mississippi
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Missouri
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Montana
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nebraska
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Nevada
|
|
|
Y
|
|
|
New Hampshire
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
New Jersey
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
New Mexico
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
New York
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
North Carolina
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
North Dakota
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Ohio
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Oklahoma
|
Y
|
|
|
|
|
Oregon
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Pennsylvania
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Rhode Island
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
South Carolina
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
South Dakota
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Tennessee
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Texas
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Utah
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Vermont
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
|
Virginia
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Washington
|
|
Y
|
|
Y
|
|
West Virginia
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Wisconsin
|
|
Y
|
|
|
|
Wyoming
|
|
Y
|
Y
|
Y
|
|
Total
|
5
|
39
|
29
|
28
|
Table B.18A: Presentation
Accommodations (1 out of 3)
A = Allowed, AC
= Allowed in Certain Circumstances, AI =
Allowed with Implications for Scoring, P
= Prohibited
AS = All Subjects, R = Reading/Language
Arts, M = Math, S = Science, W =
Writing, SS = Social Studies
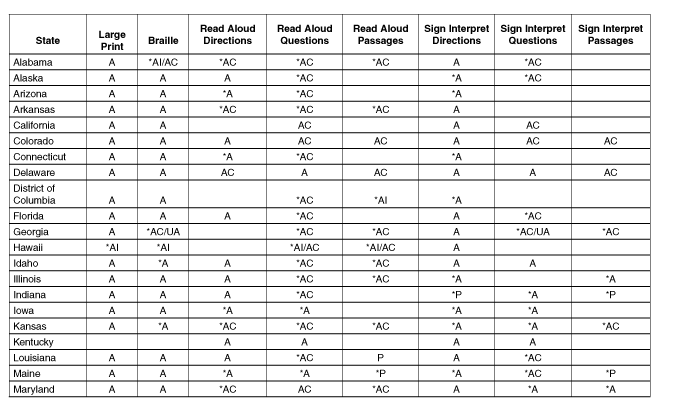
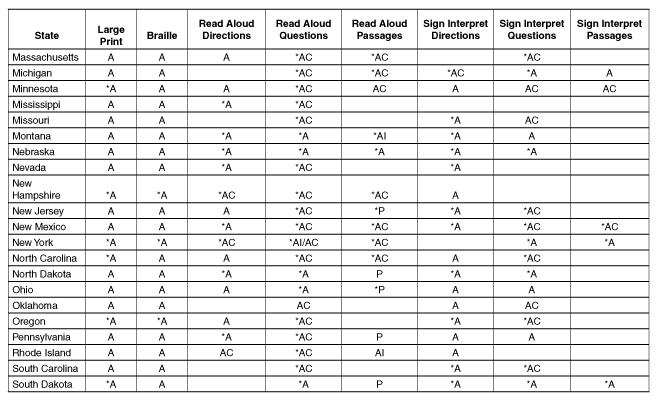
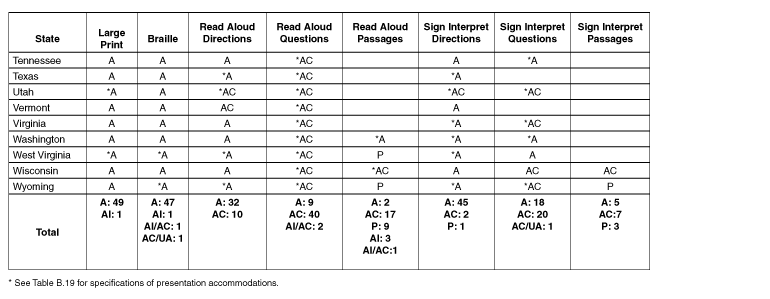
Table B.18B: Presentation
Accommodations (2 out of 3)
A = Allowed, AC
= Allowed in Certain Circumstances, AI =
Allowed with Implications for Scoring, P
= Prohibited
AS = All Subjects, R = Reading/Language
Arts, M = Math, S = Science, W =
Writing, SS = Social Studies
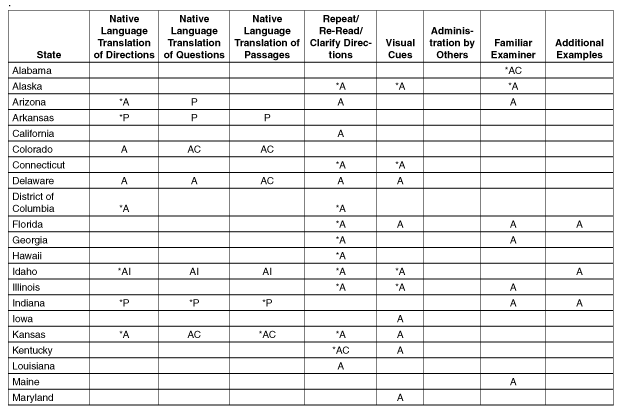
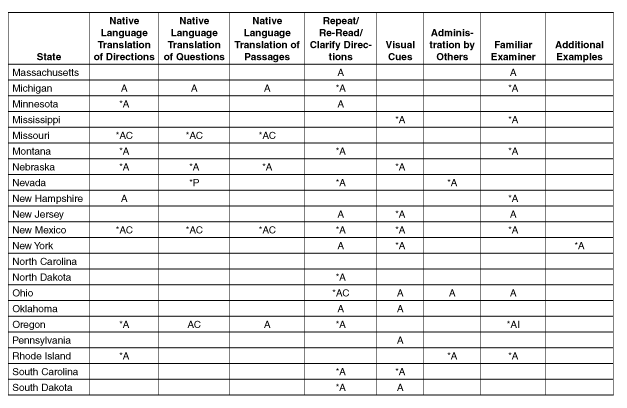
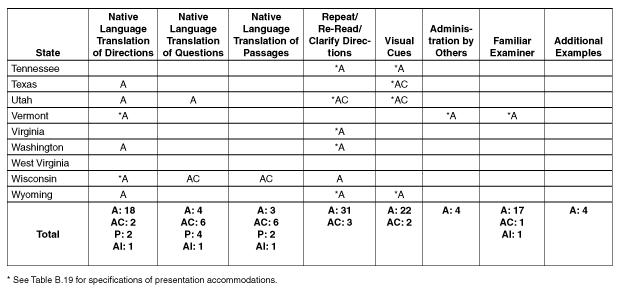
Table B.18C: Presentation
Accommodations (3 out of 3)
A = Allowed, AC
= Allowed in Certain Circumstances, AI =
Allowed with Implications for Scoring, P
= Prohibited
AS = All Subjects, R = Reading/Language
Arts, M = Math, S = Science, W =
Writing, SS = Social Studies
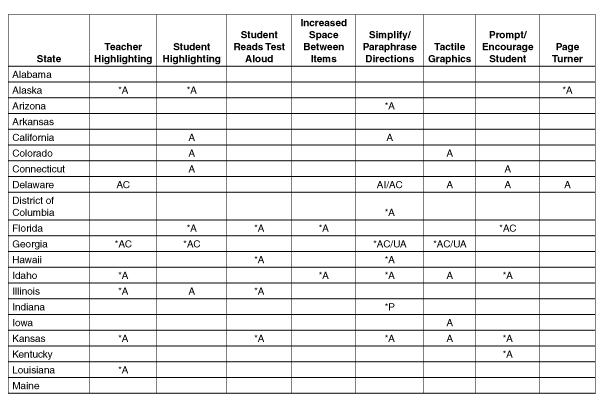
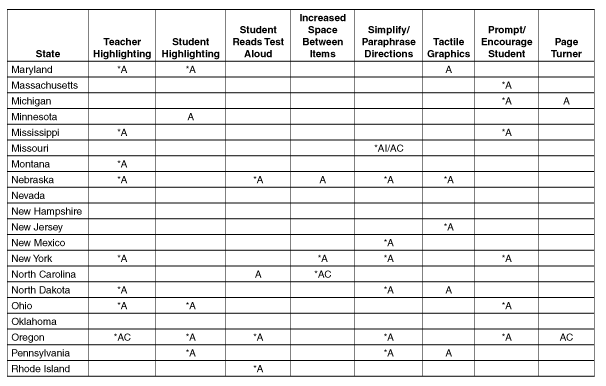
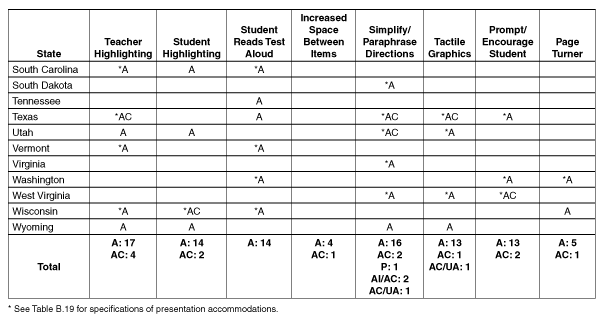
Table B.19: Specifications
and Descriptions of ďCertain
Circumstances,Ē ďImplications for
Scoring,Ē ďUnique Aggregated,Ē and
ďOtherĒ Presentation Accommodations
|
Alabama
|
Braille -
Considered non-standard on the
Stanford 10 and Dynamic
Indicators of Basic Early
Literacy Skills (DIBELS),
resulting in only raw scores
reported. Allowed as standard on
all other tests.
Read Aloud Directions -
Read aloud test. Not allowed in
reading on any test. Prohibited
on the Dynamic Indicators of
Basic Early Literacy Skills
(DIBELS), Stanford 10, and
Alabama Reading and Mathematics
Test (ARMT). Allowed on all
other tests.
Read Aloud Questions -
Read aloud test. Prohibited on
the Dynamic Indicators of Basic
Early Literacy Skills (DIBELS),
Stanford 10, and Alabama Reading
and Mathematics Test (ARMT).
Allowed on all other tests. Not
allowed in reading on any test.
Read Aloud
Passages - Read aloud test.
Prohibited on the Dynamic
Indicators of Basic Early
Literacy Skills (DIBELS),
Stanford 10, Alabama Reading and
Mathematics Test (ARMT), and
Alabama Alternate Assessment
(AAA). Allowed on all other
tests.
Sign Interpret Questions
- Allowed on the Alabama
Alternate Assessment only for
students with an IEP.
Familiar Examiner -
Administered by studentís
special education teacher.
Prohibited on the Alabama
Alternate Assessment (AAA).
Allowed only for IEP students on
all other tests.
|
|
Alaska
|
Read Aloud
Questions - Reading or
signing multi-step math or
writing test questions one step
at a time.
Sign Interpret
Directions - Allowing
student to ask for
clarifications on test
directions, and clarifying
directions by having student
restate them.
Sign Interpret Questions
- Signing is allowed as long as
the sign does not cue the
correct response to a question.
Reading or signing multi-step
math or writing test questions
one step at a time.
Repeat/Re-Read/Clarify
Directions - Allowing
student to ask for
clarifications on test
directions, and clarifying
directions by having student
restate them.
Visual Cues
- Masking portions of the test
to direct attention to uncovered
items.
Familiar Examiner - Using
a specific test proctor (e.g.,
examineeís regular or special
education teachers).
Teacher Highlighting -
Providing highlighted words in
directions.
Student
Highlighting - Allowing
student to highlight words
except in answer document area.
Page Turner
- Turning pages for student.
Other -
Assisting student in tracking or
sequencing test items. Provide
written version of oral
directions, and present
directions via overhead and
transparencies except embedded
directions. Writing helpful
verbs in the directions on the
board, or on a separate piece of
paper.
|
|
Arizona
|
Read Aloud
Directions - Read aloud the
directions that students read on
their own.
Read Aloud Questions -
May read aloud in English the
writing prompt, mathematics test
items, or science test items, as
needed upon student request. A
test item is described to
include the question and
corresponding answer choices and
any stimulus preceding the item
may also be read aloud. Reading
aloud items on the Reading test
is considered an alternate
accommodation and is only
available to students with an
IEP; use of this accommodation
on the Reading test results in
scores that are considered
invalid for comparison and
accountability purposes; results
will not be included in
aggregate results at the school,
district and state level, and
students will not count as
having tested for AYP purposes.
Sign Interpret Directions
- Or sign the directions that
students read on their own.
Native Language Translation
of Directions - Exact oral
translation of the scripted
directions or the directions
that students read on their own
as needed upon request. Only the
verbal directions stated by the
Test Administrator and the
written directions that the
student is expected to read may
be orally translated into the
studentís native language. The
translation must be an exact
translation which is as close to
verbatim as possible, and
translation is to be provided on
an as needed basis only.
Students must request the
translation. Translations that
paraphrase, simplify, or clarify
directions are not permitted.
Written translations are not
permitted. Translation of test
items is not permitted.
Translation of test items is not
permitted.
Simplify/Paraphrase
Directions - Simplify
language in the scripted
directions in English.
Other - Translations that
paraphrase, simplify, or clarify
directions are not permitted.
Written translations are not
permitted.
|
|
Arkansas
|
Read Aloud
Directions - Reading of the
math/writing/science test.
Important: No portion of the
reading test may be read to any
student.
Read Aloud
Questions - Reading of the
math/writing/science test.
Important: No portion of the
reading test may be read to any
student.
Read Aloud Passages -
Reading of the
math/writing/science test.
Important: No portion of the
reading test may be read to any
student.
Native Language
Translation of Directions -
Accommodations that currently
are not available: languages
other than English.
|
|
Connecticut
|
Read Aloud
Directions - Or student may
also have screen reader read
this content. Summary of use:
May be used for CMT Math, CMT
Science, CMT Editing & Revising
(Screen Reader only) and CAPT
Math, CAPT Science, CAPT
Interdisc. Writing, CAPT
Editing/Revising (Screen Reader
only). Read or clarify test
directions for ELLs in English.
Read Aloud Questions -
Students may also have CMT and
CAPT Mathematics, and Science
and the CAPT Interdisciplinary
Writing test items read to them
because these items are not
designed to measure reading . .
. students having this
accommodation must be tested
individually or in small groups
of no more than five students.
Or student may have screen
reader read this content.
Summary of use: May be used for
CMT Math, CMT Science, CMT
Editing & Revising (Screen
Reader only) and CAPT Math, CAPT
Science, CAPT Interdisc.
Writing, CAPT Editing/Revising
(Screen Reader only).
Sign Interpret Directions
- A sign language interpreter
may assist in test
administration by giving
directions and clarifying
information as allowed in the
CMT/CAPT Test Examinerís Manual.
Repeat/Re-Read/Clarify
Directions - May clarify
directions for ELLs.
Visual Cues - All
students are allowed to make
notes in the margins of their
test booklets. They may
underline with a pencil or a
highlighter to note key points
or keep their place. As
necessary, students may use a
piece of oak tag or point to
reduce the visual field and/or
to keep their place while
working in the test booklet.
Other - Student may have
a screen reader instead of staff
to read directions in all
content areas, or the questions
for math, science and writing.
Those students accomplished in
screen reading technology may
also use this accommodation on
the Editing & Revising subtest
on both the CMT and CAPT.) The
Editing & Revising subtest MAY
NOT be read to any student.)
English Language Learners may
use screen reader for
editing/revising.
|
|
District of
Columbia
|
Read Aloud
Questions - Assisted reading
of comprehension passages on
reading test. Assisted reading
of entire reading comprehension
test including passages,
questions and answer options.
Listed as an accommodation that
results in a non-standard
condition in which students
require on-going assistance in
taking the test.
Read Aloud Questions -
Reading of test questions (math
only).
Read Aloud Passages -
Assisted reading of
comprehension passages on
reading test. Assisted reading
of entire reading comprehension
test including passages,
questions and answer options.
Listed as an accommodation that
results in a non-standard
condition in which students
require on-going assistance in
taking the test.
Sign Interpret Directions
- Interpretation of oral
directions (signing cued speech)
although test questions may not
be interpreted.
Native Language Translation
of Directions - On the spot
translation of words or phrases,
when practical (math only).
Assistance with interpretation
of directions.
Repeat/Re-Read/Clarify
Directions - Repetition of
directions.
Simplify/Paraphrase
Directions - Simplification
of oral directions approved.
|
|
Florida
|
Read Aloud
Questions - Oral
presentation of the topic
(prompt) on the writing test and
all mathematics and science
items; passages and items on the
reading test must be read by the
student through visual or
tactile means; test
administrator may also read all
mathematics and science
questions; test questions may
not be reworded, summarized.
Also-Planning FCAT Accommodation
audio-taped directions and test
items other than reading items
are allowed.
Sign Interpret Questions
- Signed presentation of the
topic (prompt) on the writing
test and all mathematics and
science items; passages and
items on the reading test must
be read by the student through
visual or tactile means.
Repeat/Re-Read/Clarify
Directions - Directions
repeated, summarized, or
clarified.
Student Highlighting -
Use of a highlighter or
highlighter tape to mark key
words and phrases in directions,
questions, and passages; if a
highlighter is used at grade
levels where the test questions
and answers are in the same
book, the answers must be
transcribed into a separate
book; if highlighting marks are
found on an answer document, the
studentís answers must be
transcribed.
Student Reads Test Aloud
- Students may have the
opportunity to paraphrase or
repeat directions to show
understanding.
Increased Space Between Items
- Fewer items placed on each
page or increased spacing
between test items; requires
prior approval by commissioner
of education. Provide reading
passages with one complete
sentence per line.
Prompt/Encourage Student
- Verbal encouragement (e.g.,
"keep working," "make sure to
answer every question"); may not
be used to cue a student
regarding correct/incorrect
responses - it is alright as
general encouragement to
continue working.
Other - Tabbed or
modified pages for easy turning;
requires special approval from
the commissioner of education.
Limited assistance may be
provided by ESOL or heritage
language teacher including
answering student questions
about the general test
directions in the studentís
heritage language; on the
mathematics and science tests
and writing prompt, limited
assistance may be provided to
answer specific questions about
a word or phrase, but this is
not allowed on the reading test.
Printed copy of the directions
read by the teacher from the
FCAT administration script.
Fewer items on the page. Reading
passages with one complete
sentence per line. Approval
required.
|
|
Georgia
|
Braille -
Considered nonstandard on the
Norm-Referenced Test (NRT),
standard on all other tests.
Read Aloud
Questions - Considered
nonstandard on the reading
comprehension and vocabulary
subtests of the Norm-Referenced
Test (NRT). Standard on all
other tests.
Read Aloud Passages -
Considered conditional on the
Criterion-Referenced Competency
Tests (CRCT): only allowed in
grades 3-8, for students who
have a specific disability that
severely limits or prevents them
from decoding text and the
student has access to printed
materials only through a reader.
Considered nonstandard on the
reading comprehension and
vocabulary subtests of the
Norm-Referenced Tests (NRT).
Only allowed in writing on the
ACCESS for ELLS. Allowed as
standard on all other tests.
Sign Interpret Questions-
Considered nonstandard on the
Norm-Referenced Test (NRT) and
standard on all other tests.
Sign Interpret
Passages - Sign reading
passages. Prohibited on the
ACCESS for ELLS. Considered
nonstandard on the
Norm-Referenced Test (NRT).
Considered conditional on the
Criterion-Referenced Competency
Tests: only allowed in grades
3-8 for students who are deaf
and who access printed materials
only through a sign-language
interpreter. Standard on all
other tests.
Repeat/Re-Read/Clarify
Directions - Repetition of
directions (in English only).
Teacher
Highlighting - Use
directions that have been marked
by teacher. Allowed only on
ACCESS for ELLS.
Student Highlighting -
Use of highlighter by student;
allowed for ACCESS Listening,
Reading, and Writing, but not
allowed for ACCESS Speaking.
Prohibited on all other tests.
Simplify/Paraphrase Directions
- Explain or paraphrase the
directions for clarity (in
English only). Considered
nonstandard on the
Norm-Referenced Test (NRT) but
standard on all other tests.
Tactile Graphics -
Considered nonstandard on the
Norm-Referenced Test (NRT),
standard on all other tests.
|
|
Hawaii
|
Large Print
- Has scoring implications for
norm-referenced test.
Braille -
Has scoring implications for
norm-referenced test.
Read Aloud Questions - To
receive this accommodation, the
student is a non-reader who will
never be able to read any
sentences at any grade level
throughout his or her life; the
student accesses all printed
materials for every subject via
an audio format all of the time
during classroom instruction.
This accommodation results in
non-comparable scores for
norm-referenced assessment.
Read Aloud Passages - To
receive this accommodation, the
student is a non-reader who will
never be able to read any
sentences at any grade level
throughout his or her life; the
student accesses all printed
materials for every subject via
an audio format all of the time
during classroom instruction.
This accommodation on the
norm-referenced test results in
non-comparable scores.
Repeat/Re-Read/Clarify
Directions - Repeating
official directions in English
only as many times as needed,
regardless of whether a student
raises his or her hand to
request assistance.
Student Reads Test Aloud
- Reading passages, mathematics
problems, and related test
questions aloud to self in an
individual setting.
Simplify/Paraphrase
Directions - Population that
may receive accommodation
includes Hawaiian language
immersion students. Explaining
directions in English only,
using simplified vocabulary, as
many times as needed, regardless
of whether a student raises his
or her hand to request
assistance. The Test
Administrator may ask a student
if the student understands the
directions and needs additional
explanations.
Other - Any student may
raise his or her hand to request
assistance in reading a
mathematics problem and a
related test question; not
allowed for any passage or
related test questions in the
reading sessions.
|
|
Idaho
|
Braille -
Braille and/or Nemeth Braille
code.
Read Aloud Questions -
Not to be used on sections
measuring reading ability.
Read Aloud Passages -
Reading a reading test to a
student is an adaptation. If
adaptations are used, the
student is deemed not proficient
and will not be counted towards
participation. Coding the
student in the SEF file will
activate the audio accommodation
for students whose IEPs allow
for science, math, and language
usage tests to be read aloud to
the student.
Native Language Translation
of Directions - Translating
the entire test into studentís
native language is an
adaptation. If adaptations are
used, the student is deemed not
proficient and will not be
counted towards participation.
For LEP students, provide
audio-taped test directions in
native language (not test item
directions). For LEP students,
provide oral/written test
directions (not test item
directions) in native language
(provide translation of
directions).
Repeat/Re-Read/Clarify
Directions - For LEP
students, clarify/explain test
directions in English, or native
language (not test item
directions); explain the test
administration directions to the
student any time during the
test.
Visual Cues - On the
answer form, includes arrows and
stop signs (for example, using
cues on the answer form).
Teacher Highlighting -
Highlighting key words or
phrases in the (not in the test
item directions).
Increased Space Between Items
- Increasing the spaces between
the items, reducing the number
of items per page or line, or
using one complete sentence per
line in reading passages.
Increased spaces on answer
sheet, wider lines or margins.
Simplify/Paraphrase
Directions - For LEP
students, simplify language to
clarify or explain the test
directions (not test item
directions), or paraphrasing.
Simplifying the language to
clarify or explain the
directions.
Prompt/Encourage Student
- Prompting the student to stay
focused on the test, move ahead
or read entire item.
Other - Answering
questions about test items any
time during the test, even
without giving the answers. If
adaptations are used, the
student is deemed not proficient
and will not be counted towards
participation. Defining words
for the student is an
adaptation. For LEP students,
provision for student
restatement of test directions
(not test item directions) in
his or her own words. Student
repeats and explains directions
to check for understanding. For
LEP students, Clarifying,
translating, or re-reading test
items and test item directions
is an adaptation. If adaptations
are used, the student is deemed
not proficient and will not be
counted towards participation.
Increasing the size of the
answer bubbles. Answering the
questions about the test
directions and the items.
Locating the answer bubbles
directly along side of the
choices in multiple choice
exams. Writing helpful verbs in
the directions on the board or
on a separate piece of paper.
Computer reads directions and/or
items. Human readers will be
allowed for math, science, and
language usage for paper and
pencil, large print and Braille
accommodated versions.
|
|
Illinois
|
Read Aloud
Questions Ė CD, oral
presentation. ISAT, math and
science only. PSAE, all
subjects.
Read Aloud Passages Ė CD,
Oral presentation. Not allowed
for Reading. ISAT, math and
science only. PSAE, all
subjects.
Sign Interpret Directions
- Exact English Signing (EES) of
directions on grade 11 PSAE.
Also is allowed signing of
directions and test items in
sign language other than EES.
Sign Interpret Passages -
Exact English Signing (EES) of
directions and test items, for
grade 11 PSAE, ISAT, math,
science, and writing.
Repeat/Re-Read/Clarify
Directions - Clarify
directions.
Visual Cues - Providing
cues (arrows or stop signs) on
test booklets or answer
documents.
Teacher Highlighting -
Highlighting of key word or
phrases in directions only.
Student Highlighting -
Highlighter. Students may
highlight words, phrases, or
sentences in the test. Students
should not use highlighters on
their written answers to
short-response or
extended-response questions.
Student Reads Test Aloud
- Student reading aloud to self
(must be individual
administration to avoid
distraction of others).
Other - Teacher faces
test-taker. Audiocassette of
test. Emphasis may be given on
key words in directions. Student
repeats the directions to verify
understanding. Fewer items per
page.
|
|
Indiana
|
Read Aloud
Questions - May have
questions read to the student.
Oral presentation accommodation
is never an appropriate
accommodation for the reading
comprehension sections; all ELA
test questions are read to the
student except those that
measure reading comprehension.
Sign Interpret Directions
- Assessment is provided in a
language other than English.
Sign Interpret Questions
- Questions are signed to the
student by the teacher or
through an interpreter.
Sign Interpret Passages -
Assessment is provided in a
language other than English.
Native Language Translation
of Directions - Assessment
is provided in a language.
Native Language Translation
of Questions - Assessment is
provided in a language other
than English.
Native Language Translation
of Passages - Assessment is
provided in a language other
than English.
Simplify/Paraphrase
Directions - Language in the
directions is reduced in
complexity. Word problems in the
mathematical assessment use
language which is reduced in
complexity.
Other - Student is
provided color-coded prompts for
mathematical problems. Student
uses a talk assistive technology
device, (under presentation
format).
|
|
Iowa
|
Read Aloud
Directions - Document states
human reader; implied read aloud
directions.
Read Aloud Questions -
Document states human reader;
implied read aloud questions.
Sign Interpret Directions
- Document states sign language;
inferred sign interpret
directions.
Sign Interpret Questions
- Document states sign language;
inferred sign interpret
questions.
|
|
Kansas
|
Braille -
This includes Nemeth Code for
math and science.
Read Aloud Directions -
May be used for English or
Spanish versions if available
(Spanish versions are noted
separately as accommodations in
their own right). Reader is not
allowed to translate. A student
who needs this accommodation
must have documentation in: a
Pre-intervention plan, an ELL
plan, a 504 plan, or an IEP. The
read-aloud is for a student who
needs the entire assessment
(except the reading passage)
read to him. It does not refer
to an adult reading a single
word, a single distracter (sic),
a single stem, or a single
question to the student. The
student must have the read-aloud
accommodation provided in the
classroom on a regular basis for
both instructional material and
assessments/tests. See document
for details on best practice. It
is generally allowed at the
teacherís discretion to allow a
single word, distracter, stem,
or question to be pronounced and
this does not require special
coding as an accommodation.
Scripts for the general
assessment as well as for the
KAMM have been prepared for
readers to follow for the
mathematics, reading, and
science assessments. They
include all text and labels that
may be read aloud. The scripts
must be used for the read-aloud
accommodation. Two options exist
for KCA read-aloud: scripts and
computer voice. CETE has been
able to obtain the use of KCA
voice for a small fee to users.
Those who choose KCA voice will
only be able to use it with KCA
software, and it will not be
available at this time on the
formative assessment. If KCA
voice is chosen, the entire text
of the questions and answer
choices will be read to the
student. Students will not be
able to highlight special
segments of a question. The
voice will not be available for
the reading passage. Districts
and buildings may choose to use
entirely read-aloud, entirely
KCA voice, or a combination of
both. On the CETE, new option:
KCA Audio Order Form. KCA form
is used with KCA voice. Unlike
human read-aloud, KCA voice is
not given with option of
paper-and-pencil, and not given
with the option of small groups
of three or less.
Read Aloud Questions -
Allowed for English or Spanish
versions. The population is not
specified. A student who needs
this accommodation must have
documentation in: a
Pre-intervention plan, an ELL
plan, a 504 plan, or an IEP. The
read-aloud is for a student who
needs the entire assessment
(except the reading passage)
read to him. It does not refer
to an adult reading a single
word, a single distracter (sic),
a single stem, or a single
question to the student. The
student must have the read-aloud
accommodation provided in the
classroom on a regular basis for
both instructional material and
assessments/tests. See document
for details on best practice. It
is generally allowed at the
teacherís discretion to allow a
single word, distracter, stem,
or question to be pronounced and
this does not require special
coding as an accommodation.
Scripts for the general
assessment as well as for the
KAMM have been prepared for
readers to follow for the
mathematics, reading, and
science assessments. They
include all text and labels that
may be read aloud. The scripts
must be used for the read-aloud
accommodation. Two options exist
for KCA read-aloud: scripts and
computer voice. CETE has been
able to obtain the use of KCA
voice for a small fee to users.
Those who choose KCA voice will
only be able to use it with KCA
software, and it will not be
available at this time on the
formative assessment. If KCA
voice is chosen, the entire text
of the questions and answer
choices will be read to the
student. Students will not be
able to highlight special
segments of a question. The
voice will not be available for
the reading passage. Districts
and buildings may choose to use
entirely read-aloud, entirely
KCA voice, or a combination of
both. On the CETE, there will be
a new option: KCA Audio Order
Form. KCA form is used with KCA
voice. Unlike human read-aloud,
KCA voice is not given with
option of paper-and-pencil, and
not given with the option of
small groups of three or less.
Read Aloud Passages -
Either Spanish or English
version may be read aloud, but
the reader is not allowed to
translate. A student who needs
this accommodation must have
documentation in: a
Pre-intervention plan, an ELL
plan, a 504 plan, or an IEP. The
read-aloud is for a student who
needs the entire assessment
(except the reading passage)
read to him. It does not refer
to an adult reading a single
word, a single distracter (sic),
a single stem, or a single
question to the student. The
student must have the read-aloud
accommodation provided in the
classroom on a regular basis for
both instructional material and
assessments/tests. It is
generally allowed at the
teacherís discretion to allow a
single word, distracter, stem,
or question to be pronounced and
this does not require special
coding as an accommodation.
Scripts for the general
assessment as well as for the
KAMM have been prepared for
readers to follow for the
mathematics, reading, and
science assessments. They
include all text and labels that
may be read aloud. The scripts
must be used for the read-aloud
accommodation. The entire
history/government assessment
may be read to students in
English. However, the reader is
not allowed to translate. If any
student uses a modification on
the state assessment that
results in an invalid score, the
student is considered to be not
tested when calculating the
participation rate for AYP
purposes. In addition to
counting that student as not
tested, the score will not be
included when calculating the
proficiency rate for AYP
decisions. Reading any part of a
reading passage was given as an
example; this includes even
reading single words in the
passage. Reading passages, the
test questions, answer choices,
labels, graph titles, etc. may
NOT be translated into the
studentís native language.
Sign Interpret Directions
- If directions were signed to
student; may also want extended
time with this accommodation.
Sign Interpret Questions
- Specifics on what portions may
be signed for each subject.
Sign Interpret Passages -
No part of the Passages on the
Kansas Reading Assessment May be
Signed. An interpreter may sign
all parts of the Kansas
Mathematics, Science, and
History-Government (Social
Studies) Assessments.
Interpreters must not clarify,
elaborate, paraphrase, or
provide assistance with the
meaning of words, intent of test
questions, or responses to test
items. Graphic materials may be
described, but should also be
available in print or tactile
formats.
Native Language Translation
of Directions - This
accommodation may also be read
aloud.
Native Language Translation
of Passages - As appropriate
and applicable to the
assessment, a translated version
is used; unclear if writing
assessment has passages.
Calculators allowed. On the
electronic Spanish math version
of KCA, this is only appropriate
if student has received math
instruction in Spanish.
Repeat/Re-Read/Clarify
Directions - Repeat
questions.
Teacher Highlighting -
Highlight key words in
directions.
Student Reads Test Aloud
- If the student read the
assessment to a tape recorder
and played it back to himself.
Simplify/Paraphrase
Directions - Give short and
simple directions.
Prompt/Encourage Student
- Frequent cuing and prompting
for engagement; cue student to
begin working and stay on task.
Other - Have student
repeat and explain directions to
check for understanding. Allow
student multiple reads. Repeat
questions and responses from
classmates. Student uses printed
screenshots of the KAMM. If a
student also needs a Spanish
hard copy version, the district
must order screen-shots of the
Spanish KCA from CETE. Screen
shots are not considered a
response accommodation although
two people transfer answers to
KCA. Students who need access to
both Spanish and English and
take the Spanish KCA, may refer
to an English paper/pencil test.
|
|
Kansas
(Contíd)
|
Sign Interpret
Directions - If directions
were signed to student; may also
want extended time with this
accommodation.
Sign Interpret
Questions - Specifics on
what portions may be signed for
each subject.
Sign Interpret
Passages - No part of the
Passages on the Kansas Reading
Assessment May be Signed. An
interpreter may sign all parts
of the Kansas Mathematics,
Science, and History-Government
(Social Studies) Assessments.
Interpreters must not clarify,
elaborate, paraphrase, or
provide assistance with the
meaning of words, intent of test
questions, or responses to test
items. Graphic materials may be
described, but should also be
available in print or tactile
formats.
Native Language
Translation of Directions -
This accommodation may also be
read aloud.
Native Language
Translation of Passages - As
appropriate and applicable to
the assessment, a translated
version is used; unclear if
writing assessment has passages.
Calculators allowed. On the
electronic Spanish math version
of KCA, this is only appropriate
if student has received math
instruction in Spanish.
Repeat/Re-Read/Clarify
Directions - Repeat
questions.
Teacher
Highlighting - Highlight key
words in directions.
Student Reads
Test Aloud - If the student
read the assessment to a tape
recorder and played it back to
himself.
Simplify/Paraphrase Directions
- Give short and simple
directions.
Prompt/Encourage
Student - Frequent cuing and
prompting for engagement; cue
student to begin working and
stay on task.
Other - Have
student repeat and explain
directions to check for
understanding. Allow student
multiple reads. Repeat questions
and responses from classmates.
Student uses printed screenshots
of the KAMM. If a student also
needs a Spanish hard copy
version, the district must order
screen-shots of the Spanish KCA
from CETE. Screen shots are not
considered a response
accommodation although two
people transfer answers to KCA.
Students who need access to both
Spanish and English and take the
Spanish KCA, may refer to an
English paper/pencil test.
|
|
Kentucky
|
Repeat/Re-Read/Clarify
Directions - Paraphrasing
for the state assessment
includes repeating or rephrasing
the on-demand tasks, directions,
prompt, or situation; this shall
include breaking directions and
sentences into parts or segments
or using similar words or
phrases, but shall not include
defining words or concepts or
telling a student what to do
first, second, etc. Stories
(reading passages) and content
passages may not be paraphrased.
Prompt/Encourage Student
- Prompting or cueing strategies
(e.g. verbal or non-verbal cues
to begin or refocus on the
task).
Other - Reinforcement and
behavior modification
strategies.
|
|
Louisiana
|
Read Aloud
Questions - The Reading and
Responding session of the
English Language Arts Test on
LEAP 21 and GEE 21, Reading
Comprehension on ITBS and the
old GEE, and Ability to
Interpret Literary Materials on
ITED may not be read aloud; it
is a breach of test security to
read aloud the Reading and
Responding session, which
results in an invalid score.
Sign Interpret Questions
- The Reading and Responding
session of the English Language
Arts Test on LEAP 21 and GEE 21,
Reading Comprehension on ITBS
and the old GEE, and Ability to
Interpret Literary Materials on
ITED may not be signed; a score
obtained by signing the reading
test would offer no information
about a studentís reading
ability and thus be invalid.
Teacher Highlighting -
Highlighting the task or verbs
in the directions.
Other - Assisting the
student in tracking the test
items.
|
|
Maine
|
Read Aloud
Directions - A human reader
may be used for a student whose
inability to read would hinder
performance in Mathematics, or
Science. For the Reading
sessions, a human reader may be
used only for questions/answer
choices and directions, not for
the reading passages
Read Aloud
Questions - A human reader
may be used for a student whose
inability to read would hinder
performance in Mathematics, or
Science. For the Reading
sessions, a human reader may be
used only for questions/answer
choices and directions, not for
the reading passages
Read Aloud Passages - A
human reader may be used for a
student whose inability to read
would hinder performance in
Mathematics, or Science. For the
Reading sessions, a human reader
may be used only for
questions/answer choices and
directions, not for the reading
passages
Sign Interpret
Directions - Trained
personnel may use sign language
to administer the test. For
reading sessions, sign language
may be used only for directions
and most questions/answer
choices, not for reading
passages. Questions/answer
choices, assessing vocabulary
any content area may not be
signed.
Sign Interpret Questions
- Policy states using sign
language for reading sessions;
sign language may be used only
for questions and directions,
not for reading passages.
Trained personnel may use sign
language to administer the test.
For reading sessions, sign
language may be used only for
directions and most
questions/answer choices, not
for reading passages.
Questions/answer choices,
assessing vocabulary any content
area may not be signed.
Sign Interpret Passages -
Trained personnel may use sign
language to administer the test.
For reading sessions, sign
language may be used only for
directions and most
questions/answer choices, not
for reading passages.
Questions/answer choices,
assessing vocabulary any content
area may not be signed.
Other -
Using administrator verification
of student understanding
following the reading of test
directions.
|
|
Maryland
|
Read Aloud
Directions - Use of the
verbatim Reading accommodation
is permitted on all assessments
as a standard accommodation,
with the exception of: 1) the
Maryland School Assessment in
Reading, grade 3 only. . . .
students in grade 3 receiving
this accommodation on the
assessment will receive a score
based on standards 2 and 3
(comprehension of informational
and literary Reading material)
but will not receive a sub-score
for standard 1, general Reading
processes; and 2) the Maryland
Functional Reading Test. Does
not distinguish between or
specify reading directions,
questions, or passages.
Read Aloud Passages - Use
of the verbatim Reading
accommodation is permitted on
all assessments as a standard
accommodation, with the
exception of: 1) the Maryland
School Assessment in Reading,
grade 3 only. . . students in
grade 3 receiving this
accommodation on the assessment
will receive a score based on
standards 2 and 3 (comprehension
of informational and literary
Reading material) but will not
receive a sub-score for standard
1, general Reading processes;
and 2) the Maryland Functional
Reading Test. Does not
distinguish between or specify
reading directions, questions,
or passages.
Sign Interpret Questions
- Does not specify or
differentiate between
directions, questions, or
passages.
Sign Interpret Passages -
Does not specify or
differentiate between
directions, questions, or
passages.
Teacher Highlighting -
Visual organizers include
highlighters.
Student
Highlighting - Visual
organizers include highlighters.
|
|
Massachusetts
|
Read Aloud
Questions - Test
administrator may read aloud the
ELA composition writing prompt
or the mathematics, science and
technology/engineering, or
history and social science
passages and test items to the
student; reading aloud the ELA
reading comprehension test is
considered a non-standard
accommodation
Read Aloud
Passages - Test
administrator may read aloud the
ELA composition writing prompt
or the mathematics, science and
technology/engineering, or
history and social science
passages and test items to the
student; reading aloud the ELA
reading comprehension test is
considered a non-standard
accommodation.
Sign Interpret Questions
- Test administrator may sign
the ELA composition writing
prompt or the mathematics,
science and
technology/engineering, or
history and social science
passages and test items to the
student; signing the ELA reading
comprehension test is considered
a non-standard accommodation.
Prompt/Encourage Student
- Redirect the studentís
attention to the test.
Other - The test
administrator assists the
student in tracking test items
(e.g., moving from one test
question to the next).
|
|
Michigan
|
Read Aloud
Questions - Reading aloud
the MEAP mathematics, science
and social studies assessments
or the MI-Access mathematics
assessment. Reading the MEAP
English Language Arts Listening
assessment to the student in
his/her native language. Reading
aloud the MEAP reading
components of the ELA assessment
or the MI-Access accessing print
assessment to the student.
Nonstandard or not applicable
for all but MI-Access Functional
Independence Assessment.
Read Aloud Passages -
Reading aloud the MEAP
mathematics, science and social
studies assessments or the
MI-Access mathematics
assessment.
Sign Interpret Directions
- Sign the English Language arts
assessments, ELPA Listening,
Speaking, Reading and Writing
parts. Not applicable or
nonstandard on all assessments
but the ELPA for students with
IEPs and 504 plans.
Sign Interpret Questions
- Sign the mathematics, science,
and social studies assessments.
Native Language
Translation of Directions -
Reading all directions to the
student in the studentís native
language, provided that the
student is dominant in a native
language other than English and
has been determined to be at the
basic or lower intermediate
English language proficiency
levels and provided that the
student is receiving bilingual
instruction (e.g., using the
studentís native language in a
school setting.
Repeat/Re-Read/Clarify
Directions - Students asking
for clarification of directions.
Familiar Examiner -
Administration of the assessment
by Bilingual/ESL staff, or
similarly qualified person.
Prompt/Encourage Student
- Provide visual, auditory or
physical cues to student to
begin, maintain, or finish task.
Other - Provision for
student restatement of
directions in the studentís own
words.
Any assessment administration
not directly supervised by a
school district professional.
Emphasis on key words in
directions. Use of
state-produced video or audio
version of assessment, for
English language learners, read
in English for a student who is
dominant in a native language
other than English and
determined to be at the basic or
lower intermediate English
language proficiency levels in
the content areas of
mathematics, science, and social
studies. Also the writing
section of the MEAP, ELA,
MI-Access ELA Expressing Ideas
assessment, or the ELPA
Listening, Writing, and Speaking
sections.
|
|
Minnesota
|
Large Print
- Any monitor screen size may be
used for computer-delivered
assessments.
Read Aloud Questions -
Test monitor reads writing
prompt aloud to student.
Native Language Translation
of Directions - A bilingual
word-to-word dictionary contains
mathematical and scientific
terms in English and in the
first language of a given
learner. Not allowed for the
Mathematics BST, but is
permitted on the MTELL,
Mathematics MCA-II, GRAD, and
Science MCA-II.
|
|
Mississippi
|
Read Aloud
Directions - Read the test
directions (but not the test
items) to individual students or
the group.
Read Aloud Questions -
Not allowed for the reading
sections in MCT2-Reading and
English II Multiple Choice,
Vocabulary/Reading. Not allowed
on the MCT2 test, grades 3-8.
Visual Cues - Provide
cues (e.g., arrows and stop
signs) on answer document in
pencil. Cueing is assisting the
student in focusing studentís
attention. Cueing strategies
include, but are not limited to,
arrows, lines, space,
contrasting colors, position or
focal point, underlining,
labeling, size, and shading.
Cues may be used only in test
directions and in test
questions. Cues may not be used
in answer choices.
Familiar Examiner - With
a familiar teacher.
Teacher Highlighting -
Highlight key words or phrases
in directions (e.g., complete
sentences, show your work).
Prompt/Encourage Student
- Clue student to stay on task.
|
|
Missouri
|
Read Aloud
Questions - Oral reading of
assessment. (Not permissible for
English II.) The test examiner
reads items verbatim to the
student in isolated setting so
that other students will neither
benefit nor be disturbed. Oral
reading, oral reading in native
language, or the use of
bilingual dictionary during the
English II assessment will
result in the LOSS (Lowest
Obtainable Scale Score). Does
not invalidate the test for
blind/partial sight students who
cannot read Braille.
Sign Interpret Directions
- A certified sign language
interpreter or deaf education
instructor signs the Algebra I
or Biology test (directions and
test items are allowed) or the
directions only of the English
II test to the student.
Native Language Translation
of Directions - Oral reading
in native language. (Not
permissible for English II.)
Oral reading in native language
during the English II assessment
will result in the Lowest
Obtainable Scale Score.
Native Language Translation
of Questions - Oral reading
in native language. (Not
permissible for English II.)
Oral reading in native language
during the English II assessment
will result in the Lowest
Obtainable Scale Score.
Native Language Translation
of Passages - Oral reading
in native language. (Not
permissible for English II.)
Oral reading in native language
during the English II assessment
will result in the Lowest
Obtainable Scale Score.
Simplify/Paraphrase
Directions - Paraphrasing.
The test examiner paraphrases
questions to help the student
understand in an isolated
setting. Terms may be defined as
long as they: 1) are not the
actual concept of content being
assessed, 2) would not give
clues, or 3) would not disclose
the answer. Paraphrasing test
questions invalidates all EOC
assessment student scores for
accountability purposes.
|
|
Montana
|
Read Aloud
Directions - Oral
Presentation Science and
Mathematics: Tests were read to
the student by the Test
Administrator. For the reading
test, reading passages may not
be read aloud. Note: Readers
must read test items/questions
to the student word-for-word
exactly as written. Readers may
not clarify, elaborate, or
provide assistance to the
student regarding the meaning of
words, intent of test questions,
or responses to test
items/questions.
Read Aloud Questions -
Oral Presentation Science and
Mathematics: Tests were read to
the student by the Test
Administrator. For the reading
test, reading passages may not
be read aloud. Note: Readers
must read test items/questions
to the student word-for-word
exactly as written. Readers may
not clarify, elaborate, or
provide assistance to the
student regarding the meaning of
words, intent of test questions,
or responses to test
items/questions.
Read Aloud Passages Ė
Nonstandard. Reading aloud the
reading passages to a student or
the student uses test-reader
software for reading passages. A
student for which this type of
nonstandard accommodation might
be used would be a student with
a learning disability in reading
who without the text being read,
could not participate in this
portion of the test.
Sign Interpret Directions
- Test Interpretation: Tests,
including directions, were
interpreted for students who are
deaf or hearing-impaired (with
the exception of interpreting
the reading test).
Native Language Translation
of Directions - Test
directions support: An
administrator assisted students
in understanding test
directions, including giving
directions in native language.
Repeat/Re-Read/Clarify
Directions - Test directions
with verification: an
administrator gave test
directions with verification (by
using a highlighter) so that the
student understood them.
Familiar Examiner -
Change in personnel: Test is
administered by other personnel
known to the student (e.g., LEP,
Title I, special education
teacher).
Teacher Highlighting -
Test directions with
verification: An administrator
gave test directions with
verification (by using a
highlighter) so that the student
understood them.
|
|
Nebraska
|
Read Aloud
Directions Ė A qualified
person may be provided to read
orally to students who are
unable to decode text visually.
May also be presented via audio
tape.
Read Aloud Questions - A
qualified person may be provided
to read orally to students who
are unable to decode text
visually. May also be presented
via audio tape.
Read Aloud Passages - A
qualified person may be provided
to read orally to students who
are unable to decode text
visually. May also be presented
via audio tape.
Sign Interpret Directions
- Sign language interpreters may
be required for students who are
deaf or hard of hearing.
Sign Interpret Questions
- Sign language interpreters may
be required for students who are
deaf or hard of hearing.
Native Language Translation
of Directions - Provide a
language interpreter.
Native Language Translation
of Questions - Provide a
language interpreter.
Native Language Translation
of Passages - Provide a
language interpreter.
Visual Cues - Graphic
material (e.g., maps, charts,
graphs, diagrams, and
illustrations) is presented in a
raised format (paper or
thermoform).
Teacher Highlighting -
Key words or phrases in
directions highlighted.
Student Reads Test Aloud
- Allow student to quietly read
aloud.
Simplify/Paraphrase
Directions - Simplify
language in directions and read
multi-step directions in small
portions.
Tactile Graphics -
Tactile graphic images provide
graphic information through
fingers instead of eyes.
Other - One complete
sentence per line in reading
passages. Provide clear copies
of assignments and assessments.
Provide useful strategies for
decoding, vocabulary, or
comprehension. Read directions
to the student and have student
repeat directions.
|
|
Nevada
|
Read Aloud
Directions - Read or reread
aloud the directions located at
the beginning of the test, word
for word, in English, as needed.
Read Aloud Questions -
Read the mathematics test(s)
word for word, text only, in
English, to the student. It is
not permissible to verbalize,
explain, sign, or define
mathematical symbols, or to
paraphrase or explain any part
of the test. Read the science
test(s) word for word, text
only, in English, to the
student. It is not permissible
to verbalize, explain, sign, or
define scientific symbols, or to
paraphrase or explain any part
of the test. Read the writing
prompt word for word, in
English, to the student. No help
can be given on responding to
the prompt, nor may the prompt
of any part of it be translated
into another language. Read the
ITBS/ITED Language test(s)
(i.e., Spelling, Capitalization,
Punctuation, Usage and
Expression, or Revising Written
Materials tests) word for word,
in English, to the student. It
is not permissible to read any
portion of a reading test or
vocabulary test to the student
(other than the directions
located at the beginning of the
test). Never allowed for Section
504 students: Test administrator
or proctor reading the CRT or
HSPE in Reading, or the
ITBS/ITED Reading Comprehension
or Vocabulary test to the
student in any language
(includes any process for orally
transmitting the test content to
the student through the use of
any device that converts print
or other code to speech).
Sign Interpret Directions
- Provide directions located at
the beginning of the test, word
for word, in English, to a
student in sign language.
Native Language Translation
of Questions - Never allowed
for Section 504 Students: Test
administrator or proctor reading
the writing prompt, or the math,
science, or ITBS/ITED Language
test to the student in a
language other than English.
Repeat/Re-Read/Clarify
Directions - Read or reread
aloud the directions located at
the beginning of the test, word
for word, in English, as needed.
Administration by Others
- Provide test administration by
a specific individual (e.g.,
special education teacher,
guidance counselor).
Other - Provide
directions located at the
beginning of the test, word for
word, in English, on a separate
sheet for the student to use as
needed.
|
|
New
Hampshire
|
Large Print
- Large-print responses must be
transcribed by school personnel,
exactly as written by the
student, in the Student answer
Booklet.
Braille Ė Uncontracted
(younger, beginning Braille
users) and contracted Braille
users are available. Braille
responses must be transcribed by
school personnel, exactly as
written by the student, into the
Student Answer Booklet.
Read Aloud Directions -
Test and directions are read
aloud to student (math, science,
and writing only). Reading the
reading test to the student
invalidates all reading
sessions.
Read Aloud
Questions - Test and
directions are read aloud to
student (math, science, and
writing only). Reading the
reading test to the student
invalidates all reading
sessions.
Read Aloud Passages -
Test and directions are read
aloud to student (math, science,
and writing only). Reading the
reading test to the student
invalidates all reading
sessions.
Familiar Examiner -
Administer the test with special
education personnel.
Other - Student reads
test and directions aloud to
self. Teacher underlines key
information in directions (only
teacher, not subs or
paraprofessionals).
|
|
New Jersey
|
Read Aloud
Questions - Reading test
questions aloud (you may not
read aloud or sign the reading
passages in Language Arts
Literacy; you may read the
reading questions).
Read Aloud
Passages - Reading test
questions aloud (you may not
read aloud or sign the reading
passages in Language Arts
Literacy; you may read the
reading questions.)
Sign Interpret Directions
- Using an examiner who can
communicate fluently in sign
language (American Sign Language
or a form of manually coded
English).
Sign Interpret Questions
- Using a sign language or cued
speech interpreter for
administration of directions or
questions but not reading
passages.
Visual Cues - Using
tactile or visual cues for deaf
or hard of hearing students to
indicate time to begin, time
remaining, and time to end a
particular part of the test.
Tactile Graphics - Using
tactile or visual cues for deaf
or hard of hearing students to
indicate time to begin, time
remaining, and time to end a
particular part of the test.
Other - Providing written
directions on a separate sheet
or transparency.
|
|
New Mexico
|
Read Aloud
Directions - Tape recording
of test directions, stimulus
material, test items, or answer
choices. Reading aloud of test
directions, stimulus material,
test items, or answer choices.
Reading aloud or tape recording
of the directions only for the
Reading assessment. Tape
recording of test directions,
stimulus material, test items,
or answer choices. Reading aloud
of test directions, stimulus
material, test items, or answer
choices.
Read Aloud Questions -
Tape recording of test
directions, stimulus material,
test items, or answer choices.
Reading aloud of test
directions, stimulus material,
test items, or answer choices.
Reading aloud in the studentís
native language or translation
of test directions, stimulus
material, test items, or answer
choices.
Read Aloud Passages -
Reading aloud or tape recording
of stimulus material, test
items, or answer choices. Tape
recording of test directions,
stimulus material, test items,
or answer choices. Reading aloud
of test directions, stimulus
material, test items, or answer
choices.
Sign Interpret Directions
- Signing of the directions only
for the Reading assessments.
Signing of the test directions,
stimulus material, test items,
or answer choices. Signing of
the entire assessment, including
word problems.
Sign Interpret Questions
- Signing of the entire
assessment, including word
problems.
Signing of stimulus material,
test items, or answer choices.
Sign Interpret Passages -
Signing of stimulus material,
test items, or answer choices.
Signing of the entire
assessment, including word
problems. Signing of the test
directions, stimulus material,
test items, or answer choices.
Native Language Translation
of Directions - Reading
aloud or translation into the
studentís native language of the
directions only for the Reading
assessments. Directions read in
English and clarified in native
language; non-standard
administration.
Native Language Translation
of Questions - Reading aloud
in the studentís native language
or translation of stimulus
material, test items, or answer
choices. Oral or written
directions provided in native
language; non-standard.
Native Language Translation
of Passages - Reading aloud
in the studentís native language
or translation of stimulus
material, test items, or answer
choices.
Repeat/Re-Read/Clarify
Directions - Rereading the
test directions in the DFA to
all students when requested by
any student. (This does not
permit reading the test
directions aloud for individual
students).
Visual Cues - Use of
place markers to maintain place.
Familiar Examiner -
Administration of the assessment
with or without accommodations
by qualified individuals other
than the studentís usual
teacher(s).
Simplify/Paraphrase
Directions - Paraphrasing
the directions only.
Other - Paraphrase
stimulus material, test items,
or answer choices. Restate the
question with more appropriate
vocabulary or define unknown
vocabulary in question.
Clarification of English words.
|
|
New York
|
Large Print
- For state assessments, any
reproduction or reformatting of
a test booklet requires the
advance written permission of
the Office of State Assessment.
Braille - For state
assessments, any reproduction or
reformatting of a test booklet
requires the advance written
permission of the Office of
State Assessment.
Read Aloud Directions -
Tests may be read to students.
This accommodation is allowed
only for those students whose
vision is impaired. Only those
tests or parts of tests that do
not measure reading
comprehension may be read to
these students.
Read Aloud Questions -
Considered a modification
(results in invalid scores) on
certain sections of the state
grades 3-8 ELA tests because
these sections measure a
studentís reading skills
(decoding and comprehension).
Read Aloud Passages -
Test passages, questions, items
and multiple-choice responses
read to student. Oral reading or
signing of the portions of the
test that measure reading skills
prohibited.
Sign Interpret Questions
- Test passages, questions,
items and multiple-choice
responses signed to student.
Sign Interpret Passages -
Test passages, questions, items
and multiple-choice responses
signed to student.
Visual Cues - Cues (e.g.,
arrows and stop signs) on answer
form.
Additional Examples -
Additional examples provided in
the directions.
Teacher Highlighting -
Verbs/key words in directions
underlined or highlighted.
Increased Space Between Items
- Increased spacing between test
items, reduce number of test
items per page, presentation of
reading passages with one
complete sentence per line. For
state assessments, any
reproduction or reformatting of
a test booklet requires the
advance written permission of
the Office of State Assessment.
Simplify/Paraphrase
Directions - Language in
directions simplified.
Prompt/Encourage Student
- On-task focusing prompts.
Other - Verbs in
directions underlined or
highlighted. Increased size of
answer blocks/bubbles. For state
assessments, any reproduction or
reformatting of a test booklet
requires the advance written
permission of the Office of
State Assessment.
Multiple-choice items in
vertical format with answer
bubble to right of response
choices. Signing listening
section more than twice. Verbal
description of graphics. Reduce
number of test items per page.
Presentation of reading passages
with on complete sentence per
line (this is not always
possible with large type.)
Listening section repeated more
than the standard number of
times.
|
|
North
Carolina
|
Large Print
- Screen enlarging programs.
Read Aloud Questions -
Test administrator reads test
aloud in English. Reading aloud
the selection/passages, frames,
test questions, and answer
choices from North Carolina
tests that measure reading
comprehension invalidates the
results from those tests because
the test measures reading
comprehension. However, test
directions in the Test
Administratorís Manuals may be
signed/cued during the
administration of any State
test.
Read Aloud Passages -
Reading aloud the
selection/passages, frames, test
questions, and answer choices
from North Carolina tests that
measure reading comprehension
invalidates the results from
those tests because the test
measures reading comprehension.
However, test directions in the
Test Administratorís Manuals may
be signed/cued during the
administration of any State
test. Test administrator reads
test aloud in English.
Sign Interpret Questions
- Interpreter/translator
signs/cues test. Reading aloud
the selections/passages, frames,
test questions, and answer
choices from North Carolina
tests that measure reading
comprehension invalidates the
results from those tests because
the test measures reading
comprehension.
Increased Space Between Items
- One test item per page
edition.
|
|
North
Dakota
|
Read Aloud
Directions - Read aloud
internal directions only to
student.
Read Aloud Questions -
Read aloud test items and answer
choices to student; must be read
verbatim.
Sign Interpret Directions
- Presenting directions or test
items.
Sign Interpret
Questions - Presenting
directions or test items.
Repeat/Re-Read/Clarify
Directions - Human reader
paraphrases clarifies, or
simplifies internal directions.
Teacher Highlighting -
Highlighted directions or key
words.
Simplify/Paraphrase
Directions - Human reader
paraphrases clarifies, or
simplifies internal directions.
Other - Reducing the
number of test items or answer
choices. Manual
|
|
Ohio
|
Read Aloud
Questions - Represents
standardized read-aloud
accommodation for directions,
questions, and answer choices
aloud on reading tests (reading
test passages are not read aloud
on CD).
Read Aloud Passages -
Represents standardized
read-aloud accommodation for
directions, questions, and
answer choices aloud on reading
tests (reading test passages are
not read aloud on CD).
Repeat/Re-Read/Clarify
Directions - Re-reading the
directions is allowed, but
signing to define or clarify a
word or phrase in the directions
is prohibited.
Teacher Highlighting Ė
Highlighters.
Student Highlighting Ė
Highlighters.
Prompt/Encourage Student
- Verbal, gesture, or physical
prompts to stay on task. These
prompts may not cue answers.
Other - Define or clarify
word or phrase found in test
questions. Person other than
student chooses the order of
questions to answer. Reorder
questions (student may answer
questions in order of his/her
choice).
|
|
Oklahoma
|
Other - Test
administrator assists the
student in tracking or
sequencing of test items.
|
|
Oregon
|
Large Print
- For writing test: large print
version of prompts.
Braille - For writing
test, Braille version of
prompts.
Read Aloud Questions -
Read mathematics, science, and
social sciences, (not
reading/literature) items and
response choices aloud to the
student by proctor or by use of
technology. Note: Mathematics
symbols and numerals may not be
read when administering the
mathematics assessment; however,
mathematics symbols and numerals
may be read when administering
the science and social science
assessments. Read prompts aloud
to student.
Sign Interpret Directions
- Sign writing prompts.
Sign Interpret Questions
- Signing the
reading/literature, math,
science, and social sciences
passages, items, and distracters
to a student is considered a
modification. Modifications
change the content or
performance standards of what is
being measured by the test.
Native Language Translation
of Directions - Translate
directions orally.
Repeat/Re-Read/Clarify
Directions - Reread or
clarify directions to student.
Familiar Examiner -
Parent as examiner when the test
is given in the home. Considered
a modification. Modifications
change the content or
performance standards of what is
being measured by the test.
Teacher Highlighting -
Highlighter. Highlight words in
directions. For math, science,
and social sciences, (not
reading/literature), proctor
highlights vowel combinations in
passages, items and distracters.
For the reading/literature
assessment, the proctor
highlights vowel combinations in
passages, items, and
distracters. Considered a
modification. Modifications
change the content or
performance standards of what is
being measured by the test. On
the writing test: highlight
words in directions; proctor
highlights vowel combinations in
writing prompts.
Student Highlighting -
Student highlights vowel
combinations independently
without assistance. For math,
science, and social sciences,
(not reading/literature),
proctor highlights vowel
combinations in passages, items
and distracters.
Student Reads Test Aloud
- Student reads test aloud or
sub-vocalizes text to listener
or self. Student is allowed to
vocalize his or her thought
process out loud to himself or
to a neutral proctor. Student
retells story to proctor or
educational assistant in his or
her own words. Considered an
accommodation if student
responds to multiple choice
items and considered a
modification of the student does
not respond to multiple choice
items. Modifications change the
content or performance standards
of what is being measured by the
test.
Simplify/Paraphrase
Directions - Simplify
language in directions.
Prompt/Encourage Student
- Encourage a studentís work
habits during test taking-only
involves reinforcing consistent
engagement in test activity.
Interaction between a proctor
and student at the test level as
a whole is acceptable (e.g.,
reminders regarding test
directions), whereas
interactions between a proctor
and student at the individual
item level (test question level)
is not acceptable.
Other - Use
sensory/processing techniques to
allow students to attend to
task. The proctor may write
symbols or numerals exactly as
they appear in the assessment in
order to enlarge them and make
them visually accessible. The
entire formula or statement
should be duplicated so that the
context remains intact. Read
aloud audio recording of
available side-by-side tests in
Spanish/English and
Russian/English read verbatim
directly from the test booklet.
Read-aloud audio record of
available tests in
Spanish/English side-by-side,
prompts read verbatim directly
from test booklet. Synonym
provided for unknown word in
writing prompt if requested by
student. Use of physical
assistance or devices for
manipulation of test materials.
Limit the number of distracters
(answer options) on multiple
choice items. Considered a
modification. Modifications
change the content or
performance standards of what is
being measured by the test.
School staff reword or simplify
wording of testing items or the
writing prompt. Synonym or
definition is provided to
student upon request. Both are
considered modifications.
Modifications change the content
or performance standards of what
is being measured by the test.
Proctor clarifies non-construct
related vocabulary in math
assessment. Provide written
version of oral directions.
Provide written translations of
oral directions.
|
|
Oregon
(Contíd)
|
or devices for
manipulation of test materials.
Limit the number of distracters
(answer options) on multiple
choice items. Considered a
modification. Modifications
change the content or
performance standards of what is
being measured by the test.
School staff reword or simplify
wording of testing items or the
writing prompt. Synonym or
definition is provided to
student upon request. Both are
considered modifications.
Modifications change the content
or performance standards of what
is being measured by the test.
Proctor clarifies non-construct
related vocabulary in math
assessment. Provide written
version of oral directions.
Provide written translations of
oral directions.
|
|
Pennsylvania
|
Read Aloud
Directions - In some special
cases, directions may be
provided via an audiotape or CD.
For example, students might need
to have directions read to them
and the school might be limited
in the number of people to
provide this accommodation, or
reading directions aloud might
be disruptive to some students.
Verbatim sections of mathematics
assessment may also be provided.
No part of the reading
assessment or the writing
multiple-choice and passages
section may be provided.
Read Aloud Questions -
Reading any portion of the
Reading PSSA, except the
directions.
Reading the multiple choice and
passage portion of the Writing
PSSA.
Student Highlighting Ė
Highlighters.
Simplify/Paraphrase
Directions - The test
administrator may simplify the
language of the directions.
|
|
Rhode Island
|
Read Aloud
Questions - Read test aloud
to student (Mathematics and
Session 1 Writing only). Reading
the reading test to the student
invalidates all reading
sessions.
Native Language Translation
of Directions - Translate
directions into other language.
Administration by Others
- Administer the test with
special education personnel.
Familiar Examiner -
Administer the test with other
school personnel known to the
student.
Student Reads Test Aloud
- Student reads test aloud to
self.
Other - Underline key
information in directions.
Reduction of visual print by
blocking or other techniques.
|
|
South Carolina
|
Read Aloud
Questions - Considered a
modification for the PACT, the
HSAP, and the EOCEP. Allowed on
the PACT and EOCEP. Not allowed
on the HSAP. Only allowed on the
EOCEP (not PACT or HSAP).
Sign Interpret Directions
- Student repeating/signing
directions to the TA or
interpreter; the student may
need to sign the directions to
the TA for clarification or to
demonstrate his or her
understanding. Considered a
modification for the PACT, the
HSAP, and the EOCEP.
Sign Interpret Questions
- Allowed on the PACT and EOCEP.
Not allowed on the HSAP. Only
allowed on the EOCEP (not PACT
or HSAP).
Repeat/Re-Read/Clarify
Directions - Student
repeating/signing directions to
the TA or interpreter; the
student may need to sign the
directions to the TA for
clarification or to demonstrate
his or her understanding.
Visual Cues - The test
administrator may write cues,
use cue symbols, or orally cue
the directions only in the test
booklet (e.g., providing arrows,
stop signs, or phrases such as
"read this story and answer
questions six through ten.").
Teacher Highlighting -
Highlighter. Student may
highlight words, phrases,
sentences, and so on in reading
passages or test items. The test
administrator may highlight key
words or phrases for students in
the directions only.
Student Reads Test Aloud
- Student reading test aloud to
himself or herself; requires
individual administration.
Other - A
student may need to sign the
directions to the test
administrator or interpreter for
clarification, or to demonstrate
his or her understanding.
|
|
South
Dakota
|
Large Print
- Large-print test booklets
and/or answer documents.
Read Aloud
Questions - Not allowed on
reading comprehension passages.
Sign Interpret Directions
- Sign language (ASL, cued
speech).
Sign Interpret Questions
- Sign language (ASL, cued
speech).
Sign Interpret Passages -
Sign language (ASL, cued
speech).
Repeat/Re-Read/Clarify
Directions - Repeating
and/or simplifying directions.
Simplify/Paraphrase
Directions - Repeating
and/or simplifying directions.
|
|
Tennessee
|
Read Aloud
Questions - Only the
questions on certain subtests on
the TCAP Achievement and TCAP
EOC/Gateway may be read aloud
for 504 students, but questions
from all subtests may be read
aloud for students with IEPs.
Can only be used for questions
not measuring reading/language
arts for students with 504s but
for all questions for students
with IEPs.
Sign Interpret Questions
- Allowed only for students with
a hearing impairment/deafness.
Repeat/Re-Read/Clarify
Directions - Directions
normally read aloud or signed to
students may be re-read/signed
verbatim, including prompts for
the writing assessment.
Visual Cues - Pointers.
Other - Modified answer
document or test booklet. Only
for students with an IEP or 504
Plan on the writing assessment,
available for all students on
other assessments.
|
|
Texas
|
Read Aloud
Directions - Allowed on
TAKS, and TAKS-Alt.
Read Aloud Questions -
Allowed on TAKS, and TAKS-Alt.
Only allowed on the TAKS
Modified. Part of dyslexia
bundle including orally reading
all proper nouns associated with
each passage before students
begin individual reading, orally
reading all test questions and
answer choices to students, and
extending the testing time over
a two-day period. These three
accommodations must be bundled
meaning they must be provided
together. Only students who meet
the eligibility criteria
outlined in Appendix B may use
this accommodation.
Sign Interpret Directions
- Allowed on TAKS, and TAKS-Alt.
Visual Cues - Pictures or
objects to convey meaning and
stamps, stickers, or stencils to
communicate. Placement to
facilitate eye gaze or intense
focus and visual scanning
techniques allowed on TAKS-Alt.
Teacher Highlighting -
Under category of Presentation
Supports/Materials for TAKS-alt
and subcategory Physical Access:
highlight or draw information.
Simplify/Paraphrase Directions
- Breaking verbal directions
into parts or chunks and
shortened text Allowed on
TAKS-Alt.
Tactile Graphics -
Tactile symbols and books
allowed on TALS-alt. Textured
surfaces and tactile materials
to explore allowed on the
TAKS-Alt.
Prompt/Encourage Student
- Visual, verbal, or tactile
reminders to stay on task.
Other - Communication
Symbols allowed on TAKS-Alt.
Photocopies of Test.
|
|
Utah
|
Large Print
- Must be in at least 18-point
type.
Read Aloud Directions -
Includes screen reader. Allowed
on all tests but the UALPA.
Read Aloud Questions -
Includes screen reader. Not
allowed on language arts subtest
of the UBSCT, the UALPA, or on
the reading and vocabulary
subtests of the Iowa Tests.
Passages, questions, and options
may not be read aloud on the CRT
secondary language arts test.
Math and science passages,
questions and options on the CRT
may be read aloud in English.
Sign Interpret Directions
- Allowed on all tests but the
UALPA.
Sign Interpret
Questions - Not allowed on
language arts subtest of the
UBSCT, the UALPA, or on the
reading and vocabulary subtests
of the Iowa Tests. Passages,
questions, and options may not
be signed on the CRT secondary
language arts test. Math and
science passages, questions and
options on the CRT may be
signed.
Repeat/Re-Read/Clarify
Directions - Allowed only on
the CRT. Clarification,
paraphrasing, and re-signing are
allowed.
Visual Cues - Visual cues
- hearing impaired.
Simplify/Paraphrase
Directions - Paraphrasing
allowed only on the CRT.
Tactile Graphics -
Tactile graphics.
|
|
Vermont
|
Read Aloud
Questions - Read test aloud
to student (mathematics and
session 1 writing only). Reading
aloud any portion of the reading
test to a student is considered
a modification and invalidates
all reading sessions and no
credit will be given.
Native Language Translation
of Directions - Translate
directions into other language.
Administration by Others
- Administer the test with
special education personnel.
Familiar Examiner -
Administer the test with other
school personnel known to the
student.
Teacher Highlighting -
Underline key information in
directions.
Student Reads Test Aloud
- Student reads test aloud to
self.
Other - Reduction of
visual print by blocking or
other techniques.
|
|
Virginia
|
Read Aloud
Questions - Allowed for all
students with an IEP or 504 Plan
on the math, science,
history/social science, and
writing assessments. Only
allowed on the reading test for
students with a visual
impairment, including blindness,
and those students with a
specific disability that
severely limits or prevents them
from decoding text at any level
of difficulty. If a read-aloud
accommodation is used on the
reading test for students with
disabilities who have not been
determined as eligible by the
school division according to the
criteria stated above, it will
be considered a non-standard
accommodation.
Sign Interpret Directions
- Allowed for students who are
deaf or have a hearing
impairment.
Sign Interpret Questions
- Allowed for students who are
deaf or hard of hearing, except
on reading tests.
Interpreting/transliterating
(e.g., cued speech) test items
(except for reading tests) for
students who are deaf or hard of
hearing.
Repeat/Re-Read/Clarify
Directions - Clarifying
directions.
Simplify/Paraphrase
Directions - Simplifying
directions. Plain English
version.
Other - Written
directions to accompany oral
directions.
|
|
Washington
|
Read Aloud
Questions - Students in
Grades 3-8 may not use this
accommodation in reading.
Provide human reader for
mathematics, science, and
writing directions and items.
Provide an audio CD presentation
of directions and items. Have
the human reader increase wait
time between item stems. Have
the human reader decrease
reading pace. Accommodations
available to English Language
Learners. Students may not use
any print or electronic
dictionaries or thesaurus.
Read Aloud Passages -
Provide an audio CD presentation
of reading passages and items.
(High School ONLY).
Sign Interpret Directions
- Give directions and items from
mathematics, science, and
writing tests in sign language
including American Sign Language
or Signing Exact English.
Interpreters use the method of
signing that is familiar to the
student. Signers must not
paraphrase, clarify, elaborate,
or provide assistance.
Sign Interpret Questions
- Give directions and items from
mathematics, science, and
writing tests in sign language
including American Sign Language
or Signing Exact English.
Interpreters use the method of
signing that is familiar to the
student. Signers must not
paraphrase, clarify, elaborate,
or provide assistance.
Repeat/Re-Read/Clarify
Directions - Reread
assessment directions verbatim.
Student Reads Test Aloud
- Allow the student to read the
directions or test items aloud
as long as it is read in a
separate location so it does not
distract other students.
Prompt/Encourage Student
- Cue student to begin working
and stay on task.
Page Turner - Provide
assistance in turning pages,
handling booklets, etc.
Other - Direct students
to underline or mark assessment
directions with a No. 2 pencil.
|
Table B.20A: Equipment and
Materials Accommodations (1 out of 4)
A = Allowed, AC
= Allowed in Certain Circumstances, AI =
Allowed with Implications for Scoring, P
= Prohibited
AS = All Subjects, R = Reading/Language
Arts, M = Math, S = Science, W =
Writing, SS = Social Studies
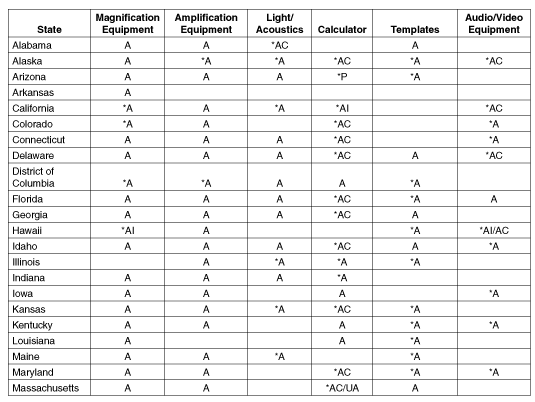
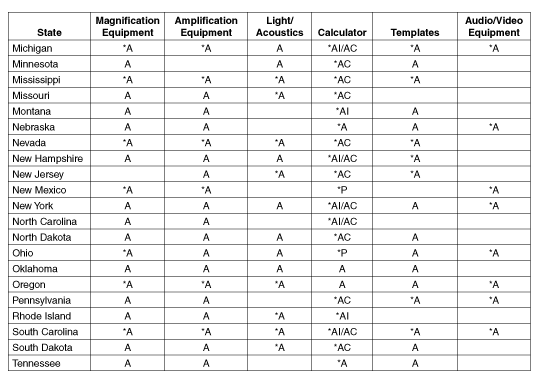
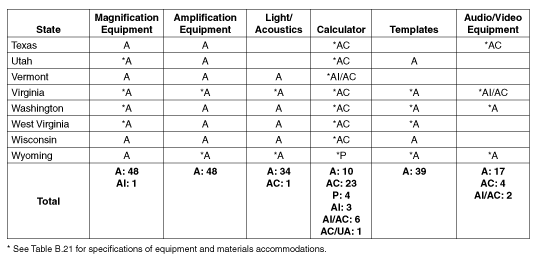
Table B.20B: Equipment and
Materials Accommodations (2 out of 4)
A = Allowed, AC
= Allowed in Certain Circumstances, AI =
Allowed with Implications for Scoring, P
= Prohibited
AS = All Subjects, R = Reading/Language
Arts, M = Math, S = Science, W =
Writing, SS = Social Studies
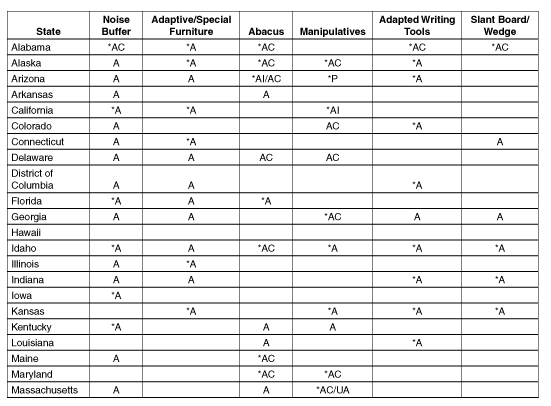
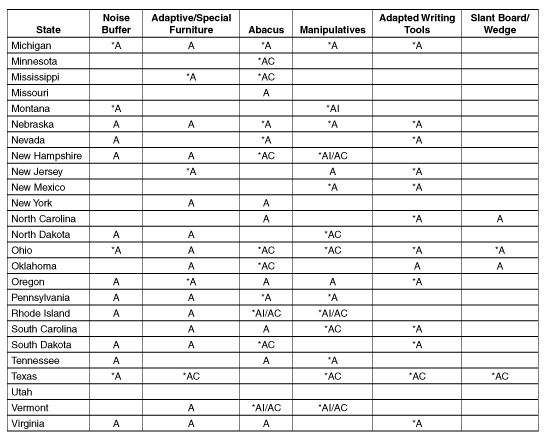
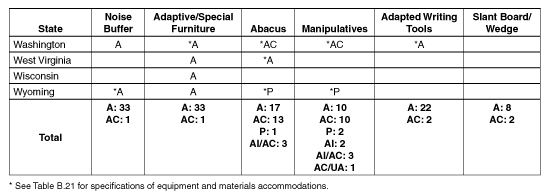
Table B.20C: Equipment and
Materials Accommodations (3 out of 4)
A = Allowed, AC
= Allowed in Certain Circumstances, AI =
Allowed with Implications for Scoring, P
= Prohibited
AS = All Subjects, R = Reading/Language
Arts, M = Math, S = Science, W =
Writing, SS = Social Studies
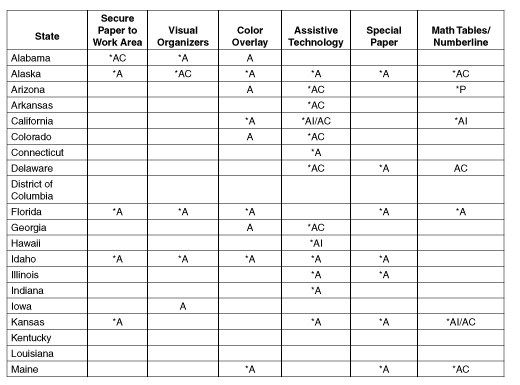
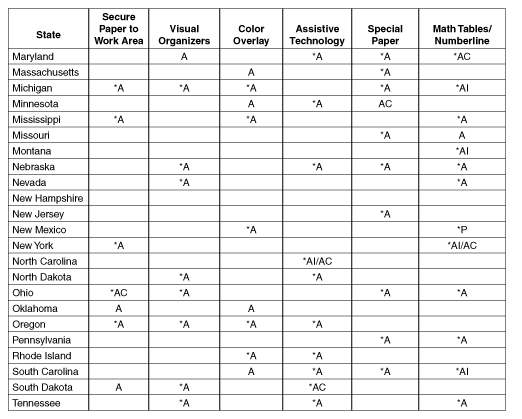
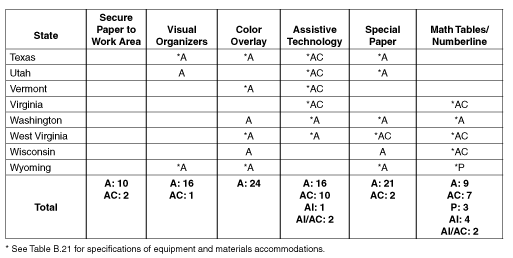
Table B.20D: Equipment and
Materials Accommodations (4 out of 4)
A = Allowed, AC
= Allowed in Certain Circumstances, AI =
Allowed with Implications for Scoring, P
= Prohibited
AS = All Subjects, R = Reading/Language
Arts, M = Math, S = Science, W =
Writing, SS = Social Studies
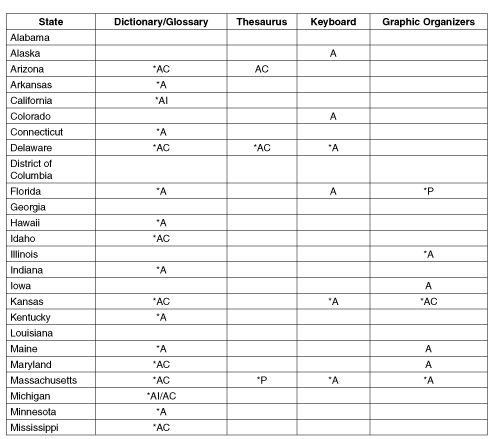
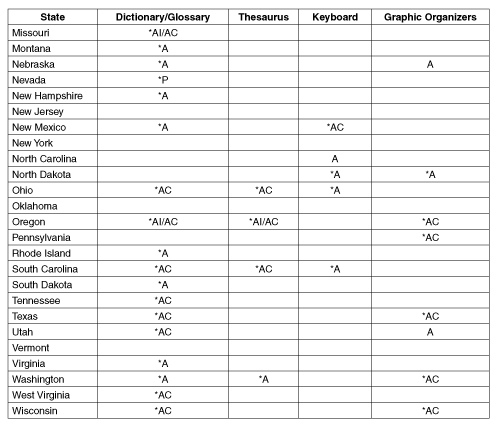
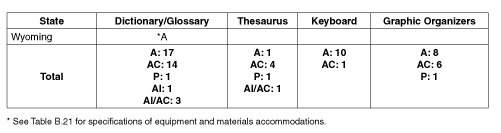
Table B.21: Specifications
and Descriptions of ďCertain
Circumstances,Ē ďImplications for
Scoring,Ē ďUnique Aggregated,Ē and
ďOtherĒ Equipment and Materials
Accommodations
|
Alabama
|
Light/Acoustics
- Only allowed for IEP students
on the Alabama Science
Assessment (ASA). Allowed for
IEP and 504 on all other
assessments.
Noise Buffer
- Prohibited on the Dynamic
Indicators of Basic Early
Literacy Skills (DIBELS).
Allowed for IEP students but not
504 students on the Alabama
Science Assessment (ASA).
Allowed for IEP and 504 on all
other assessments.
Adaptive/
Special Furniture - Only
allowed for IEP students on the
Alabama Science Assessment
(ASA). Allowed for IEP and 504
on all other assessments.
Abacus -
Prohibited on the Dynamic
Indicators of Basic Early
Literacy Skills (DIBELS) and the
Alabama Direct Assessment of
Writing (ADAW). Allowed on all
other assessments
Adapted Writing Tools -
Allowed only on the Stanford 10,
the Alabama Reading and
Mathematics Test (ARMT), and the
Alabama Alternate Assessment
(AAA).
Slant Board/Wedge -
Prohibited on the Dynamic
Indicators of Basic Early
Literacy Skills (DIBELS),
Alabama High School Graduation
Exam (AHSGE), and the Alabama
Direct Assessment of Writing
(ADAW). Allowed for students
with an IEP only on the Alabama
Science Assessment (ASA).
Allowed for IEP and 504 students
on all other assessments.
Secure Paper to Work Area
- Allowed only on the Stanford
10 and the Alabama Reading and
Mathematics Test (ARMT).
Visual
Organizers - Marker to
maintain place.
|
|
Alaska
|
Amplification
Equipment - Using auditory
amplification device, hearing
aid.
Light/Acoustics - Provide
special lighting and acoustics.
Calculator - Using a
calculator with minimal
functions: having only addition,
subtraction, division,
multiplication, percentage,
square root, and memory
functions. Listed with an
asterisk indicates state
restrictions on the use of the
accommodation for particular
assessments.
Templates -
Using templates to reduce
visible print.
Audio/Video
Equipment - Using test
contractor tape-recorded version
of HSGQE writing and mathematics
test.
Adaptive/Special
Furniture - Provide adaptive
or special furniture.
Abacus - If
a studentís disability affects
mathematics calculation but not
reasoning, a calculator or other
assistive device (abacus,
arithmetic table, manipulatives,
or number chart) may be used.
Listed with an asterisk
indicates state restrictions on
the use of accommodations for
particular assessments.
Manipulatives
- If a studentís disability
affects mathematics calculation
but not reasoning, a calculator
or other assistive device
(abacus, arithmetic table,
manipulatives, or number chart)
may be used. Listed with an
asterisk indicates state
restrictions on the use of
accommodations for particular
assessments.
Adapted Writing Tools -
Using special pen or pencil such
as felt-tip marker or ink pen.
(Student responses must be
transcribed by the test
administrator/proctor according
to procedures detailed in the
test administration directions.)
Secure Paper to Work Area
- Securing papers to work area
with tapes/magnets.
Visual Organizers - Using
masks or markers to maintain
place. Using ruler or object to
maintain place in test. Listed
with an asterisk indicates state
restrictions on the use of the
accommodation for particular
assessments.
Color Overlay - Using
color screens to direct
attention to specific sections
on the page.
Assistive Technology -
Using adaptive equipment to
deliver test. (Required
consultation with the department
for security reasons.) Using
typewriter or computer without
spell or grammar checker.
Special Paper - Using
graph paper and using scratch
paper for reading and/or science
tests.
Math Tables/Numberline Ė
Using math manipulatives. If a
studentís disability affects
mathematics calculation but not
reasoning, a calculator or other
assistive device (abacus,
arithmetic table, manipulatives,
or number chart) may be used.
Listed with an asterisk
indicates state restrictions on
the use of accommodations for
particular assessments.
Other - Using a shield to
reduce glare.
|
|
Arizona
|
Calculator Ė
(No grade specified.)
Accommodations no longer allowed
include...the use of a
calculator or other
manipulatives for mathematics.
Templates Ė Place marker
use.
Abacus Ė For a student
who is blind, use of an abacus
for mathematics test items.
Abacus may not be used on any
portion of AIMS HS.
Manipulatives Ė
Accommodations no longer allowed
include the use of . . .
manipulatives for mathematics.
Math manipulatives, charts, and
aids, including, but not limited
to, a ruler, number line,
compass, and an abacus, may not
be used on any portion of AIMS
HS.
Adapted Writing Tools Ė
Special furniture or pencil.
Assistive Technology Ė
Use assistive technology with
spell check, grammar check, and
predict ahead functions turned
off, is allowed. Studentsí
electronic responses must be
transferred to a regular answer
document according to guidelines
provided, to be scored.
Math Tables/Numberline Ė
Number line . . . may not be
used on any portion of AIMS HS.
Dictionary/Glossary Ė
Students may use a commercially
published paper dictionary or a
commercially published paper
thesaurus for the AIMS HS
writing test only, although
neither item is required to be
used by students. Provide a
word-for-word published, paper
translation dictionary [ELL
section text]. For a student who
is blind, use of an electronic
dictionary and thesaurus with
grammar check, spell check,
encyclopedia, translation, and
internet access turned off
[SpEd/504 section text].
Other Ė A ruler is not
allowed on any portion of AIMS
HS. A compass is not allowed on
any portion of the AIMS HS.
Mathematics sections - use of
personal whiteboard which can be
seen by only the student and is
erased after every problem.
|
|
Arkansas
|
Assistive
Technology Ė In special
circumstances, limited assistive
devices may be required and will
be considered for use on the
Augmented Benchmark,
End-of-Course, and Grade 11
Literacy Examinations.
Dictionary/Glossary Ė
Word-to-word dictionary. Limited
English proficient students may
use an English/Native Language
Word-to-Word dictionary that
contains no definitions or
pictures, if it is a part of the
studentís LPAC Plan.
Other Ė Accommodations
currently not available:
audiocassettes.
|
|
California
|
Magnification
Equipment - Students may
have these testing variations if
regularly used in the classroom.
Light/Acoustics -
Students may have these testing
variations if regularly used in
the classroom.
Calculator - Considered a
modification with implications
for scoring on STAR, CAHSEE and
CELDT tests.
Audio/Video Equipment -
Audio presentation (CD) of test
questions is considered a
modification in reading with
implications for scoring on
STAR, CAHSEE, and CELDT tests.
Noise Buffer - Students
may have these testing
variations if regularly used in
the classroom.
Adaptive/ Special Furniture
- Students may have these
testing variations if regularly
used in the classroom.
Manipulatives -
Considered a modification with
implications for scoring on
STAR, CAHSEE, and CELDT tests.
Color Overlay - Students
may have these testing
variations if regularly used in
the classroom.
Assistive Technology -
Assistive devices are allowed as
an accommodation on multiple
choice and essay questions if
they do not interfere with the
independent work of the student.
If they do interfere, it is
considered a modification with
implications for scoring.
Math Tables/Numberline -
Considered a modification with
implications for scoring on
STAR, CAHSEE, and CELDT tests.
Dictionary/Glossary -
Considered a modification with
implications for scoring on all
STAR, CAHSEE and CELDT tests.
|
|
Colorado
|
Magnification
Equipment - Handheld
magnifiers.
Calculator - Talking
calculator (only on the 9th and
10th grade math assessment where
calculators are used for all
students).
Audio/Video
Equipment - Closed circuit
television.
Adapted Writing Tools -
Pencil grips or large #2
pencils. Studentís preferred
writing tool only allowed for
alternate assessment.
Assistive Technology -
Only on CSAPA (alternate
assessment).
|
|
Connecticut
|
Calculator Ė
Talking calculators. Calculators
may be used by all students for
sections that do not measure
computation skills. They cannot
be used on computation sections
even as an accommodation. Those
who use talking calculators must
be tested separately. PDAs and
Palm Pilots are not permitted.
Audio/Video Equipment Ė
Students may use closed-circuit
TV equipment (e.g., Optelec,
Visualtec).
Adaptive/ Special Furniture
Ė Adaptive furniture (e.g.,
special tables, corner chairs,
slant boards, etc.). This
accommodation does not extend to
the use of some communication
devices that alter the
presentation or response mode of
the test.
Assistive Technology Ė
The student may use
voice-recognition/assistive
technology for open-ended items
and subtests requiring an
extended response. It is not
available to students who have
slow or labored handwriting or
fine-motor problems, but are
otherwise capable of providing a
handwritten or typed response.
Dictionary/Glossary Ė A
word to word dictionary is
permitted for word-to-word
translations only. Dictionaries
containing definitions are not
allowed to be used in the
testing situation.
|
|
Delaware
|
Calculator Ė
Using a calculator on the two
parts of the math test for which
calculators are not permitted.
Audio/Video
Equipment - Present test
questions and writing prompts on
audiotape or videotape. For
written responses, student uses
an audio recorder as an
organizational or pre-writing
tool. For written responses,
deaf student records a videotape
as an organizational or
pre-writing tool. Student
responses can be recorded by
audio or video taping.
Assistive Technology -
Present the test via Kurzweil
software. Must also select the
read aloud/sign interpret
questions and passages
accommodations.
Special Paper - Graph
paper, acetate color sheets.
Dictionary/Glossary -
Electronic dictionary prohibited
for 504 and IEP, but allowed for
ELL/IEP. Bilingual dictionaries
allowed for ELL/IEP.
For the writing
test, using an electronic
dictionary whenever dictionary
use is permitted for other
students is allowed for 504, IEP
and ELL/IEP. Bilingual
dictionaries allowed for
ELL/IEP.
Thesaurus - For the
writing test, using an
electronic thesaurus whenever
thesaurus use is permitted for
other students.
Keyboard -
Adapted keyboard.
Other -
Three-dimensional
representations of pictures in
the test such as supplying real
coins when a picture of coins is
presented.
|
|
District of
Columbia
|
Magnification
Equipment - Magnifying
glass.
Amplification Equipment -
Amplification equipment such as
hearing aid or auditory trainer.
Templates - Masks or
markers to maintain place.
Adapted Writing Tools -
Pencil grip.
|
|
Florida
|
Calculator -
Calculators are not allowed to
be used for basic computation on
the FCAT mathematics or science
in grades 3-6. Students with
disabilities may use adapted
calculators for the FCAT
mathematics in grades 7-10 and
FCAT science in grades 8 and 11.
Templates - Means to
maintain or enhance visual
attention to items, such as a
pointer, template, blank card,
or non calibrated ruler.
Noise Buffer - White
noise (sound machines) to reduce
auditory distractions.
Abacus - For students
with visual impairments.
Secure Paper to Work Area
- Papers secured to the work
area; requires prior approval by
commissioner of education.
Visual Organizers - Means
to mask portions of the test to
direct attention to uncovered
items.
Color Overlay - Colored
transparencies or overlays.
Special Paper - Special
paper with raised, shaded, or
color-coded lines.
Math Tables/Numberline -
Math guides (gridded paper) to
organize mathematical
computation.
Dictionary/Glossary - Use
of an English/sign language
dictionary for students who use
sign language as their primary
means of communication. The
dictionary may not contain
definitions of words, but may
contain the sign picture, the
word, synonyms, and an index.
Access to an English-to-heritage
language/heritage
language-to-English dictionary
such as those typically used in
instructional settings or a
dictionary with definitions
written exclusively in the
heritage language or English
shall not be allowed. Electronic
dictionaries are strictly
prohibited and may be cause for
invalidation.
Graphic Organizers - Use
of graphic organizer software to
assist in preparing responses
Other -
Switches. A writing guide (grid)
to produce legible answers.
Also, a math guide to organize
mathematical computation is
allowed. Positioning tools such
as a reading stand.
|
|
Georgia
|
Calculator Ė
Considered a conditional
accommodation on the
Criterion-Referenced Competency
Tests (CRCT) in math: Only
students with a specific
disability that severely limits
their ability to calculate
mathematically and the students
have access to mathematical
calculation only through the use
of a calculator. Allowed for all
students in math and science on
the Georgia High School
Graduation Tests (GHSGT) and for
all students in Algebra 1,
Geometry,
Economics/Business/Free
Enterprise, and Physical Science
tests of the End-of-Course Tests
(EOCT). Prohibited on all other
tests.
Manipulatives -
Substitute manipulative. Only
allowed on the Georgia
Kindergarten Inventory of
Developing Skills (GKIDS).
Assistive
Technology
test questions or passages in
English only by reader or
assistive technology. Considered
conditional for passages but
standard for questions on the
Criterion-Referenced Competency
Tests (CRCT): only allowed in
grades 3-8, for students who
have a specific disability that
severely limits or prevents them
from decoding text and the
student has access to printed
materials only through a reader.
Considered nonstandard on the
reading comprehension and
vocabulary subtests of the
Norm-Referenced Tests (NRT).
Only allowed in writing on the
ACCESS for ELLS. Allowed as
standard on all other tests.
Other - Photograph used.
Only allowed on the Georgia
Kindergarten Inventory of
Developing Skills (GKIDS).
|
|
Hawaii
|
Magnification
Equipment - Using a
closed-circuit TV or a
magnifying glass to enlarge
regular-sized Test Booklet.
Scores are non-comparable if
this accommodation is used for
the norm-referenced test.
Templates - School
provides.
Audio/Video Equipment -
Presentation via audio CD; in
order to receive this
accommodation: 1. The student
has a specific disability that
prevents the student from
decoding text at any level, even
after varied and repeated
attempts to teach the student to
do so (i.e., the student is a
non-reader who will never be
able to read any sentences at
any grade level throughout his
or her life); and 2. The student
is able to access printed
materials only through a person
who reads the text or is
provided with spoken text on
audio CD, video, applicable
software programs, or other
electronic formats during
routine classroom instruction
(i.e., the student accesses all
printed materials for every
subject via an audio format all
of the time during classroom
instruction). Use of closed
circuit TV on norm referenced
test results in scores that are
not comparable.
Assistive Technology -
Using a computer, including an
Alpha Smart computer, to record
multiple-choice and written
responses. Criterion-referenced
and non-comparable separate
national norm-referenced scores
will be provided.
Dictionary/Glossary -
English dictionary. Also allowed
for Hawaiian language immersion
students in grade 5 who are
transitioning to the use of
English during a portion of each
instructional day (for reading
and math tests). Electronic and
bilingual dictionaries are not
allowed.
Other - Electronic and
bilingual dictionaries are not
allowed. Place marker (school
provides). Highlighting film
that is placed on each test
booklet page (school provides).
Highlighter pen. For grade 3,
students must use a yellow
highlighter pen to ensure that
responses are scored correctly
in their scannable test
booklets.
|
|
Idaho
|
Calculator -
Not to be used on sections
measuring math computation
skills.
Audio/Video Equipment -
Audio taped administration (need
to notify SDE in advance). For
LEP students, this accommodation
replaces human readers to read
and audio devices to record/play
back test components.
Noise Buffer - White
noise; noise buffer.
Abacus - Not to be used
on sections measuring math
computation skills.
Manipulatives or abacus for
calculation.
Manipulatives Ė
Manipulatives or abacus for
calculation.
Adapted Writing Tools -
Pencil grip or large diameter
pencil.
Slant Board/Wedge Ė Slant
board or wedge.
Secure Paper to Work Area
- Magnets or tape to secure
papers to work area.
Visual Organizers -
Markers to maintain place.
Color Overlay Ė Markers
or masks to maintain place.
Assistive Technology -
Head wand. Computer reads
directions and/or items. Screen
reader. Also, assistive
communication device.
Special Paper Ė Use graph
paper to keep numbers in proper
columns.
Dictionary/Glossary -
Student uses an English
dictionary glossary. For LEP
students, provide district
approved English or bilingual
word-to-word dictionary (this
word-to-word dictionary may be
electronic or paperback.) Using
dictionaries that provide
definitions are an adaptation.
If adaptations are used, the
student is deemed not proficient
and will not be counted towards
participation. For students with
IEPs/504, using dictionaries
that provide definitions.
Other Ė Dark or raised
lines.
|
|
Illinois
|
Light/Acoustics
Ė Allowed on grade 11 PSAE.
Calculator - Allowed for
all students on the ISAT math
tests at grade 4-8. Allowed as
an accommodation for students
with an IEP or 504 Plan at grade
3.
Templates Ė Templates,
rulers or other devices used to
help students keep their place
on the answer documents or test
booklets.
Adaptive/ Special Furniture
Ė Includes Study carrel or
carrel desk; allows for grade 11
PSAE.
Assistive Technology Ė
Spell-check, grammar check, word
prediction or text organization
computer features must be
disabled. Includes adaptive or
augmentative technology.
Special Paper - Blank
scratch paper for all students
for use in Session 1 of the math
test. Available as an
accommodation for students with
an IEP or 504 Plan on all tests.
Students with IEP/504 may have
large paper or large spaced
paper to write answers on.
Graphic Organizers -
Graphic organizer.
Other - Paper ruler.
|
|
Indiana
|
Calculator -
Student must still show his or
her work for a given problem.
Adapted Writing Tools -
Student is provided pencil grip
or specialized writing
instrument.
Slant Board/Wedge - Slant
board to hold testing materials
at correct angle.
Assistive Technology -
Student uses a talk assistive
technology device.
Dictionary/Glossary -
Permitted and documented in
ISTEP+ student information
questionnaire. Student uses an
approved bilingual word-to-word
dictionary. Note The studentís
Individual Learning Plan must
document use of a bilingual
word-to-word dictionary in class
and on standardized tests.
|
|
Iowa
|
Audio/Video
Equipment - Assessment on
audiotape or compact disk, books
on tape, videotape and
descriptive video.
Noise Buffer
- Sound blocking headphones.
|
|
Kansas
|
Light/Acoustics
Ė Extra bright or very low
lighting; appropriate lighting
behind interpreter.
Calculator Ė As
appropriate and applicable to
the assessment, if a calculator
was used. If any student uses a
modification on the state
assessment that results in an
invalid score, the student is
considered to be not tested when
calculating the participation
rate for AYP purposes. In
addition to counting that
student as not tested, the score
will not be included when
calculating the proficiency rate
for AYP decisions. Example given
is using calculator on
non-calculator portion of math
assessment. It is allowed on the
calculator portions. This
applies for both the regular
assessment and KAMM, as both
have non-calculator portions.
Also, as appropriate and
applicable to the assessment, if
a calculator was used for
writing, that has a separate
entry. The use of calculation
devices on non-calculator
portions of the Kansas State
Assessment is considered a
modification of the assessment.
For all students including those
with IEPs, this modification
will result in the state
assessment score being counted
as not tested and will count
against the participation rate.
On portions of the assessment
that allow calculator use,
calculation devices such as math
tables are permitted. Graphing
calculators are permitted in
grade 8 and in high school.
Calculators may be used on any
part of the science assessment.
However, they are not required.
For KCA testing, an on-screen
calculator is available.
Templates Ė Masks that
cover a portion of the text and
single line window.
Adaptive/ Special Furniture
Ė Adjustable height desk.
Manipulatives Ė Allowable
manipulatives: student chosen in
this testing environment, are
allowed to use manipulatives,
graph paper, blank paper, and
other materials as specified in
the test directions. (These are
to be provided, as available, by
the school.) Individual students
may receive allowable
accommodations that are
regularly provided during
classroom instruction and
assessment activities. If
applicable, these accommodations
should be specified in a
studentís Individual Education
Plan (IEP) or Section 504 Plan,
or should be a part of a student
assistance plan resulting from a
schoolís Student Intervention
Team (SIT) process or an English
Language Proficiency assessment.
Manipulatives that are routinely
used in the classroom may be
used by the student on the
Kansas State Assessments. The
manipulative must be chosen by
the student. The teacher may
neither suggest a particular
manipulative nor insist that a
manipulative be used. Examples
of manipulatives are listed.
Graphic organizers that are
generated solely by the student
on blank paper during the
assessment are allowed. Not all
of the manipulatives in the list
below will be found in every
classroom. Manipulatives will
not be useful on the assessment
if they have not been used
regularly during the year. Use
of manipulatives is optional.
Examples appropriate for the
math and science assessments:
Base 10 blocks, chips, two color
counters, two-sided counters,
clock or clock face, color tiles
(squares), cubes: multilink,
connecting color, wooden,
unifix, multilink cubes,
Cuisenaire rods, geoboards,
geometric solids, graph paper,
hundreds chart, integer number
line, money, number cubes,
pattern blocks, rules, meter
sticks, protractors, compass,
snap blocks, spinners,
transparent mirror or mira. For
the Science Assessment,
measurement tools cannot be
labeled to indicate what they
measure. For instance, a meter
stick may have the cm labeled on
it, but the stick may not be
labeled that it measures length.
Adapted Writing Tools Ė
Thick pencil or pencil grip.
Slant Board/Wedge Ė Slant
top surface.
Secure Paper to Work Area
Ė Tape paper to desk.
Assistive Technology Ė
Includes other types, but does
not specify, also, voice
recognition assistive
technology.
Special Paper Ė Braille
paper. Bold line writing paper.
This is different from Braille
paper. Raised lines on paper.
Use graph paper to keep numbers
in proper columns.
Math Tables/Numberline Ė
The use of calculation devices
on non-calculator portions of
the Kansas State Assessment is
considered a modification of the
assessment. For all students
including those with IEPs, this
modification will result in the
state assessment score being
counted as not tested and will
count against the participation
rate. On portions of the
assessment that allow calculator
use, calculation devices such as
math tables are permitted.
Dictionary/Glossary Ė
Textbooks, dictionaries, and
other instructional/curricular
materials are not to be used
during testing. Student used a
translation dictionary is listed
as an accommodation with a code.
ELL students are allowed to use
any type of dictionary including
a translation dictionary. It
seems to suggest here that for
ELLs it is not considered an
accommodation, but a general
testing practice, whereas for
other students it is an
accommodation. If student used a
translation dictionary,
electronic translators and
bilingual dictionaries may be
used.
Keyboard Ė Adapted
keyboard.
Graphic Organizers Ė
Organization tools (e.g.,
diagrams, Venn Diagrams, or flow
charts that are made during the
assessment). State had these
under presentation and response
categories. Use of
commercially-made, teacher-made,
or teacher-generated graphic
organizers is prohibited. For
Exam Manual for Writing, this is
not treated as an accommodation,
but is addressed under general
guidelines to prohibit teachers
from handing out graphic
organizers on the day of
testing, or lists of transition
words.
Other - The
use of journals is considered a
modification of the Kansas State
Assessment. For all students
including those with IEPs, this
modification will result in the
state assessment score being
counted as not tested and will
count against the participation
rate. Students may use graphic
organizers that are developed
during the assessment, but
should not use previously
generated organizers. Journals
previously generated will result
in an invalid score.
Previously-created materials,
specific to the Kansas Writing
Assessment, may not be used: all
subjects are covered in this
prohibition. Textbooks,
dictionaries and other
instructional/curricular
materials are not to be used
during testing. This includes
classroom posters, teacher or
student-generated journals, and
other instructional materials
that may have been used during
the course of instruction.
Electronic translators and
bilingual dictionaries may be
used to read directions, test
questions and answer choices.
They cannot be used on the
reading passage of the Kansas
Reading Assessment.
|
|
Kansas
(contíd)
|
Slant
Board/Wedge Ė Slant top
surface.
Secure Paper to
Work Area Ė Tape paper to
desk.
Assistive
Technology Ė Includes other
types, but does not specify,
also, voice recognition
assistive technology.
Special Paper Ė
Braille paper. Bold line writing
paper. This is different from
Braille paper. Raised lines on
paper. Use graph paper to keep
numbers in proper columns.
Math
Tables/Numberline Ė The use
of calculation devices on
non-calculator portions of the
Kansas State Assessment is
considered a modification of the
assessment. For all students
including those with IEPs, this
modification will result in the
state assessment score being
counted as not tested and will
count against the participation
rate. On portions of the
assessment that allow calculator
use, calculation devices such as
math tables are permitted.
Dictionary/Glossary Ė Textbooks,
dictionaries, and other
instructional/curricular
materials are not to be used
during testing. Student used a
translation dictionary is listed
as an accommodation with a code.
ELL students are allowed to use
any type of dictionary including
a translation dictionary. It
seems to suggest here that for
ELLs it is not considered an
accommodation, but a general
testing practice, whereas for
other students it is an
accommodation. If student used a
translation dictionary,
electronic translators and
bilingual dictionaries may be
used.
Keyboard Ė
Adapted keyboard.
Graphic
Organizers Ė Organization
tools (e.g., diagrams, Venn
Diagrams, or flow charts that
are made during the assessment).
State had these under
presentation and response
categories. Use of
commercially-made, teacher-made,
or teacher-generated graphic
organizers is prohibited. For
Exam Manual for Writing, this is
not treated as an accommodation,
but is addressed under general
guidelines to prohibit teachers
from handing out graphic
organizers on the day of
testing, or lists of transition
words.
Other - The
use of journals is considered a
modification of the Kansas State
Assessment. For all students
including those with IEPs, this
modification will result in the
state assessment score being
counted as not tested and will
count against the participation
rate. Students may use graphic
organizers that are developed
during the assessment, but
should not use previously
generated organizers. Journals
previously generated will result
in an invalid score.
Previously-created materials,
specific to the Kansas Writing
Assessment, may not be used: all
subjects are covered in this
prohibition. Textbooks,
dictionaries and other
instructional/curricular
materials are not to be used
during testing. This includes
classroom posters, teacher or
student-generated journals, and
other instructional materials
that may have been used during
the course of instruction.
Electronic translators and
bilingual dictionaries may be
used to read directions, test
questions and answer choices.
They cannot be used on the
reading passage of the Kansas
Reading Assessment.
|
|
Kentucky
|
Templates -
Non-calibrated rule or template.
Audio/Video Equipment -
Close-captioned or video
materials, audio taped
directions.
Noise Buffer - Auditory
trainer.
Dictionary/Glossary -
Electronic dictionaries.
|
|
Louisiana
|
Templates -
Mask or marker to maintain
place.
Adapted Writing Tools -
Grip for pencil.
|
|
Maine
|
Light/Acoustics
- Special lighting.
Templates - Markers,
filters.
Abacus - For visually
impaired only.
Color Overlay - Color
overlays.
Special Paper -
Large-spaced paper.
Math Tables/Numberline -
Arithmetic tables; only allowed
in the calculator-allowed
session of the Mathematics test.
Dictionary/Glossary -
Word-to-word bilingual
dictionary that does not include
definitions as needed. Must be
listed at
http://www.maine.gov/education/mea/admininfo.html.
|
|
Maryland
|
Calculator -
Calculation device: If a
studentís disability affects
mathematics calculation but not
reasoning, a calculator or other
assistive device (e.g., abacus,
arithmetic table, manipulatives,
or number chart) may be used.
Calculators may be adapted with
large keys or voice output
(talking calculators).
Templates - Visual
organizers include . . .
templates.
Audio/Video Equipment - A
standard video presentation of a
test using American Sign
Language, signed English, cued
speech, or oral transliteration
may be used to increase quality,
consistency, pacing and
accuracy.
Abacus - In
some cases, an abacus may be
useful for students when
mathematics problems are to be
calculated without a calculator.
The abacus functions as paper
and pencil for students with
visual impairments.
Manipulatives -
Calculation device: If a
studentís disability affects
mathematics calculation but not
reasoning, a calculator or other
assistive device (e.g., abacus,
arithmetic table, manipulatives,
or number chart) may be used.
Calculators may be adapted with
large keys or voice output
(talking calculators).
Assistive Technology -
Assistive device.
Special Paper - Graph
paper.
Math Tables/Numberline -
Calculation device: If a
studentís disability affects
mathematics calculation but not
reasoning, a calculator or other
assistive device (e.g., abacus,
arithmetic table, manipulatives,
or number chart) may be used.
Calculators may be adapted with
large keys or voice output
(talking calculators).
Dictionary/Glossary -
Spelling and grammar devices:
The use of a dictionary may be
allowed on assignments that
require an extended response or
essay. Spelling and grammar can
also be checked with pocket
spellcheckers. Spelling and
grammar devices are not
permitted to be used on the
English high school assessment.
Other - Bilingual
dictionaries: Students
identified as English language
learners who have an ELL plan
may use published or electronic
bilingual dictionaries.
Allowable dictionaries and
devices do not contain
definitions of English words in
the studentís native language.
Talking materials: many
classroom materials include
calculators, talking clocks,
thermometers, timers, and
voltmeters.
|
|
Massachusetts
|
Calculator -
Considered a non-standard
accommodation if used on the
mathematics test.
Manipulatives -
Considered a non-standard
accommodation if used on the
non-calculator portion of the
mathematics test.
Special Paper - Answers
recorded in test booklet: the
student records answers directly
in the test booklet or uses
special paper for drafts or
computation (e.g., graph paper).
Dictionary/Glossary - All
LEP and former LEP students may
use approved word-to-word
bilingual dictionaries on all
MCAS tests.
Thesaurus -
The use of a thesaurus is not
permitted on any test, including
the ELA Composition.
Keyboard -
Alpha-Smart or similar
electronic keyboard.
Graphic
Organizers - Graphic
organizer, checklist, or
individualized mathematics
reference sheet.
|
|
Michigan
|
Magnification
Equipment - Use of
magnification devices.
Amplification Equipment -
Use of auditory amplification
devices or special sound
systems.
Calculator - Use of
calculator/talking calculator on
the non-calculator sections of
the mathematics assessment.
Nonstandard. Use of
calculator/talking calculator on
the calculator permitted
sections of the mathematics
assessment. Standard/allowed.
Use of calculator on the science
and social studies assessments.
Templates - Studentís use
of acetate colored shield,
highlighters, highlighter tape,
page flags, and reading guides.
Audio/Video Equipment -
Use of closed circuit
television.
Noise Buffer - Background
music or noise buffers.
Abacus - Standard or not
applicable on some tests (ELPA).
Manipulatives - Use of
actual coins and bills and use
of manipulatives for mathematics
assessments, such as base 10
blocks.
Adapted Writing
Tools - Use of special
adaptive writing tools such as
pencil grip or larger pencil.
Secure Paper to Work Area
- Use of non-skid surface that
will not damage the answer
document or scanning equipment
(do not use tape or other
adhesive). Studentís use of
acetate colored shield,
highlighters, highlighter tape,
page flags, and reading guides.
Visual
Organizers - Studentís use
of acetate colored shield,
highlighters, highlighter tape,
page flags, and reading guides.
Color Overlay
- Studentís use of acetate
colored shield, highlighters,
highlighter tape, page flags,
and reading guides.
Special Paper - Adapted
paper, lined or grid paper for
recording answers.
Math Tables/Numberline -
Use of arithmetic tables
nonstandard or non-applicable
(ELPA).
Dictionary/Glossary - Use
of bilingual word-for-word non
electronic translation glossary
for English language learners
allowed for students with IEP,
504, and ELL. Use of bilingual
dictionaries that define or
explain words or terms, not
standard for all students. Use
of dictionary, thesaurus,
spelling book, or grammar book
for mathematics, science, social
studies, and English Language
Arts, not standard for all
student groups.
Other - Use of screen
reader for English language arts
reading assessment, nonstandard.
Use of screen reader for ELPA
listening, writing and speaking
parts. Use of rulers as provided
by the State and use of adapted
rulers, protractors, Braille and
large print rulers and
protractors. Use of list of
formulae as provided by the
state. Tools to assist with
concentration.
|
|
Minnesota
|
Calculator Ė
Student uses calculator (except
where specifically prohibited).
Abacus - Student uses an
abacus (except where
specifically prohibited).
Assistive Technology -
Assistive technology for
computer-delivered assessments
refers to technology that is
used to maintain, increase, or
improve the functional
capabilities of students with
disabilities who take
computer-delivered assessments.
Dictionary/Glossary -A
bilingual word-to-word
dictionary contains mathematical
and scientific terms in English
and in the first language of a
given learner; no definitions
provided, only direct
translations of the mathematical
and scientific words.
|
|
Mississippi
|
Magnification
Equipment - Magnifying
glasses/magnifying equipment.
Amplification Equipment -
Hearing aids.
Light/Acoustics - With
special lighting.
Calculator Ė Prohibited
on Elementary and Middle Grades
Science Tests. Prohibited on the
Biology I Subject Area Testing
Program. Not allowed on English
II Multiple Choice Subject Area
Testing Program. Not allowed on
the US History from 1877
Assessment. Use of a calculator
(on mathematics assessment where
calculators are not used by all
students taking the test).
Templates - Templates to
reduce visible print.
Adaptive/Special Furniture
- Specialized table to fit a
studentís wheelchair. Adapted
keyboards.
Abacus - Only a student
who is visually-impaired may use
the abacus to solve mathematics
problems.
Secure Paper to Work Area
- Secure paper to work area with
magnets/tape.
Color Overlay -
Transparent color overlays.
Math Tables/Numberline -
Use of memory aids, fact charts,
or resource sheets . . . relates
to the use of memory aids. A
memory aid, fact chart, or
resource sheet is something that
helps a student remember how to
find the answer; it should not
give him/her the answer. This
accommodation cannot interfere
with what the test purports to
measure . . . The memory aids,
fact charts, and/or resource
sheets for state assessments
must: 1) be based upon the
individual studentís learning
needs, 2) be documented in the
studentís IEP, 3) used for
routine classroom instruction
and classroom assessments, and
4) must be limited to 1-3 pages
per content area.
Dictionary/Glossary -
Spelling dictionaries (i.e.,
dictionaries that show the
correct spelling of English
words but do not give
definitions). For Reading and
Writing portions of MCT2 only.
Not allowed on the Writing
Assessment Grades 4 and 7 Tests.
Not allowed on the Subject Area
Testing Program English II
Multiple Choice. Not allowed on
the English II Writing
Assessment.
Other -
Memory aids. Use of memory aids,
fact charts, or resource sheets
. . . relates to the use of
memory aids. A memory aid, fact
chart, and/or resource sheet is
something that helps a student
remember how to find the answer;
it should not give him/her the
answer. This accommodation
cannot interfere with what the
test purports to measure. . .
The memory aids, fact charts,
and/or resource sheets for state
assessments must: 1) be based
upon the individual studentís
learning needs, 2) be documented
in the studentís IEP, 3) used
for routine classroom
instruction and classroom
assessments, and 4) must be
limited to 1-3 pages per content
area.
Other - Auditory
trainers.
|
|
Missouri
|
Light/Acoustics
- Visual aids include any type
of optical or non-optical
devices used to enhance visual
capability. Examples of visual
aids include bold-line felt-tip
markers, lamps, filters,
bold-lined paper, writing
guides, or other adaptations
that alter the visual
environment by adjusting the
space, illumination, color,
contrast, or other physical
features of the environment.
Calculator - The use of a
calculator represents an
accommodation when it is used on
a section of the assessment for
which calculator use is not
allowed. Students may use
talking calculators, but only in
an isolated setting.
Special Paper - Visual
aids include any type of optical
or non-optical devices used to
enhance visual capability.
Examples of visual aids include
bold-line felt-tip markers,
lamps, filters, bold-lined
paper, writing guides, or other
adaptations that alter the
visual environment by adjusting
the space, illumination, color,
contrast, or other physical
features of the environment.
Dictionary/Glossary - Use
of bilingual dictionary (not
permissible for English II).
|
|
Montana
|
Calculator -
Student uses a calculator,
number chart, arithmetic table,
or manipulatives on the no
calculator sections of the
mathematics test. A student for
which this type of nonstandard
accommodation might be used
would be a student with a
learning disability in
mathematics who, without the use
of a calculator, would not be
able to perform any mathematics
calculations or functions.
Noise Buffer - Student
(not groups of students) wears
equipment to reduce
environmental noises.
Manipulatives - Student
uses a calculator, number chart,
arithmetic table, or
manipulatives on the no
calculator sections of the
mathematics test. A student for
which this type of nonstandard
accommodation might be used
would be a student with a
learning disability in
mathematics who, without the use
of a calculator, would not be
able to perform any mathematics
calculations or functions.
Math Tables/Numberline -
Student uses a calculator,
number chart, arithmetic table,
or manipulatives on the no
calculator sections of the
mathematics test. A student for
which this type of nonstandard
accommodation might be used
would be a student with a
learning disability in
mathematics who, without the use
of a calculator, would not be
able to perform any mathematics
calculations or functions.
Dictionary/Glossary -
Bilingual dictionary: student
uses a bilingual dictionary
(note: Bilingual dictionary
could include a simplified
English dictionary or glossary,
subject area vocabulary list).
|
|
Nebraska
|
Calculator -
Calculation devices. If a
studentís disability affects
mathematics calculation but not
reasoning, a calculator or other
assistive device (e.g., abacus,
arithmetic table, manipulatives,
or number chart) may be used.
Audio/Video Equipment -
Some students also use Closed
Circuit Television (CCTV) to
enlarge print and display
printed material with various
image enhancements on a screen.
Many books have been made into
movies, giving students a visual
and auditory way to access
literature. Videotapes are now
often close-captioned. Captions
are visible when activated by a
decoder . . . Descriptive video
is a descriptive narration of
key visual elements, making
television programs, feature
films, home videos, and other
visual media accessible to
people who are visually
impaired.
Abacus - Calculation
devices. If a studentís
disability affects mathematics
calculation but not reasoning, a
calculator or other assistive
device (e.g., abacus, arithmetic
table, manipulatives, or number
chart) may be used.
Manipulatives -
Calculation devices. If a
studentís disability affects
mathematics calculation but not
reasoning, a calculator or other
assistive device (e.g., abacus,
arithmetic table, manipulatives,
or number chart) may be used.
Adapted Writing Tools -
Use pencil grips and large
pencils.
Visual Organizers -
Visual organizers include graph
paper, highlighters, place
markers, scratch paper, and
templates. Spelling and grammar
devices. The use of a dictionary
may be allowed on assignments
that require an extended
response or essay. Spelling and
grammar can also be checked with
pocket spell checkers.
Assistive Technology -
Assistive technology that can be
used for typing includes
customized keyboards, mouth or
headstick or other pointing
devices, sticky keys, touch
screen, and trackball.
Special Paper - Visual
organizers include graph paper,
highlighters, place markers,
scratch paper, and templates.
Spelling and grammar devices.
The use of a dictionary may be
allowed on assignments that
require an extended response or
essay. Spelling and grammar can
also be checked with pocket
spell checkers.
Math Tables/Numberline -
Calculation devices. If a
studentís disability affects
mathematics calculation but not
reasoning, a calculator or other
assistive device (e.g., abacus,
arithmetic table, manipulatives,
or number chart) may be used.
Dictionary/Glossary -
Spelling and grammar devices.
The use of a dictionary may be
allowed on assignments that
require an extended response or
essay. Spelling and grammar can
also be checked with pocket
spell checkers.
Other - Note takers.
Students may have another
student take notes or use an
electronic note-taking device.
Written notes may be taken by
another student and copied. A
teacher could provide a print
copy of instructions and
assignments. Students could also
be given a detailed outline of
the material to be covered
during the class period and an
outline of material to be
covered (syllabus) at the
beginning of each grading
period. Table indicates
accommodation applied to
assessment as well as
instruction. Talking materials.
Many classroom materials are now
available with auditory
components. These include
calculators, talking clocks,
thermometers, timers, and
voltmeters.
|
|
Nevada
|
Magnification
Equipment - IEP and 504
Accommodations Forms.
Amplification Equipment -
Provide for special acoustics
such as an amplifier for verbal
instructions.
Light/Acoustics - Provide
for special lighting and provide
for special acoustics such as an
amplifier for verbal
instructions.
Calculator -
A calculator, abacus, or
multiplication chart on the CRT
or HSPE in Math and a calculator
on designated sections of the
ITBS/ITED (not permitted on the
Math Computation test or on Part
2 of Math Concepts and
Estimation test).
Templates - A mask or
colored overlay to cover
portions of the test.
Abacus - A calculator,
abacus, or multiplication chart
on the CRT or HSPE in Math.
Adapted Writing Tools -
Use pencils adapted in size or
grip diameter.
Visual Organizers -
Markers to maintain his/her
place.
Math Tables/Numberline -
A calculator, abacus, or
multiplication chart on the CRT
or HSPE in Math.
Dictionary/Glossary -
Never allowed: student using a
bilingual dictionary on the HSPE
in Reading, Math, Science, or
Writing.
|
|
New Hampshire
|
Calculator -
Considered a modification: Using
calculator or manipulatives on
Session 1 of the Mathematics
test or a scientific or graphing
calculator on session 3 of the
Science test.
Templates - Reduction of
visual print by blocking or
other techniques and acetate
shield.
Abacus - Abacus use for
student with severe visual
impairment or blindness.
Manipulatives
- Considered a modification:
Using calculator or
manipulatives on Session 1 of
the Mathematics test.
Dictionary/Glossary -
Word-to-word translation
dictionary, non-electronic with
no definitions (For ELL students
in Math, Science, and Writing
only).
|
|
New Jersey
|
Light/Acoustics
- Providing special lighting.
Calculator - Using large
face calculators (except for
non-calculator section) and
using talking calculators
(except for non-calculator
section).
Templates -
Masking a portion of the test
booklet or answer folder to
eliminate visual distractions or
providing reading windows.
Adaptive/
Special Furniture -
Providing special furniture.
Adapted Writing Tools -
Using a large diameter or
modified special grip No. 2
pencil.
Special Paper
- Using graph paper for math
section and allowing separate
additional continuation pages
for writing tasks. These pages
must be properly marked to link
them to the correct student for
credit.
|
|
New Mexico
|
Magnification
Equipment - Low vision
devices, such as magnifiers.
Amplification Equipment -
Amplification equipment, such as
FM systems.
Calculator - Sharing
calculators in the same session.
Using calculators in Grades 3-7
SBAs. Using calculators with
QWERTY keyboards; attached
electronic pens; printing
attachments; ability to
communicate with raised screens,
and attached cords. Using
calculators in prohibited
sessions (NMHSCE).
Audio/Video Equipment -
Closed circuit TV.
Manipulatives - Use of
additional manipulatives for the
mathematics assessment, such as
number lines, Touch Math and
counting beans.
Adapted Writing Tools -
Use of devices normally used by
students for kinesthetic
assistance (e.g., pencil grips).
Color Overlay - Use of
devices normally used by
students for visual assistance
(e.g., colored overlays).
Math
Tables/Numberline - Use of
arithmetic tables.
Dictionary/Glossary - Use
of a word-to-word translation
dictionary or word list (with no
definitions).
Keyboard - Adaptive
keyboards provided if used in
class. Not mentioned for other
tests.
Other - Word predictor
programs.
|
|
New York
|
Calculator -
Considered a modification
(invalidates test score) if used
on sections measuring
calculation skills
Audio/Video
Equipment - Audio tape of
questions, items, and passages.
Secure Paper to Work Area
- Papers secured to work area
with tape/magnets.
Math Tables/Numberline -
Mathematics tables, considered a
modification (invalidates test
score) if used on sections
measuring calculation skills.
Other - Adapted measuring
devices such as scales,
graduated cylinders,
Braille/large print rulers,
tactile measuring tools, etc.
Grammar-check device, considered
a modification measuring writing
skills.
|
|
North Carolina
|
Calculator -
Use of a calculator on a
calculator inactive portion of a
mathematics test invalidates the
results of that test.
Adapted Writing Tools -
Pencil grips.
Assistive Technology -
Alternative/customized
keyboards, stickie keys, touch
screens, and trackballs may be
used as accommodations unless
use of the AT devices would
invalidate test results. Devices
that read aloud reading
comprehension tests invalidate
test results. Prediction
software, electronic spellers,
spell check and grammar check
utilities invalidate the results
of the writing assessment.
|
|
North Dakota
|
Calculator -
Calculators may not be used in
part 1 of the mathematics test
for grades 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, and
11, but may be used in the
remaining tests, calculators are
not allowed in any part of the
grade 3 NDSA.
Manipulatives -
Manipulatives, including
counting objects, base 10
blocks, number lines, Touch
Math.
Visual Organizers Ė
Masks.
Assistive Technology -
Word predictor programs.
Keyboard - Personal
portable keyboards such as an
AlphaSmart.
Graphic Organizers -
Visual/graphic organizers.
|
|
Ohio
|
Magnification
Equipment - Magnification
device and visual aids.
Calculator - Used to
perform all mathematical
operations, not allowable.
Calculator allowed for all
students grade 6 and above. May
be allowed as accommodation for
some grade 5 students per four
criteria. All Calculators must
meet guidelines of ODE-approved
calculator-see test
administration guidelines.
Specialized calculator (i.e.,
talking, Braille) per IEP
documentation is allowed.
Audio/Video Equipment -
Closed circuit television.
Noise Buffer -
Headphones, ear plugs.
Abacus - Not allowed on
reading passages/selections.
Manipulatives - Student
uses manipulatives to enact
response before writing response
in test booklet and answer
document, allowed. Student
without visual impairments uses
manipulatives to enact response
before writing response in test
booklet and answer document.
Prohibited for math.
Adapted Writing
Tools - Colored pencils,
pencil grip, weighted pencil.
Slant Board/Wedge - Slant
board.
Secure Paper to Work Area
- Tape or magnets to secure
paper to work area, (magnets may
not be used in any way on
science tests.
Visual
Organizers - Filters to
cover parts of test.
Special Paper - Different
paper, graph paper, wide-ruled
paper.
Math Tables/Numberline -
Arithmetic tables, formula
sheet.
Dictionary/Glossary -
Only for students classified as
Limited English Proficiency
(LEP), must be the same
dictionary that is used for
classroom instruction.
Dictionary, thesaurus, students
who are not classified as
Limited English Proficient.
Thesaurus - Dictionaries
or thesauri are not allowed on
reading and writing tests, but
are allowed on mathematics,
social studies, and science
tests.
Keyboard - Word
processor, computer, keyboarding
device, typewriter to key
responses.
Other - List of formulae
or other reference information,
explanation of use of formulae,
not allowable. Formula sheet is
provided for all students at
grade 8 and OGT. Must be
specific formula sheet provided
by state for test
administration, allowable. List
of formulae or other reference
information, not allowable.
Explanation of use of formulae,
not allowable. Weighted lap
object or vest, bead cushion,
vibrating pillow. Reading
guides.
|
|
Oklahoma
|
Abacus -
Students using a Braille test
may be provided with an abacus.
|
|
Oregon
|
Magnification
Equipment - Visual
magnification devices.
Amplification
Equipment - Auditory
amplification devices, hearing
aids.
Light/Acoustics
- Special lighting.
Audio/Video Equipment -
Answers recorded (CD, video).
Adaptive/
Special Furniture - Adaptive
equipment/furniture.
Adapted Writing
Tools - Allow response aids,
e.g. adaptive pencils, track
ball, key guards, and skins.
Secure Paper to
Work Area - Stabilize test
materials/papers, e.g., tape,
magnets, clips, clamps.
Visual
Organizers - Masks/markers
to limit distractions. Use of
masking device while copying
from rough to final.
Color Overlay - Provide
transparent sheets (clear or
tinted) to protect test
materials or to improve focus or
contrast sheeting.
Assistive
Technology - Students using
any assistive technology device
that serves as their primary
communication mode (adaptive
keyboard, word processor, etc.).
Dictionary/Glossary - Use
of math content dictionary for
math assessment only is a
modification. Modifications
change the content or
performance standards of what is
being measured by the test,
knowledge and skills
modifications table. Thesaurus
or dictionary, English or other
language/English. Use of a
thesaurus (English, other
language, or combination
language) or dictionary is
considered a modification on the
knowledge and skills tests.
Modifications change the content
or performance standards of what
is being measured by the test,
knowledge and skills
modifications table. Handbooks
and locally developed handouts
which go beyond word
definitions, usage, or spelling
guides are considered
modifications on the writing
test.
Thesaurus - Thesaurus or
dictionary, English or other
language/English. Upon student
request only. Use of a thesaurus
(English, other language, or
combination language) or
dictionary is considered a
modification on the knowledge
and skills tests. Modifications
change the content or
performance standards of what is
being measured by the test.
Handbooks and locally developed
handouts which go beyond word
definitions, usage, or spelling
guides are considered
modifications on the writing
test.
Graphic Organizers - A
variety of graphic organizers,
without text prompts, may be
made available from which
students may choose.
Other -
Commercially, or locally
published materials that only
include word definitions, and
spelling list (with or without
spelling rules) and that do not
incorporate instructional or
learning strategies for guidance
in the writing process,
including a contractions list
(in Braille, English, or other
languages) that provides a
spelling of the contracted
symbol(s), not definitions. The
abbreviations or contractions in
one language would be spelled
out in the same language.
Correction fluid, white-out
correction tape. Electronic
language translation devices
used to translate into languages
not provided by the state is
considered a modification.
Modifications change the content
or performance standards of what
is being measured by the test.
|
|
Pennsylvania
|
Calculator -
Not permitted in the
non-calculator section of the
mathematics test.
Templates - Masking
allowed.
Audio/Video Equipment -
Closed circuit television.
Abacus - If a studentís
disability affects mathematics
calculation but not reasoning, a
calculation but not reasoning, a
calculator, number line, or
Cranmer abacus may be used.
Manipulatives - Use of
any manipulative other than
described in these guidelines
during the PSSA.
Special Paper - Large
lined paper, widely spaced
paper, scratch.
Math Tables/Numberline -
Number lines.
Graphic Organizers -
Graphic organizers help students
arrange information into
patterns in order to organize
their work and stay focused on
the content. Graphic organizers
are especially helpful for
writing reports and essays. Use
of pre-printed graphic organizer
for the PSSA test prohibited.
Other -
Reference materials. The only
reference material allowed is a
copy of the original formula
sheet and scoring guidelines
provided in the mathematics,
reading, and writing handbooks
posted on the PDE website at
www.pde.state.pa.us and in the
handbook for assessment
coordinators and administrators.
The only exception is for
students who have a documented
need for number lines specified
in an IEP, 504 Service plan, or
ELL program.
|
|
Rhode Island
|
Light/Acoustics
- Special acoustics. Special
lighting.
Calculator - Using a
calculator on session 1 of the
math test is considered a
modification and invalidates the
session it was used in and no
credit will be given.
Abacus - For student with
severe visual impairment or
blindness (mathematics-all
sessions). If used by a student
without a visual impairment on
session 1 of the math test is
considered a modification with
implications for scoring.
Manipulatives - Using
manipulatives on session 1 of
the math test is considered a
modification and invalidates the
session it was used in and no
credit will be given.
Color Overlay - Acetate
shield.
Assistive Technology -
Student dictates constructed
responses using assistive
technology (reading and math
only).
Dictionary/Glossary -
Word-to-word translation
dictionary, non-electronic with
no definitions (For ELL students
in Mathematics and Writing
only).
|
|
South Carolina
|
Magnification
Equipment - E.g.,
closed-circuit television,
optical low-vision aid.
Amplification
Equipment - Amplification
equipment or special acoustics
(e.g., auditory trainer, sound
field system.
Light/Acoustics
- Special lighting.
Calculator - Considered a
modification with implications
for scoring on the PACT. Allowed
for all students without
implications for scoring on the
math section of the HSAP, the
Algebra I/Math for the
Technologies 2 and Physical
Science end-of-course exams.
Templates -
Pointer, non-calibrated ruler,
template, or other devices to
assist in maintaining visual
attention.
Audio/Video
Equipment - Television
monitor and VCR.
Manipulatives
- Certain manipulatives may be
used as an accommodation
depending on the subject area
and the purpose of the tactile
device. Generally, if the
manipulative is used for
counting, it is considered an
accommodation.
Adapted Writing
Tools - Pencil grips or
large-diameter pencil.
Assistive
Technology - Special
adaptive/assistive devices
(e.g., adaptive keyboard, voice
synthesizer).
Special Paper
- Respond on separate paper.
Math Tables/Numberline -
Number line. If the student
creates his or her own number
line or the TA gives the student
a blank number line, this is an
accommodation. If the TA gives
the student a completed number
line, it is a modification with
implications for scoring.
Dictionary/Glossary - All
students may use a dictionary on
the extended-response portion of
the English Language Arts test
of the HSAP.
Thesaurus - All students
may use a thesaurus during the
extended-response portion of the
English Language Arts test of
the HSAP.
Keyboard - Adaptive
keyboard.
|
|
South Dakota
|
Light/Acoustics
- Special lighting.
Calculator - Any
four-function, scientific, or
graphing calculator is allowed
on the DSTEP Math and Science
test unless on the prohibited
list. Prohibited calculators:
pocket organizers, handheld or
laptop computers, electronic
writing pads or pen-input
devices, calculators built into
cellular phones or other
wireless communication devices,
calculators with a typewriter
keypad (keys in QWERTY format),
and calculators with built-in
Computer Algebra Systems.
Talking calculators provided;
the student is tested
individually or with the use of
headphones. Students in grades
2-7 should not be allowed to use
a calculator while taking the
Math Performance Series exam.
Abacus - For visually
impaired students.
Adapted Writing Tools -
Large-diameter pencil, pencil
grip, special pencil or pen.
Visual Organizers -
Visual organizers (i.e. masks,
markers, rulers).
Assistive Technology -
Assistive or augmentative
technology, contact the SD DOE
for approval.
Dictionary/Glossary -
Translation dictionaries, word
lists, glossaries.
|
|
Tennessee
|
Calculator -
Calculator/mathematics tables
(only addition, subtraction,
multiplication, and division).
Calculators or mathematics
tables may be used for test
items, and are permitted on all
TCAP Achievement tests and the
Algebra I Gateway Test.
Mathematics tables include only
tables for the whole number
operations - addition,
subtraction, multiplication, and
division.
Manipulatives - IEP or
504 Service Plan goal in
mathematics where manipulatives
are consistently used.
Visual
Organizers - Masks.
Assistive Technology -
IEP or 504 Service Plan where
technology is used consistently
throughout educational program
(grammar, spell-check, and
thesaurus not allowed).
Math Tables/Numberline -
Calculator/mathematics tables
(only addition, subtraction,
multiplication, and division).
Calculators or mathematics
tables may be used for test
items, and are permitted on all
TCAP Achievement tests and the
Algebra I Gateway Test.
Mathematics tables include only
tables for the whole number
operations: addition,
subtraction, multiplication, and
division.
Dictionary/Glossary -
Bilingual dictionary. Not
allowed on the language arts,
reading, spelling, word analysis
nor vocabulary subtests of the
achievement tests. Not allowed
on the writing assessment, nor
the English I or II subtests of
the EOC/Gateway.
Other - Pointers.
|
|
Texas
|
Calculator -
For TAKS (accommodated) math
tests at grades 3-6 . . . TAKS-M
math if the above conditions are
met. Graphing calculators must
be provided to all students
taking TAKS, including TAKS
(Accommodated), and the TAKS-M
math tests at grades 9-11 and
exit level. Four-function,
scientific, or graphing
calculators must be provided to
students taking TAKS, including
TAKS (accommodated), and the
TAKS-M math tests at grades 9-11
and exit level. These are not
accommodations, but a part of
standard test administration
procedures required for all
these tests. Interactive
software, text readers, audio
tapes, adaptive listening
devices, and talking calculator,
allowed on TAKS-Alt.
Audio/Video Equipment -
Video clips, allowed on
TAKS-Alt.
Noise Buffer - Allowed on
all tests.
Adaptive/Special Furniture
- Standers, special chairs,
support cushions, slat or
vertical boards, adaptive tables
and modified keyboards, touch
screens, joysticks, modified
mouse, head mouse, allowed on
the TAKS-Alt.
Manipulatives - The
following manipulatives are
approved for use on TAKS
(accommodated) without
submission of an Accommodation
Request Form: figures, coins,
clocks with gears, base-ten
blocks, non-labeled fraction
pieces, and various types of
counters (e.g., beans, blocks,
etc.). Manipulatives that serve
as a tool and not a source of
direct answers are allowed on
TAKS-M without the submission of
an Accommodation Request Form.
Magnetic or manipulative letters
allowed on TAKS-Alt.
Adapted Writing
Toolsg
equipment, pencil grips, tactile
paper with raised lines, allowed
on TAKS-Alt.
Slant
Board/Wedge - Allowed on
TAKS-Alt.
Visual Organizers - A
student may use a blank place
marker on the test and answer
document. These place markers
may include index cards,
adhesive notes, etc.
|
|
Texass
(Contíd)
|
Color Overlay
Ė Color coding and colored
overlays allowed on TAKS-Alt.
Assistive Technology -
Interactive software, text
readers, audio tapes, adaptive
listening devices, computer
accessible equipment, activation
of switches to record answers,
word prediction software,
switches, and pictures to text
software, allowed on TAKS-Alt.
Special Paper - Scratch
paper (blank, lined, or graph
paper). Heat sensitive paper
allowed on TAKS-Alt.
Dictionary/Glossary -
Allowed on the entire grade 9
reading test, the written
composition section of the grade
7 writing test, the written
composition and reading sections
of the grades 10 and 11 exit
level ELA tests, and the LAT
administration of the grade 10
ELA test. Audio tapes under
verbal access category,
reference materials and picture
dictionaries, allowed on
TAKS-Alt.
Graphic Organizers -
Graphic organizers that contain
any words, numbers, or symbols
are considered supplemental
aids. An Accommodation Request
Form is not required for the use
of blank graphic organizers. For
the TELPAS reading, decisions
regarding blank graphic
organizers should be made in
accordance with whether the
student will also be assessed
with TAKS (accommodated) or
TAKS-M. Graphic organizers,
charts, maps, outlines,
timelines, concept maps allowed
on the TAKS-alt.
Other - Positioning
device under physical access
category allowed for TAKS-Alt,
page 37. Light box and laser
lights and pens, under visual
access in Presentation
Supports/Materials for TAKS-Alt.
|
|
|
Magnification
Equipment Ė Eyeglass-mounted
magnifiers, free-standing or
handheld magnifiers, enlarged
computer monitors, computers
with screen enlargement
programs, and closed-circuit
televisions (CCTV).
Calculator -
May be used on CRT
non-calculator section as well
as IBSCT. Must be Texas
Instrument 89 or lower.
Assistive
Technology - Talking
materials, including
calculators, talking clocks,
thermometers, timers, and
voltmeters. Screen reader, not
allowed on language arts subtest
of the UBSCT, the UALPA, or on
the reading and vocabulary
subtests of the Iowa Tests.
Passages, questions, and options
on the CRT secondary language
arts test may not be converted
to speech. Math and science
passages, questions and options
on the CRT may be converted to
speech.
Special Paper - Graph and
scratch paper.
Dictionary/Glossary -
Bilingual word lists and
definitions or explanations are
not allowed. CRT and Iowa basic
skills, bilingual word list not
provided or allowed. UBSCT,
allowed. Only bilingual word
lists provided by the USOE
allowed.
Other - Translated
formulas, not allowed on the
Iowa Tests.
|
|
Vermont
|
Calculator -
Using a calculator on session 1
of the math test is considered a
modification and invalidates the
session it was used in and no
credit will be given.
Abacus - Abacus use for
students with severe visual
impairment or blindness. Use of
an abacus on session 1 of the
math test for students without
severe visual impairment or
blindness is considered a
modification and invalidates the
session it was used in and no
credit will be given.
Manipulatives
- Using manipulatives on session
1 of the math test is considered
a modification and invalidates
the session it was used in and
no credit will be given.
Color Overlay - Acetate
shield.
Assistive Technology -
Student dictates constructed
responses using assistive
technology (reading and math
only).
|
|
Virginia
|
Magnification
Equipment - Magnifying
glass.
Amplification Equipment -
Amplification equipment (e.g.,
hearing aid or auditory
trainer).
Light/Acoustics - Special
lighting.
Calculator - Allowed on
the grade 3 mathematics test and
on the computation section of
the grades 4, 5, 6, and 7
mathematics test (calculators
are not routinely supplied to
all students). Use of calculator
with additional functions to
those routinely supplied to all
students.
Templates - Templates.
Masks or markers to maintain
place.
Audio/Video Equipment -
Audio-tape version of test
items. Allowed for all students
with an IEP or 504 Plan on the
math, science, history/social
science, and writing
assessments. Only allowed on the
reading test for students with a
visual impairment, including
blindness, and those students
with a specific disability that
severely limits or prevents them
from decoding text at any level
of difficulty. If the audio
accommodation is used on the
reading test for students with
disabilities who have not been
determined as eligible by the
school division according to the
criteria stated above, it will
be considered a non-standard
accommodation.
Adapted Writing Tools -
Large diameter/special grip
pencil.
Assistive Technology -
Word prediction/selection
software is allowed on the
writing prompt component of the
SOL writing assessments only.
Math
Tables/Numberline -
Arithmetic tables (only if test
allows calculator). Allowed on
grade 3 mathematics test and on
the computation section of the
grades 4, 5, 6, and 7
mathematics tests.
Dictionary/Glossary -
Spelling dictionary.
|
|
Washington
|
Magnification
Equipment - Provide low
vision devices such as
magnifiers, closed circuit TV
(CCTV), and other tools familiar
to students.
Calculator -
Student uses calculator on
mathematics test sections (High
school only).
Templates - Use tools to
adjust color backgrounds like
overlays, student uses a strip
of heavy paper to assist in
tracking.
Audio/Video
Equipment - Provide low
vision devices such as
magnifiers, closed circuit TV
(CCTV), and other tools familiar
to students.
Adaptive/Special Furniture
- Decision to provide
accommodation must be made on an
individual basis and must not be
used for the first time on state
tests.
Abacus - Student uses an
abacus and other manipulatives
for students on the tools day of
the mathematics test.
Manipulatives
- Student uses an abacus and
other manipulatives for students
on the tools day of the
mathematics test.
Adapted Writing
Tools - Student uses a No. 2
pencil adapted in size or grip.
Assistive Technology -
Student dictates responses via
an assistive communication
device, pointing, sign language,
or speech. Scribes record
studentsí responses verbatim
into a regular test booklet.
Special Paper - Student
uses visual/graphic organizers
such as graph paper, place
markers, scratch paper and
templates, and semantic mapping
software.
Math Tables/Numberline -
Arithmetic table and number
chart.
Dictionary/Glossary -
Student uses a glossary during
mathematics and science tests
(if provided by OSPI). Student
uses spelling and grammar
devices such as electronic
dictionaries, thesauruses,
and/or spelling devices on any
test for which the Section 504
plan or IEP stipulates the use
(writing only).
Thesaurus - Student uses
spelling and grammar devices
such as electronic dictionaries,
thesauruses, or spelling devices
on any test for which the
Section 504 plan or IEP
stipulates the use (writing
only).
Graphic Organizers -
Student uses visual/graphic
organizers such as graph paper,
place markers, scratch paper and
templates, and semantic mapping
software. No visual/graphic
organizers or semantic mapping
software can be used for the
state assessments.
Other - Whisper phone.
Provide headphones if the
student plays audio-recordings
or uses speech-to-text software.
|
|
West Virginia
|
Magnification
Equipment Ė On the online
writing assessment, use a
magnifying screen cover when it
is the studentís typical mode of
accessing written material.
Calculator - Calculators
may be used on all sessions of
the mathematics and science
tests EXCEPT session 1, part 1,
of the mathematics test.
Calculators allowed on all
sections of the APTA math test.
Calculators may be used on the
EXPLORE Math test.
Templates -
Template (i.e., typoscope),
graph paper, place markers.
Abacus - Abacus for
computations and note taking
while reading and responding to
questions is permissible in all
content areas. Use an abacus on
all parts of the mathematics
test for blind students. Abacus
allowed on all sessions of the
APTA math test.
Color Overlay - Color
visual overlays.
Assistive Technology -
Use a computer, typewriter, or
other assistive technology
device to respond.
Special Paper
- Scratch and graph paper. Not
allowed on ACT PLAN.
Math Tables/Numberline -
Arithmetic tables allowed for
all students taking the APTA.
Allowed on all sessions of the
APTA math test.
Dictionary/Glossary - Use an
electronic translator or
sign-dictionary to respond. Use
an electronic translator or
bilingual dictionary to present
directions, stimulus material,
questions and/or answer choices
verbatim for the math, science,
social studies, and both writing
assessments. May only be used to
present directions for the
reading/language arts test. Use
an electronic translator or
bilingual dictionary to respond.
For LEP students on APTA.
Allowed on ACT PLAN.
Other - On EXPLORE: Use a
secure electronic Braille note
taker for directions and test
stimulus materials. Line guide.
|
|
Wisconsin
|
Calculator -
Students in grade 3 or 4 uses a
calculator or multiplication
table on all sections of the
Mathematics test except sections
measuring computation skills.
Math Tables/Numberline -
Students in grade 3 or 4 uses a
calculator or multiplication
table on all sections of the
Mathematics test except sections
measuring computation skills.
Dictionary/Glossary -
Provide bilingual word lists or
word-to-word translations.
Graphic Organizers -
Graphic organizer (with no
text).
Other - Use page markers
(e.g., bookmark or straight
edge) to maintain place.
|
|
Wyoming
|
Amplification
Equipment - Use of auditory
amplification devices, such as
hearing aids/noise buffers.
Light/Acoustics - Provide
special lighting.
Calculator - If a
studentís disability affects
mathematics calculation but not
reasoning, a calculator or other
assistive devise (e.g., abacus,
arithmetic table, manipulatives,
or number chart) may be used.
Calculators may be adapted with
large keys or voice output
(talking calculators).
Templates -
Uses templates to reduce glare
or enhance text.
Audio/Video Equipment -
Closed Circuit Television.
Noise Buffer - Use of
auditory amplification devices,
such as hearing aids/noise
buffers.
Abacus - If a studentís
disability affects mathematics
calculation but not reasoning, a
calculator or other assistive
devise (e.g., abacus, arithmetic
table, manipulatives, or number
chart) may be used. Calculators
may be adapted with large keys
or voice output (talking
calculators). Listed as
nonstandard and instruction
only.
Manipulatives - If a
studentís disability affects
mathematics calculation but not
reasoning, a calculator or other
assistive devise (e.g., abacus,
arithmetic table, manipulatives,
or number chart) may be used.
Calculators may be adapted with
large keys or voice output
(talking calculators). Listed as
nonstandard and instruction
only.
Visual Organizers -
Visual organizers include graph
paper, highlighters, place
markers, scratch paper, and
templates.
Color Overlay - Color
overlays to reduce glare or
enhance text.
Special Paper - Visual
organizers include graph paper,
highlighters, place markers,
scratch paper, and templates.
Math Tables/Numberline -
If a studentís disability
affects mathematics calculation
but not reasoning, a calculator
or other assistive devise (e.g.,
abacus, arithmetic table,
manipulatives, or number chart)
may be used. Calculators may be
adapted with large keys or voice
output (talking calculators).
Listed as nonstandard and
instruction only.
Dictionary/Glossary -
Student uses a bilingual
dictionary provided by the
school.
Other - Use of a computer
monitor screen cover.
|
Table B.22A: Response
Accommodations (1 out of 2)
A = Allowed, AC
= Allowed in Certain Circumstances, AI =
Allowed with Implications for Scoring, P
= Prohibited
AS = All Subjects, R = Reading/Language
Arts, M = Math, S = Science, W =
Writing, SS = Social Studies
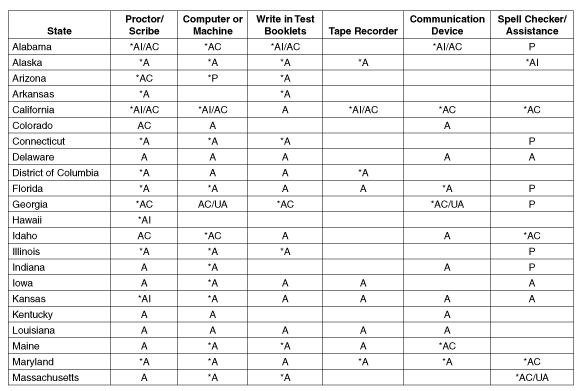
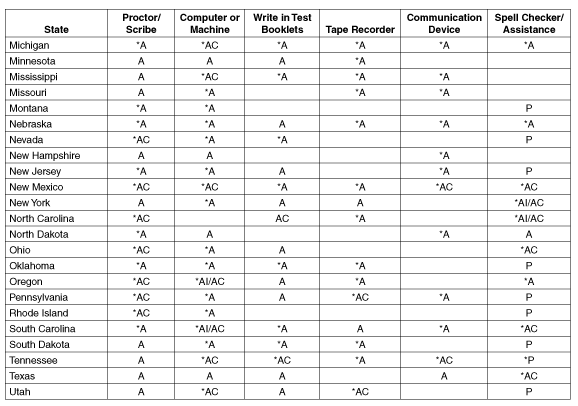
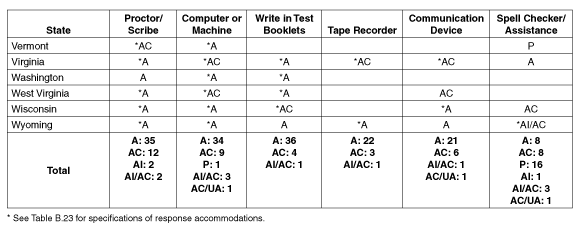
Table B.22B: Response
Accommodations (2 out of 2)
A = Allowed, AC
= Allowed in Certain Circumstances, AI =
Allowed with Implications for Scoring, P
= Prohibited
AS = All Subjects, R = Reading/Language
Arts, M = Math, S = Science, W =
Writing, SS = Social Studies
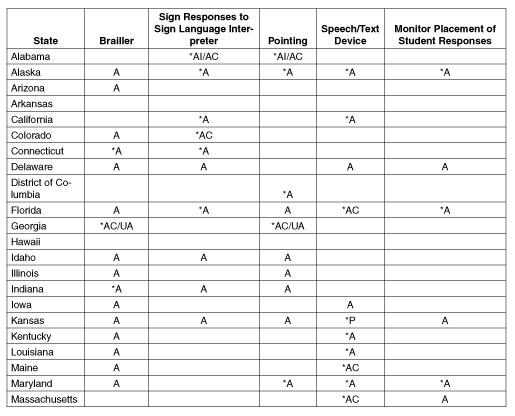
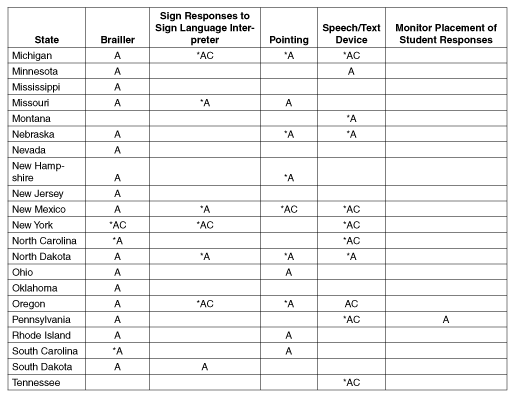
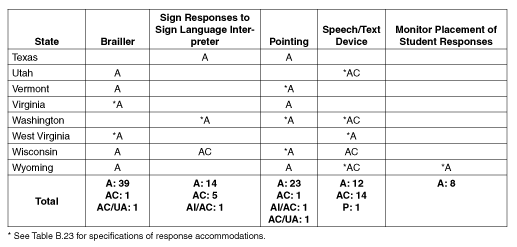
Table B.23: Specifications
and Descriptions of ďCertain
Circumstances,Ē ďImplications for
Scoring,Ē ďUnique Aggregated,Ē and
ďOtherĒ Response Accommodations
|
Alabama
|
Proctor/Scribe
- Allowed only on Stanford 10
(considered non-standard),
Alabama Reading and Mathematics
Test (ARMT), Alabama Science
Assessment (ASA), Alabama
Alternate Assessment (AAA), and
Alabama High School Graduation
Exam (AHSGE). Prohibited on all
other tests.
Computer or Machine -
Allowed on the Alabama Direct
Assessment of Writing (ADAW) if
spell/grammar checker and
dictionary programs are turned
off. Allowed on the Alabama High
School Graduation Exam (AHSGE)
and the Alabama Alternate
Assessment (AAA). Prohibited on
all other tests.
Write in Test Booklets -
Allowed only on Stanford 10
(considered non-standard),
Alabama Reading and Mathematics
Test (ARMT), Alabama Science
Assessment (ASA), and Alabama
High School Graduation Exam
(AHSGE). Prohibited on all other
tests.
Communication Device -
Allowed only on Stanford 10
(considered non-standard),
Alabama Reading and Mathematics
Test (ARMT), Alabama Science
Assessment (ASA), and Alabama
Alternate Assessment (AAA).
Prohibited on all other tests.
Sign Responses to Sign
Language Interpreter -
Allowed only on Stanford 10
(considered non-standard),
Alabama Reading and Mathematics
Test (ARMT), Alabama Science
Assessment (ASA), and Alabama
Alternate Assessment (AAA).
Prohibited on all other tests.
Pointing - Allowed only
on Stanford 10 (considered
non-standard), Alabama Reading
and Mathematics Test (ARMT),
Alabama Science Assessment
(ASA), and Alabama Alternate
Assessment (AAA). Prohibited on
all other tests.
|
|
Alaska
|
Proctor/Scribe
- Using typewriter or computer
without spell or grammar
checker.
Computer or Machine -
Using typewriter or computer
without spell or grammar
checker.
Write in Test Booklets -
Allowing students to mark
responses in test booklet if
test employs a separate answer
sheet. (Student responses must
be transcribed by the test
administrator/proctor according
to procedures detailed in the
test administration directions.)
Tape Recorder - Allowing
student to tape response for
later verbatim transcription.
Spell Checker/Assistance
- Spelling and grammar can also
be checked with pocket spell
checkers... Pg. 39
Accommodations Manual.
Considered nonstandard: use of
the accommodation on state
assessments will result in a
nonscorable (invalid) assessment
Sign Responses
to Sign Language Interpreterllowing alternative responses
such as oral, sign, typed, and
pointing.
Pointing - Allowing
alternative responses such as
oral, sign, typed, and pointing.
Speech/Text Device -
Speech to text conversion or
voice recognition allows
students to use their voices as
input devices.
Monitor Placement of Student
Responses - Providing
detailed monitoring to ensure
student marks responses in
correct answer area.
Other - Providing student
with additional room for writing
response. (Student responses
must be transcribed by the test
administrator/proctor according
to procedures detailed in the
test administration directions.)
|
|
Arizona
|
Proctor/Scribe
- It is allowed as a standard
accommodation, for all students
if they have an injury that
makes it difficult to
participate. They may record or
dictate their responses to
multiple choice questions to a
scribe. A student may record or
dictate multiple choice
responses to a scribe. However,
it is not allowed for the
writing test.
Computer or Machine -
Electronic devices, including,
but not limited to, computers,
cell phones, digital watches,
personal digital assistants, and
portable music players are
prohibited during AIMS testing.
Write in Test Booklets -
A student with an injury, such
as a broken hand or arm, that
would make it difficult to
participate in state assessments
may receive the following
standard accommodations as
needed.
|
|
Arkansas
|
Proctor/Scribe
- A teacher records the
studentís verbal responses. This
means that the teacher writes
the studentís verbal responses
into his/her answer document.
This must be done in an
individual setting. This
accommodation is difficult on
the Writing portions of the
Augmented Benchmark and Grade 11
Literacy Exams. Because the
writing is scored for mechanics
and usage, the student must
spell each word and must provide
each mark of capitalization and
punctuation as he/she dictates
his/her response.
Write in Test Booklets -
Student must write all answers
in the test booklet. This must
be done in an individual
setting. The student may not
have extra paper. The teacher is
to copy the studentís answers
into the answer document exactly
as the student wrote them. This
accommodation is used with Large
Print and Braille test booklets.
|
|
California
|
Proctor/Scribe
- Allowed as an accommodation on
selected-response items and
essay questions if the student
provides all spelling and
language conventions. If scribe
provides spelling, grammar, and
language conventions for essay
responses, considered a
modification with implications
for scoring on STAR, CAHSEE, and
CELDT tests.
Computer or Machine -
Word processing software is
allowed as an accommodation for
essay responses if spell and
grammar check tools are turned
off. If spelling and grammar
check tools are on, it is
considered a modification with
implications for scoring on
STAR, CAHSEE and CELDT tests.
Tape Recorder - Allowed
as an accommodation on essay
questions if the student
provides all spelling and
language conventions. If scribe
provides spelling, grammar, and
language conventions for essay
responses, considered a
modification with implications
for scoring on STAR, CAHSEE, and
CELDT tests.
Communication Device -
Augmentative communication
device, allowed only on CAPA
(Alt. assessment).
Spell Checker/Assistance
- Word processing software with
spell and grammar check tools
enabled on the essay responses
writing portion of test.
Considered modification for
STAR, CAHSEE and CELDT for
eligible students.
Sign Responses to Sign
Language Interpreter -
Eligible students shall be
permitted to take the
examination/test with
accommodations if specified in
the eligible studentís IEP or
Section 504 Plan for use on the
examination, standardized
testing, or for use during
classroom instruction and
assessment.
Sign Responses
to Sign Language Interpreter
- Eligible students shall be
permitted to take the
examination/test with
accommodations if specified in
the eligible studentís IEP or
Section 504 Plan for use on the
examination, standardized
testing, or for use during
classroom instruction and
assessment. Only allowed if
student provides all spelling
and language conventions.
Speech/Text
Device - Allowed only if
student provides all spelling
and language conventions.
Other - Allow nonverbal
students to respond with
gestures, movements, or
vocalization in place of speech.
When appropriate, accept eye
gaze as a way of indicating
response. Allowed only on CAPA
(Alt. assessment).
|
|
Colorado
|
Sign Responses
to Sign Language Interpreter
- Use of signing to respond to a
scribe
Other - Eye Gaze only
allowed on alternate assessment.
|
|
Connecticut
|
Proctor/Scribe
- Bubblers. School staff may
bubble student verbal and
nonverbal (pointing, gesturing)
responses during testing to
multiple-choice and grid-in
items ONLY. For CAPT and CMT,
Bubblers can only be used for
multiple choice/grid-in items,
and not for open ended/extended
response items.
Computer or Machine -
Word processor. Students may use
a word processor without using
spell check or grammar check to
complete open-ended or extended
response items.
Write in Test Booklets -
All students are allowed to make
notes in the margins of their
test booklets. Students may
respond to multiple choice and
grid-in items in their Large
Print test booklet. Students may
respond to the open-ended items
in their large Print test
booklet. They may also type
their responses without using
spell check and grammar check
capabilities.
Brailler - Blind students
may record their responses using
Braille onto a separate sheet of
paper or use a word processor
without using spell check and
grammar check capabilities.
Students may not dictate their
responses to open-ended or
extended response items.
Sign Responses to Sign
Language Interpreter - Deaf
and hard of hearing students may
sign responses to
multiple-choice and griddable
items only. This is for students
for whom circling answers in the
test booklet is not a sufficient
accommodation and must be
administered in an alternate
setting.
Other - If necessary,
students may circle
multiple-choice answers in their
test booklet; however they must
avoid marking the bubbles on CMT
test booklets.
|
|
Delaware
|
Other -
Student responds to the test by
writing responses in Spanish.
Only allowed for the first draft
of the writing test.
|
|
District of
Columbia
|
Proctor/Scribe
- Oral response to tests. A
student dictates to examiner
responses to constructed
response items. Dictation may be
transcribed later, but it may
not be edited by anyone other
than the student.
Tape Recorder - Student
responds to constructed-response
items on audio tape for later
verbatim transcription.
Pointing - Students
indicate answers to
multiple-choice questions by
pointing or other method.
|
|
Florida
|
Proctor/Scribe
- for FCAT writing + (essay),
punctuation must be indicated
and unfamiliar words must be
spelled by the student.
Computer or Machine -
spell and grammar check must be
inactive. Also, computerized
version of test (may provide
visual /auditory adaptations).
Communication
Device - examples include
those from the Prentke Romich
Company (Pathfinder, Vanguard,
or Vantage) and DynaVox Systems
(DV4 or MT4).
Sign Responses to Sign
Language Interpreter - for
FCAT writing + (essay),
punctuation must be indicated
and unfamiliar words must be
spelled by the student.
Speech/Text Device -
text-to-speech technology to
communicate directions and test
items other than reading
passages and items;
text-to-speech software for
passages and items testing
reading skills is not allowed;
students may use speech-to-text
technology to indicate answers;
for speech-to-text technology,
the spell check and grammar
check must be inactive.
Monitor Placement of Student
Responses - students may be
monitored periodically by the
test proctor to ensure that the
answers are marked in the proper
space for the item.
|
|
Georgia
|
Proctor/Scribe
- Not allowed on the speaking
portion of ACCESS for ELLs.
Allowed as a standard
accommodation on all other
tests.
Write in Test
Booklets - Not allowed on
the Georgia Kindergarten
Inventory of Developing Skills
(GKIDS), the Writing test, or
the speaking portion of ACCESS
for ELLs. Allowed as a standard
accommodation on all other
tests.
Communication
Device - Grammar and spell
check devices must be disabled.
Considered nonstandard on the
Norm-Referenced Test (NRT),
standard on all other tests.
Brailler - Nonstandard on
NRT. Not allowed on ACCESS.
Standard on all other tests.
Pointing - Not allowed on
the Writing test or the speaking
portion of ACCESS for ELLs.
Considered nonstandard on the
Norm-Referenced Test (NRT).
Allowed as a standard
accommodation on all other
tests.
Other - Verbal responses
in English only. Not allowed on
the Writing test or the writing
portion of ACCESS for ELLS.
Considered nonstandard on the
Norm-Referenced Test (NRT).
Allowed as a standard
accommodation on all other
tests.
|
|
Hawaii
|
Proctor/Scribe
- Having a scribe who meets the
Test Administrator requirements
on page 40 bubble and write
responses for a student in an
individual setting only.
Criterion-referenced and
non-comparable separate national
norm-referenced scores will be
provided.
Other - Circle
multiple-choice responses in
test booklets instead of
darkening bubbles in response
booklet (gr.4-8, 10), Circling
own multiple choice responses
rather than darkening bubbles
directly in test booklets
(gr.3), p.27.
|
|
Idaho
|
Computer or
Machine - Spell checker not
allowed if spelling is being
tested. Type on or speak to a
word processor.
Spell Checker/Assistance
- not allowed if spelling is
being tested; excludes mechanics
on written composition. Use
spelling and grammar assistive
device (not when assessing
writing mechanics).
Other - Wider lines or
margins.
Other - Reading answer
choices that actually give the
student the correct response.
|
|
Illinois
|
Proctor/Scribe
- Respond orally to a test
administrator IL Board of Ed.
More guidance on scribes for
students with IEPs or 504s are
given. Day1 ACT writing test,
may dictate responses to be
transcribed to standard answer
folder.
Computer or Machine -
Word processor. Spell-check,
grammar check, word prediction
and/or text organization
features must be disabled.)
Employs an alternative response
mode (via computer, grammar
check must be disabled).
Write in Test Booklets -
Students may mark their answers
on the test itself. Students may
underline with a pencil or pen
words, phrases, or sentences in
the test.
Other - IL
Board of Ed. Students write
answers on large paper or
large-spaced paper.
|
|
Indiana
|
Computer or
Machine - no access to spell
check or grammar check.
Brailler - no access to
spell check or grammar check
Other - Student responds
in a language other than
English, response is then
transcribed into English for
scoring purposes.
Other - student is
allowed to circle the answers to
questions rather than bubble
them; answers are then bubbled
in by another.
Other -
student uses an answer sheet
which has been enlarged.
|
|
Iowa
|
Computer or
Machine - Computer with Word
Processing Program
|
|
Kansas
|
Proctor/Scribe
- Express response to a scribe
through speech. When using this
accommodation, the student
should give the answer choice
they select either orally or by
signing to the scribe.
Computer or Machine -
Type on or speak to word
processor. Spelling and grammar
assistive devices (e.g.,
electronic spelling device,
spell-check on computer).
Speech/Text Device - A
screen reader is not allowed on
any Kansas State Assessment.
Only human readers may provide
the read-aloud accommodation for
the Kansas State Assessments.
Other -
Augmentative devices for single
or multiple messages
|
|
Kentucky
|
Speech/Text
Device - text-talk
converters; speech synthesizer;
speech recognition software
|
|
Louisiana
|
Speech/Text
Device - speech synthesizer;
electronic reader
|
|
Maine
|
Computer or
Machine - Word processor.
Write in Test Booklets -
Using side-by-side placement of
two test booklets.
Communication Device -
Assistive Technology that is
part of the studentís
communication system.
Communication Device -
technology may not be used to
read the reading passages for
the student.
Speech/Text Device - e.g.
Dynaboxes; may not be used for
the writing session.
|
|
Maryland
|
Proctor/Scribe
- As scribe is someone who
writes down what a student
dictates by an assistive
communication device, pointing,
communication by the student via
interpretation, or speech.
Computer or Machine -
Electronic note-takers and word
processors: Students may use an
electronic device to create
written responses or for
note-taking.
Tape Recorder - Tape
recorder: A student uses a tape
recorder to record class work or
test responses rather than
writing on paper.
Communication Device - As
scribe is someone who writes
down what a student dictates by
an assistive communication
device, pointing, communication
by the student via
interpretation, or speech.
Spell Checker/Assistance
- Spelling and grammar devices:
The use of a dictionary may be
allowed on assignments that
require an extended response or
essay. Spelling and grammar can
also be checked with pocket
spellcheckers. Spelling and
grammar devices are not
permitted to be used on the
English high school assessment.
Pointing - As scribe is
someone who writes down what a
student dictates by an assistive
communication device, pointing,
communication by the student via
interpretation, or speech.
Speech/Text Device -
Speech-to-text conversion or
voice recognition allows a
student to use their voice as an
input device. Pg. 5-10
Monitor Placement of Student
Responses - Monitor test
response: monitor placement of
student responses on the answer
sheet.
|
|
Massachusetts
|
Computer or
Machine - Typed response.
The student uses a word
processor, Alpha-Smart, or
similar electronic keyboard to
type the ELA Composition,
answers to open-response
questions, or answers to
short-answer questions on any
MCAS test.
Write in Test
Booklets - Answers recorded
in test booklet: the student
records answers directly in the
test booklet or uses special
paper for drafts or computation
(e.g., graph paper).
Spell
Checker/Assistance - Use of
a spell- or grammar-checking
function or word-prediction
software for the ELA composition
test is considered a nonstandard
accommodation.
Speech/Text
Device - student may use an
electronic text reader for the
ELA composition writing prompt,
or the mathematics and/or
science and
technology/engineering tests;
use of an electronic text reader
on the ELA reading comprehension
test is considered a
non-standard accommodation;
student may use a speech-to-text
conversion device to record
responses on all tests except
for ELA composition.
|
|
Michigan
|
Proctor/Scribe
- Use of a scribe for
constructed response items
(student must indicate
punctuation and spell all key
words. Use of a scribe for
constructed response items
(student must indicate
punctuation, format and spell
all key words) for ELA
assessments.
Computer or Machine - Use
of computer or word processor
with spell check, thesaurus, and
grammar check disabled for ELA
assessment
Write in Test
Booklets - Student points to
answers or writes directly in
assessment booklet (transferred
to answer document by teacher).
Tape Recorder
- Student dictates responses
into a tape recorder and teacher
transcribes response exactly as
dictated for mathematics,
science, and social studies
assessments.
Communication Device -
Use of augmentative
communication devices. Pg. 10
Assessment Accommodation Summary
Table
Spell Checker/Assistance
- Use of computer or word
processor with spell check,
thesaurus, and grammar check NOT
disabled for Mathematics,
science and social studies.
Sign Responses to Sign
Language Interpreter -
Respond in sign language for
mathematics, science and social
studies assessments.
Pointing -
Student points to answers or
writes directly in assessment
booklet (transferred to answer
document by teacher).
Speech/Text Device - Use
of speech to text word processor
for responses for mathematics,
science and social studies.
Other -
Responding in the studentís
native language to the
constructed response items on
assessments.
|
|
Minnesota
|
Tape Recorder
- Tape recorders may be used by
student to record and edit
answers of unable to mark a
scannable answer book.
Other - Large print
answer books.
|
|
Mississippi
|
Computer or
Machine - Typewriter or word
processor (without
grammar/syntax checker, with OR
without word
completion/prediction feature
activated).
Write in Test Booklets -
Pg. 6 Testing Accommodations
Manual
Tape Recorder - Tape
record responses for later
verbatim translation. Pg. 6
Testing Accommodations Manual
Communication Device -
Communication board.
Augmentative communication
device.
Other - Transferring
answers from one answer document
to another answer document by
the test administrator (includes
large print).
|
|
Missouri
|
Computer or
Machine - An assistive
device, which permits a student
to read and/or respond to the
assessment, is used. Examples of
assistive devices include
computers that assist students
with fine-motor problems, text
enlargers that enable students
to independently read and answer
test questions, or augmentative
communication devices. The
student uses a computer/word
processor to write the
responses. (Provide a
nonnetworked computer to avoid
inappropriate use of the
computer to access answers.) The
student uses a typewriter to
write the responses.
Tape Recorder - The
student speaks responses into a
tape recorder in an isolated
setting so that other students
cannot benefit or be disturbed.
The test examiner must be
present at all times.
Communication Device - An
assistive device, which permits
a student to read and/or respond
to the assessment, is used.
Examples of assistive devices
include computers that assist
students with fine-motor
problems, text enlargers that
enable students to independently
read and answer test questions,
or augmentative communication
devices.
Sign Responses to Sign
Language Interpreter - The
student uses sign language to
convey responses. A certified
sign language interpreter or
deaf education instructor
records responses.
Other - The
student provides oral responses
to the test examiner.
|
|
Montana
|
Proctor/Scribe
- Dictation: The student
dictates answers to a Test
Administrator who records them
in the Test Booklet.
Computer or
Machine - Writing tools:
student uses a typewriter or
word processor (without
activating spell checker).
Speech/Text Device -
Voice activation: Student speaks
response into computer equipped
with voice activation software.
|
|
Nebraska
|
Proctor/Scribe
- A scribe is someone who writes
down what a student dictates by
an assistive communication
device, pointing, sign language,
or speech.
Computer or Machine -
Word processor.
Tape Recorder - Tape
recorder. A student uses a tape
recorder to record class work or
test responses rather than
writing on paper.
Communication Device - A
scribe is someone who writes
down what a student dictates by
an assistive communication
device, pointing, sign language,
or speech.
Spell Checker/Assistance
- Spelling and grammar devices.
The use of a dictionary may be
allowed on assignments that
require an extended response or
essay. Spelling and grammar can
also be checked with pocket
spell checkers.
Pointing - A scribe is
someone who writes down what a
student dictates by an assistive
communication device, pointing,
sign language, or speech.
Speech/Text Device - A
screen reader is a computer
application that converts text
to synthesized speech or to
Braille (read with an auxiliary
Braille display).
Other -
Multiple-choice questions
followed by answer down side
with bubbles to the right.
|
|
Nevada
|
Proctor/Scribe
- record the studentís responses
to multiple-choice or
constructed-response questions
onto the studentís answer
document. (This option is NOT
available to students taking a
writing assessment.)
Computer or Machine -
type written responses using a
keyboard or typewriter. (The use
of electronic aids such as
spelling, grammar, or
hyphenation checks is NOT
permitted on the writing
assessment
Write in Test
Booklets - record responses
to multiple-choice questions or
writing prompts in the test
booklet or on a separate sheet
of paper.
|
|
New Hampshire
|
Communication
Device - Student dictates
constructed responses or
observations using assistive
technology.
Pointing -
Student indicates responses to
multiple-choice items.
|
|
New Jersey
|
Proctor/Scribe
- dictating oral responses to a
scribe (person who writes from
dictation) student must indicate
all punctuation and must spell
all keywords
Computer or Machine -
Recording responses on a word
processor (tools, e.g., spelling
and grammar tools are not
permitted)
Communication Device -
Using an Augmentative
Communication device.
|
|
New Mexico
|
Proctor/Scribe
- Use of scribe to write oral
responses or fill in bubbles in
test booklet (grade 3) or answer
documents (grades 4 and above).
Use of a scribe to write oral
responses to
constructed-response items. Use
of a scribe to translate a
studentís oral responses from a
language other than English into
the test booklet... Student
dictates answers to items
(Writing Conventions, NMELPA,
Non-standard).
Computer or
Machine - Computers and
Personal portable keyboards.
Student types answers with Word
Processor; Non-standard on the
NMELPA.
Write in Test Booklets -
Includes writing responses on
large-print answer documents.
Tape Recorder - Record
responses on audio tape.
Communication Device -
Voice output must be disabled
during the Reading assessments.
If the communication device
produces a typed response, the
response must be transcribed
into a test booklet (grade 3) or
answer document (grades 4 and
above) for scoring exactly as it
is written.
Spell Checker/Assistance
- Spelling words to students who
request it, with the exception
of the Writing assessment where
points are earned for spelling.
Spell Checker/Assistance
- Spelling words to students who
request it, with the exception
of the Writing assessment where
points are earned for spelling.
Non-standard for NMELPA.
Sign Responses to Sign
Language Interpreter - Use
of signing or pointing to
alternative responses (for
multiple choice items only).
Pointing - Use of signing
or pointing to alternative
responses (for multiple choice
items only).
Speech/Text Device - Use
of communication devices (e.g.,
text-talk converter) to read
test items. Allowed on NMELPA
Other -
Large print answer sheets.
Standard administration for
NMELPA.
Other - Use
of a scribe to translate a
studentís oral responses from a
language other than English into
the test booklet.
|
|
New York
|
Computer or
Machine - Students must not
have access to any programs,
dictionaries, thesaurus,
internet, etc
Spell
Checker/Assistance -
considered a modification
(invalidates test score) if used
on tests measuring writing
skills.
Brailler - Based on the
unique needs of students with
blindness and visual impairments
the following accommodations
should be considered when making
appropriate decisions: Brailler.
Sign Responses
to Sign Language Interpreter
- Student with hearing
impairment can use scribe to
translate studentís signed
response. Grades 3-8 ELA only
students with hearing
impairments who may have
additional disabilities that
preclude them from writing their
own responses would be using a
scribe through a sign language
interpreter to respond to
questions measuring a studentís
writing skills.
Speech/Text
Device - talking word
processor; text-to-speech
software programs; use of spell
or grammar checkers on portions
of the tests measuring writing
skills prohibited.
Other - Answers may be
recorded in any manner. (When
answering questions designed to
measure writing ability in
English or a second language,
students must provide all
punctuation, paragraphing and
spelling of more difficult
words.)
Other -
Waiving spelling, paragraphing,
and/or punctuation requirements.
Prohibited on portions of the
tests measuring writing skills
|
|
North Carolina
|
Proctor/Scribe
- Use of dictation to a scribe
on the state writing assessment
invalidates the conventions
score of the writing assessment
Tape Recorder - Students
may use audiotapes to record
responses during the
administration of state tests.
Spell
Checker/Assistance - use of
electronic spellers or spell
check on the state writing
assessment invalidates the
results of that test.
Brailler -
Braille Writer/Slate and Stylus
(Braille Paper
Speech/Text
Devicee
speech recognition systems. The
use of speech recognition
systems during the
administration of the state
writing assessment would result
in invalid conventions score.
Students may use talking
processors/screen reading (i.e.,
the computer reads aloud what
the student has entered) as an
accommodation.
|
|
North Dakota
|
Proctor/Scribe
- Scribe writes down what a
student dictates by an assistive
communication device, pointing,
sign language, or speech. Note:
This does NOT include
transcription, i.e., copying
verbatim the studentís recorded
response into a standard test
book from large print, Braille,
or electronic word processor.
Communication Device -
Scribe writes down what a
student dictates by an assistive
communication device, pointing,
sign language, or speech. Note:
This does NOT include
transcription, i.e., copying
verbatim the studentís recorded
response into a standard test
book from large print, Braille,
or electronic word processor.
Sign Responses
to Sign Language Interpreter
- Scribe writes down what a
student dictates by an assistive
communication device, pointing,
sign language, or speech. Note:
This does NOT include
transcription, i.e., copying
verbatim the studentís recorded
response into a standard test
book from large print, Braille,
or electronic word processor.
Pointing - Scribe writes
down what a student dictates by
an assistive communication
device, pointing, sign language,
or speech. Note: This does NOT
include transcription, i.e.,
copying verbatim the studentís
recorded response into a
standard test book from large
print, Braille, or electronic
word processor.
Speech/Text Device -
Screen reader to convert text to
synthesized speech; speech to
text converters or voice
recognition devices
Other - Word
predictor programs
|
|
Ohio
|
Proctor/Scribe
- Scribing accommodations are
intended for students who cannot
physically write or record their
responses during testing.
Scribes are an appropriate
accommodation for students who
are able to write but cannot
record their responses because
of factors such as a processing
disability (as documented in the
ETR), or indecipherable
handwriting. (Note: scribes are
not an allowable accommodation
for children who have difficulty
focusing, sitting still or
staying on task.
Computer or Machine -
Word processor - computer,
keyboarding device, typewriter
to key responses. Statewide
Assessment Accommodations. Spell
check, thesaurus, and grammar
check must be turned off for
writing test items where these
skills are directly assessed.
Spell Checker/Assistance
- Portable electronic spell
checker. Only spell check
features are allowable (without
definitions, synonyms).
Other -
Portable electronic grammar
checker. Pg. 22 SAA
|
|
Oklahoma
|
Proctor/Scribe
- Dictate words to scribe
(Writing test only). Test
Administrator must transcribe
words verbatim into a standard
Student Answer Document.
Computer or Machine -
Utilize typewriter, word
processor, or computer without
the use of help features, such
as spell check, etc. (Writing
test only). If a student types
the response, the response must
be transcribed verbatim into a
Standard Scannable Answer
Document.
Write in Test Booklets -
Mark answers in test book and
not on answer document, for
later transfer by Test
Administrator to answer
document.
Tape Recorder
- Student tapes response for
verbatim transcription at a
later time (Writing test only).
(Tapes need to be destroyed by
District Test Coordinator).
|
|
Oregon
|
Proctor/Scribe
- Dictate multiple-choice
responses to a scribe. Respond
orally to a scribe. Dictate
writing sample and edits to
scribe is considered a
modification on the writing
test. Modifications change the
content and/or performance
standards of what is being
measured by the test.
Computer or
Machine - For writing and
ELPA tests: must turn off
formatting, spell check, grammar
check, and word prediction. If
these functions are not turned
off, it is considered a
modification. Modifications
change the content and/or
performance standards of what is
being measured by the test.
Tape Recorder - Answers
recorded (audio cassette).
Student is allowed to use a
recording device to record/play
back questions, passages, and
responses.
Spell Checker/Assistance
- If the student initiates the
process of checking spelling at
an individual word level, an
electronic spell check is
allowed. Technology that
automatically identifies errors
for the student is not allowed.
Sign Responses to Sign
Language Interpreter -
Students responds in sign
language on the writing
assessment is considered a
modification. Modifications
change the content and/or
performance standards of what is
being measured by the test.
Pointing - Point to
multiple-choice responses to a
scribe.
Other - Students who
require increased spacing, wider
lines or margins should have
additional room beyond what is
in the writing folder to
complete their response.
Other - Verbally coaching
the student through the writing
process at any step is
considered a modification.
Modifications change the content
and/or performance standards of
what is being measured by the
test.
Other - Responding to the
writing prompts in a language
other than English is considered
a modification. Modifications
change the content and/or
performance standards of what is
being measured by the test.
Other - Peer editing or
response groups during writing
process is considered a
modification. Modifications
change the content and/or
performance standards of what is
being measured by the test.
Other - Assistance with
grammar on the writing test is
considered a modification.
Modifications change the content
and/or performance standards of
what is being measured by the
test.
|
|
Pennsylvania
|
Proctor/Scribe
- Allowed for all students who
normally dictate their answers
to a scribe as part of their
regular classroom
accommodations. Student cannot
dictate in any language but
English. Not allowed on the
writing prompt.
Computer or Machine -
Word processor or typewriter
with spell checker, grammar
checker, word prediction
functions, and other supports
turned off; students may use the
typing function only.
Tape Recorder - A student
uses a tape/CD/Electronic
recorder (with NO speech
recognition) to record test
responses rather than writing on
paper.
Communication Device -
spelling/grammar checkers and
word prediction functions must
be turned off for the writing
PSSA
Speech/Text Device -
Screen reader software is a
computer application that
converts text on a computer
screen to synthesized speech or
Braille (read with an auxiliary
Braille display). Speech
recognition software used to
respond to any open-ended
questions with word prediction
function enabled not allowed for
PSSA. Speech recognition
software used to respond to
writing essay prompts. Word
prediction function may cue
studentís response.
Other - Note-taking
devices and adapted PDAs.
Other - Large
print/answer areas for
responses.
|
|
Rhode Island
|
Proctor/Scribe
- Student indicates response to
multiple-choice items. (The
student indicates by naming
their answers) Student dictates
constructed responses to school
personnel (reading and math
only). Scribing the writing
test, only for students for whom
it is impossible to produce a
written document (e.g. a student
with a recent or short-term
physical injury.
Computer or Machine -
Student writes using word
processor, typewriter, or
computer. Spell and grammar
checks must be turned off. This
accommodation is intended for
unique individual needs, not an
entire class.
Other - Student hand
writes responses on separate
paper
|
|
South Carolina
|
Proctor/Scribe
- Students may dictate their
answers to multiple-choice,
constructed response, and
extended-response items to a
scribe.
Computer or Machine -
Type responses using a
typewriter or computer. As a
modification with implications
for scoring, students may use
word processors with
voice-activated processors with
spell check, grammar-check, and
word prediction programs on the
extended response section of
Time to Write.
Write in Test Booklets -
Students may circle their
answers to the multiple-choice
questions in the test booklet.
Communication Device -
Cannot include spell-check,
grammar-check or word prediction
programs.
Spell Checker/Assistance
- Poor spellerís dictionary,
electronic speller (that has
only spelling corrections,
listing of words, and easily
confused word applications).
Only allowed on the
extended-response portion of the
English Language Arts test.
Brailler -
Braille writer, slate and
stylus, or electronic Braille
note-taking device.
Other - Non-verbal
indication of answer choices for
multiple-choice items.
Other - Alternative
scoring for the extended
response section of Time to
Write. Alternative scoring
focuses more on content of the
response and less on the writing
mechanics.
|
|
South Dakota
|
Computer or
Machine - Typewriter or word
processor (turn off spelling and
grammar check).
Write in Test Booklets -
Responses marked directly on
test booklet or on large-print
answer document.
Tape Recorder -
Tape-recorded responses for
verbatim translation.
|
|
Tennessee
|
Computer or
Machine - Assistive
Technology can include, but is
not limited to: computers,
speech-synthesizers,
communication devices, word
processors with or without
talk-text technology, and
electronic readers. Any device
that would read aloud the
Reading/Language Arts portions
of the Achievement, EOC, or
Gateway Assessments requires IEP
documentation of Accommodations
B and C. Students may not use
any device that reads aloud
internal test items on the
Reading/Language Arts sections
of TCAP Assessments.
Write in Test Booklets -
With the exception of the
Achievement Tests in grades K-2,
students may mark in test
booklets. This includes
highlighting or underlining
words or phrases.
Tape Recorder - Student
reads into auditory
recorder/plays back immediately
for comprehension.
Communication Device -
Assistive Technology can
include, but is not limited to:
computers, speech-synthesizers,
communication devices, word
processors with or without
talk-text technology, and
electronic readers. Any device
that would read aloud the
Reading/Language Arts portions
of the Achievement, EOC, or
Gateway Assessments requires IEP
documentation of Accommodations
B and C. Students may not use
any device that reads aloud
internal test items on the
Reading/Language Arts sections
of TCAP Assessments.
Communication Device -
Assistive Technology can
include, but is not limited to:
computers, speech-synthesizers,
communication devices, word
processors with or without
talk-text technology, and
electronic readers. Any device
that would read aloud the
Reading/Language Arts portions
of the Achievement, EOC, or
Gateway Assessments requires IEP
documentation of Accommodations
B and C. Students may not use
any device that reads aloud
internal test items on the
Reading/Language Arts sections
of TCAP Assessments.
Spell
Checker/Assistance - IEP or
504 Service Plan where
technology is used consistently
throughout educational program
(grammar, spell-check, and
thesaurus not allowed).
2008-2009
Speech/Text Device -
Assistive Technology can
include, but is not limited to:
computers, speech-synthesizers,
communication devices, word
processors with or without
talk-text technology, and
electronic readers. Any device
that would read aloud the
Reading/Language Arts portions
of the Achievement, EOC, or
Gateway Assessments requires IEP
documentation of Accommodations
B and C. Students may not use
any device that reads aloud
internal test items on the
Reading/Language Arts sections
of TCAP Assessments.
Other - Record answers on
a separate piece of paper.
|
|
Texas
|
Spell
Checker/Assistance - Allowed
on the grade 4 TAKS-M writing
test and 7 TAKS-M writing test
if student is capable of
organizing thoughts and ideas in
written responses but has a
disability that affects the
physical reproduction of letters
and words or the ability to
remember spelling rules, word
structures, or letter patterns,
spelling assistance may be used.
Allowed on the grade 9 reading
test if student is capable of
organizing thoughts and ideas in
written responses but has a
disability that affects the
physical reproduction of letters
and words or the ability to
remember spelling rules, word
structures, or letter patterns,
spelling assistance may be used.
Allowed on TAKS (A) and TAKS-M
Pg.
|
|
Utah
|
Computer or
Machine - Allowed on
Language Arts CRT and Reading
UBSCT. Grammar check and spell
check must be turned off.
Computer or Machine -
Spell check must be turned off.
Tape Recorder - Recording
Device listed as allowed on
Audiotape or Compact Disc for
Instruction only ( Instruction
box checked; Assess box NOT
checked) Document is unclear as
to why there is a discrepancy.
Speech/Text Device -
Allowed on all tests but the
Iowa Tests.
|
|
Vermont
|
Proctor/Scribe
- Student indicates response to
multiple-choice items. (The
student indicates by naming
their answers) Student dictates
constructed responses to school
personnel (reading and math
only) p.5 of accommodations,
guidelines, and procedures.
Scribing the writing test, only
for students for whom it is
impossible to produce a written
document (e.g. a student with a
recent or short-term physical
injury.
Computer or Machine -
Student writes using word
processor, typewriter, or
computer. Spell and grammar
checks must be turned off. This
accommodation is intended for
unique individual needs, not an
entire class.
Pointing - Students
indicate response to
multiple-choice items by
pointing at their answers.
Other - Student hand
writes responses on separate
paper.
|
|
Virginia
|
Proctor/Scribe
- Student responds verbally, or
indicates an answer and
Examiner/Proctor marks answer
document. Dictation to a scribe
(direct writing component of the
English test only).
Computer or Machine -
Word processor, typewriter. For
students who are blind or have
visual impairments and who do
not read Braille, as well as
students who have an orthopedic
impairment, a specific learning
disability or other disability
that interferes with the
composing process. For the
direct-writing assessment of the
SOL English tests.
Write in Test Booklets -
Student marks test booklet and
Examiner/Proctor transfers
responses to answer document.
Tape Recorder - Only for
pre-writing activity to tape
response for the direct writing
component of the English test.
Communication Device -
Augmentative device with
auditory output, augmentative
communication device. Only
devices which produce student
responses verbatim may be used.
For students who are blind or
have visual impairments and who
do not read Braille, as well as
students who have an orthopedic
impairment, a specific learning
disability or other disability
that interferes with the
composing process. For the
direct-writing assessment of the
SOL English tests.
Brailler - Blind and
low-vision students may use a
Braille writer to respond to the
writing prompt/direct-writing
component of the English test or
record responses to
multiple-choice questions on the
SOL test.
Other - Enlarging the
answer document.
|
|
Washington
|
Computer or
Machine - For the Writing
assessment, student uses a word
processor to generate responses
to items including writing
prompts.
Write in Test Booklets -
Direct students to underline or
mark assessment directions with
a No.2 pencil. Decision to
provide accommodation must be
made on an individual basis and
must not be used for the first
time on state tests. Allow
response in large print editions
of the assessment for students
with an IEP or 504 plan who use
large print materials.
Sign Responses to Sign
Language Interpreter -
Student dictates responses via
an assistive communication
device, pointing, sign language,
or speech. Scribes record
studentsí responses verbatim
into a regular test booklet.
Pointing - Student
dictates responses via an
assistive communication device,
pointing, sign language, or
speech. Scribes record studentsí
responses verbatim into a
regular test booklet.
Speech/Text Device -
Provide text-to-speech software
that allows students to listen
to text as it is displayed on a
computer screen. Accommodations
Available to Students with
Disabilities. Text-to-speech
software/technology may NOT be
used for reading the reading
test for grades 3-8.
|
|
West Virginia
|
Proctor/Scribe
- Use of a scribe when a
short-term medical condition
precludes the student from
writing with the dominant hand
to mark responses in test
booklet, e.g. a fractured arm in
a cast. For students with an
IEP/504 Plan and ELLs with
disabilities: Indicate responses
to a scribe for
selected-response items and when
the student is physically unable
to respond otherwise-indicate
responses to a scribe for
constructed response items.
Computer or
Machine - Use a computer,
typewriter, or other assistive
technology device to respond.
Hand-held minicomputers,
personal digital assistants or
laptop computers may NOT be
used.
Write in Test Booklets -
Allowing the student to record
answers in large print test
booklets.
Brailler - Use Braille or
other tactile form of print when
that is the studentís typical
mode of responding to written
material.
Speech/Text Device - Use
a text-talk converter to present
directions, stimulus material,
questions and/or answer choices
verbatim for a blind/partially
sighted student, when that is
the studentís typical mode of
accessing written material. Have
test presented through text-talk
converter.
Other - If the student is
provided routine support by an
aide and the aide has been
trained as an examiner.
|
|
Wisconsin
|
Proctor/Scribe
- For selected response
items...and for constructed
response items, student
indicates response orally to a
scribe. A scribe may also be
used to complete the Writing
prompt for a student who is
unable to provide a written
response that can be scored.
Computer or Machine - For
Language Arts and Writing tests,
all spell- and grammar-checking
devices must be turned off, for
the Mathematics test, the
calculator function must be
turned off for non-calculator
sessions.
Write in Test Booklets -
Allow student to mark test book
in approved locations with a #2
pencil.
Communication Device -
For selected response items,
student indicates response by
using a communication device
Pointing - For selected
response items, student
indicates responses by pointing.
Other - Provide an extra
test book for student to view so
he/she does not need to flip
back and forth in test book.
Other - Student responds
orally or in writing in his/her
native language and a translator
records/translates student
responses to a scribe.
|
|
Wyoming
|
Proctor/Scribe
- Student dictates to a scribe
who writes responses verbatim
(including punctuation).
Computer or Machine -
Student uses a word processing
device to type answers.
Tape Recorder
- Student tapes a response for
later verbatim transcription.
Spell Checker/Assistance
- Listed as Nonstandard and
Instruction only.
Speech/Text Device -
Student uses a communication
devise to communicate answers
(Speech to text).
Monitor Placement of Student
Responses - Monitor
placement of student responses
on answer sheet. Students who
are able to use bubbled answer
sheets may benefit from having
an adult simply monitor the
placement of their responses to
ensure they are actually
responding to the intended
question.
|
Table B.24: Scheduling-Timing
Accommodations
A = Allowed, AC
= Allowed in Certain Circumstances, AI =
Allowed with Implications for Scoring, P
= Prohibited
AS = All Subjects, R = Reading/Language
Arts, M = Math, S = Science, W =
Writing, SS = Social Studies
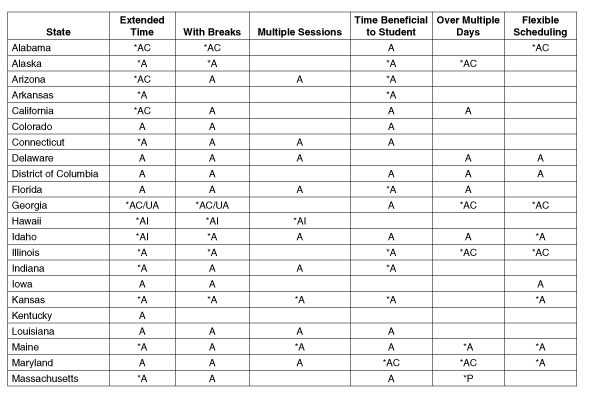
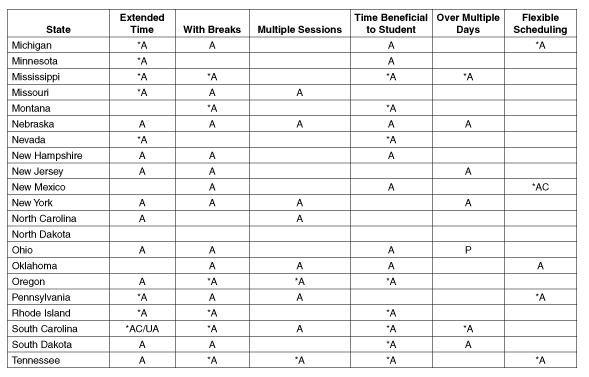
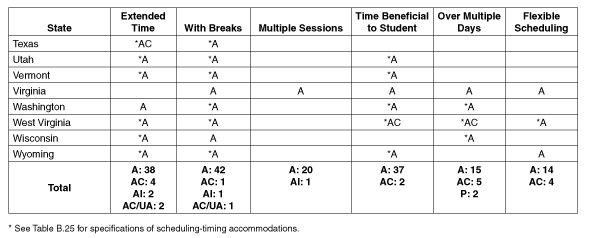
Table B.25: Specifications
and Descriptions of ďCertain
Circumstances,Ē ďImplications for
Scoring,Ē ďUnique Aggregated,Ē and
ďOtherĒ Scheduling/Timing Accommodations
|
Alabama
|
Extended Time
- Allowed on the Alabama Direct
Assessment of Writing (ADAW) and
the Alabama High School
Graduation Exam (AHSGE).
Prohibited on all other tests.
Extended Time -
Prohibited on the Alabama Direct
Assessment of Writing (ADAW).
Allowed on all other tests.
With Breaks - Prohibited
on the Alabama Direct Assessment
of Writing (ADAW). Allowed on
all other tests.
Flexible Scheduling -
Allowed on the Dynamic
Indicators of Basic Early
Literacy Skills (DIBELS),
Stanford Achievement Test
(Stanford 10), and the Alabama
Reading and Mathematics Test
(ARMT). Prohibited on all other
tests.
|
|
Alaska
|
Extended Time
- Allowing additional time.
With Breaks - Allowing
frequent breaks during testing.
Time Beneficial to Student
- Administering at a time of day
most beneficial to the student.
Over Multiple Days -
Administering the test over
several days completing the
testing on or before the last
day of the test window. For
grade 10 SBA-HSGQE and HSGQE
Retest, districts must submit an
application to the department no
later than 5 days prior to the
first day of planned testing.
These students MUST have an EED
approved application prior to
the first day of planned
testing.)
|
|
Arizona
|
Extended Time
Ė Extended time for Terra Nova
testing in grades 2 and 9.
Time Beneficial to Student
Ė Test at a different time of
day.
|
|
Arkansas
|
Extended Time
ĖAll testing scheduled for a
given day must be completed by
the conclusion of that school
day [no population specified
Time Beneficial
to Student - Individualized
scheduling [no population
specified]. LEP population
specified.
Other - Longer breaks.
Students tested individually or
in small groups may take longer
breaks between sessions. Breaks
are not permitted during a
session.
|
|
California
|
Extended Time
- Extra time on a test within a
testing day. Allowed only for
students with an IEP or 504 plan
on the California Achievement
Tests, allowed for all students
on all other tests. Test may be
administered over more than one
day for students who have IEPs
or 504 plans.
|
|
Connecticut
|
Extended Time
Ė For each testing session, time
may be extended for as long as
necessary; provided the student
does not suffer from fatigue and
the test session is not carried
over to another day. . . .
Students who receive extended
time must be tested separately
from those under regular time
limits
|
|
Florida
|
Time Beneficial
to Student - Students may
take a specific session at a
specific time of the day, page
18 of guide.
|
|
Georgia
|
Extended Time
- Considered nonstandard on the
Norm-Referenced Test (NRT),
standard on all other tests. .
With Breaks - Considered
nonstandard on the
Norm-Referenced Test (NRT),
standard on all other tests.
Over Multiple Days -
Allowed for the listening and
reading subtests of ACCESS for
ELLs. Prohibited on all other
tests.
Flexible Scheduling -
Flexibility in the order of
administration for content
areas. Allowed as a standard
accommodation on the
Criterion-Referenced Competency
Tests (CRCT), Norm-Referenced
Test (NRT) and ACCESS for ELLs.
Prohibited on all other tests.
|
|
Hawaii
|
Extended Time
- Receiving extended time for a
norm-referenced session. Also
allowed for Hawaiian language
immersion students in grade 5
who is transitioning to the use
of English during a portion of
each instructional day (for
reading and math tests). A
student may be given up to
double the exact time required,
but no session may be extended
to a second day. Non-comparable
separate national
norm-referenced scores will be
provided (for norm referenced
sessions.)
With Breaks - Taking
student-initiated breaks during
a session. Criterion-referenced
and non-comparable separate
national norm-referenced scores
will be provided.
Multiple Sessions -
Breaking a single session into
shorter sessions. Also allowed
for Hawaiian language immersion
students in grade 5 who is
transitioning to the use of
English during a portion of each
instructional day (for reading
and math tests). Non-comparable
separate national
norm-referenced scores will be
provided.
|
|
Idaho
|
Extended Time
Ė Next day restart-extended time
(student must not have access to
items). It is an adaptation to
allow extended time if there is
a time limit in the test
administration, e.g., extending
one minute fluency probes. If
adaptations are used, the
student is deemed not proficient
and will not be counted towards
participation.
With Breaks - Some
accommodations create fatigue,
such as the use of magnification
equipment, tape recorders, and
earphones. The use of these
accommodations may require
additional breaks, but not more
total working time. Multiple or
frequent breaks.
Flexible Scheduling -
Administering subtests in a
different order.
|
|
Illinois
|
Extended Time
- Pre-planned extended-time
sessions that exceed the extra
10 minutes allowed for all
students. There is no specified
time limit for these sessions
other than they must begin and
end in a single school day.
Students receiving this
provision must be tested
separately from students getting
standard time. PSAE, grade 11,
may have standard time for Day 1
ACT multiple-choice tests and
extended time for Day 1 ACT
writing test.
With Breaks Ė Breaks may
be in-seat or out-of-seat.
Breaks for each individual test
session must begin and end in
the same day. For grade 11,
allows standard time with "stop
the clock" breaks.
Time Beneficial to Student
Ė For grade 11 test/PSAE,
subject-area test needs to be
completed in one day and in the
prescribed order.
Over Multiple Days - On
PSAE and ISAT tests. IAA - must
be administered within 3 weeks.
Flexible Scheduling Ė
This includes changing the order
of the content tests. Allowed
for ISAT and IAA. Not allowed
for PSAE.
|
|
Indiana
|
Extended Time
- Student provided extended
testing time for each test
session (e.g., 50% more time,
double time). For ELLs, is
permitted with documentation on
ISTEP+ Student information
questionnaire. This
accommodation is available to
all LEP students, but do not let
the assessment go on
indefinitely if the student is
not making progress.
Time Beneficial to Student
- Time of day for administration
is altered.
Other - Student is
provided unlimited time for each
test section.
|
|
Kansas
|
Extended Time
Ė Decisions to provide extended
time should be made on a
case-by-case basis, keeping in
mind the type of accommodations
being provided, the disability
involved, and the type of test.
For example, if a reader or
scribe is used, double time may
be appropriate. Usually
"unlimited time" is not
appropriate or feasible. NOTE:
In examiner manuals for reading,
math, science, social studies
and writing the manuals say
there is no code for this
accommodation anymore because it
is not longer considered an
accommodation.
With Breaks - If frequent
breaks during the assessment are
provided.
Multiple Sessions Ė It is
recommended that a maximum of
two test parts be completed on
any one day. In general, the
entire part of an assessment
should be completed in one
sitting. However, in grades
three and four and for selected
IEP students, each test part may
be administered over two
separate test sessions.
Time Beneficial to Student
Ė Choose optimum time to
administer tests.
Flexible Scheduling Ė
Change testing schedule.
Other Ė Some other
accommodation was used.
Other Ė Multiple or
frequent breaks. This other
category highlights "frequent
breaks" as different from
multiple.
|
|
Maine
|
Extended Time
- Time extended beyond standard
administration. Same day and
several days within the MEA test
administration window.
Multiple Sessions - In
appropriate blocks of time for
individual student needs.
Over Multiple Days - With
time extended beyond standard
administration (several days);
inferred multiple days.
Flexible Scheduling -
Using flexibility in the order
in which content area tests are
given.
|
|
Maryland
|
Time Beneficial
to Student - Accommodation
3-C is not permitted for the
High School Assessments unless
justified in writing by the
school and specifically approved
by both the local school system
and MSDE.
Over Multiple Days -
Accommodation 3-C is not
permitted for the High School
Assessments unless justified in
writing by the school and
specifically approved by both
the local school system and
MSDE.
Flexible Scheduling -
Students who require
accommodation 3-D on the MSA
Science assessment must take the
paper-and-pencil test edition,
as this accommodation is not
feasible using the computerized
online test edition.
|
|
Massachusetts
|
Extended Time
- Since any student may be given
additional time beyond the
scheduled test administration
session, additional time is not
considered an MCAS
accommodation. However, no
single test session may extend
beyond the end of the regular
school day, and any single test
session must be completed on the
same day in which it begins.
Over Multiple Days - No
single test session may extend
beyond the end of the regular
school day, and any single test
session must be completed on the
same day in which it begins.
|
|
Michigan
|
Extended Time
- Extended assessment time
within reason (approximately 1.5
times the estimated assessment
time).
Flexible Scheduling -
Administer assessment sections
in any order for English
language arts, science, and
social studies.
Other - Clock or method
of informing students of
remaining time.
|
|
Minnesota
|
Extended Time
- Testing time in same day is
extended (not applicable to
TEAE, a timed test).
|
|
Mississippi
|
Extended Time
- Additional time to complete
test (within a reasonable time,
not to exceed one school day.)
With Breaks - With
scheduled rest breaks.
Time Beneficial
to Student - At a time of
day to accommodate the studentís
disability.
Over Multiple Days -
Administer the test in several
sessions, specifying the
duration of each session.
Administer the test over several
days, specifying the duration of
each dayís session. However, the
entire assessment must be
completed within the testing
window. Any extension that
exceeds or goes beyond the day
the test administration is
scheduled must be prearranged,
the procedure must be
documented, and on file with the
District Test Coordinator. If
the student is testing over
several days, he/she is not
allowed to change responses to
questions answered during the
previous testing sessions or
preview questions that will be
administered in a future
session.
Other - Until, in the
test administratorís judgment,
the pupil can no longer continue
the activity.
|
|
Missouri
|
Extended Time
- Administer assessment using
more than allotted periods.
|
|
Montana
|
With Breaks
- Session duration: test is
administered in appropriate
blocks of time for individual
student needs, followed by rest
breaks.
Time Beneficial to Student
- Change in Administration Time:
Test is administered at a time
of day or a day of the week
based on student needs.
|
|
Nevada
|
Extended Time
- Student will receive extended
time to counter fatigue or to
allow for altered testing
procedures. The Department
recommends not exceeding twice
the normal time.
Time Beneficial
to Student - Tests
administered at a time of day
when the student is expected to
do his/her best work.
|
|
New Jersey
|
Other -
Terminating a section of the
test when a student has
indicated that he or she has
completed all the items he or
she can.
|
|
New Mexico
|
Flexible
Scheduling - Scheduling
sessions in a different order,
except for the Writing
assessment.
|
|
North Carolina
|
Other -
Testing before schoolís
scheduled testing date.
|
|
Oregon
|
With Breaks
- Frequent breaks.
Multiple
Sessions - Divide testing
over several sessions.
Time Beneficial to Student
- Administer at time of day most
beneficial to students.
Other -
Schedule assessment for an
individual student outside the
official testing window. This is
considered a modification.
Modifications change the content
and/or performance standards of
what is being measured by the
test.
|
|
Pennsylvania
|
Extended Time
- Scheduled extended time, or a
student can request extended
time during the assessment
process as long as they are
working productively.
Flexible Scheduling - Change
schedule.
|
|
Rhode Island
|
Extended Time
- Allow extended time, beyond
what is recommended, until in
the administratorís judgment,
the student can no longer
sustain the activity.
With Breaks
- Allow short, supervised breaks
during testing.
Time Beneficial to Student
- Administer the test at the
time of day that takes into
account the studentís medical
needs or learning style.
|
|
South Carolina
|
Extended Time
- If a studentís response will
be scored using the alternative
extended-response scoring
rubric, make sure that this
modification is coded on the
studentís test booklet. This
will alert scorers that
alternative scoring will be used
. . . which focuses more on the
content of the response and less
on the writing mechanics.
With Breaks - Frequent or
extended breaks with or without
contact with other students.
Time Beneficial to Student
- Administering the test in the
afternoon rather than the
morning.
Over Multiple Days - As
long as all testing is completed
by the last day of make-up
testing.
|
|
South Dakota
|
Time Beneficial
to Student - Scheduling -
time of day.
|
|
Tennessee
|
With Breaks
- Extended breaks between
subtests.
Multiple Sessions -
Within school day. TCAP tests or
subtests may be given in smaller
segments adhering to the
allotted time for that
test/subtest as specified in the
Test Administration Manual.
Achievement and EOC tests are
timed and the administration
must remain within the overall
time allotted.
Time Beneficial to Student
- Flexible time of day.
Flexible Scheduling -
Flexible scheduling of the
subtests. The student may be
administered fewer Achievement
Assessment subtests during a
given day than the recommended
system schedule. Extended breaks
between subtests may be given to
the student. Achievement
subtests, End-of-Course tests,
and the Writing assessment may
be given at a different time of
day than the recommended
assessment schedule for
individual students who may
perform better.
Other - An individual
student may be administered
fewer Achievement subtests
during a given day than the
recommended system schedule.
|
|
Texas
|
Extended Time
- Must be approved - will be
approved for only a small number
of students who are in unique
situations (e.g., those who take
the Braille version, have a
serious medical condition). Part
of dyslexia bundle including
"orally reading all proper nouns
associated with each passage
before students begin individual
reading, orally reading all test
questions and answer choices to
students, and extending the
testing time over a two-day
period. These three
accommodations must be "bundled"
meaning they must be provided
together. Only students who meet
the eligibility criteria
outlined in Appendix B may use
this accommodation.
Extended Time - Must be
approved - will be approved for
only a small number of students
who are in unique situations
(e.g., those who take the
Braille version, have a serious
medical condition). .
With Breaks - The test
booklet may be divided into
short sections (e.g., by using
paper clips or adhesive notes)
so that students can take a
break between each section. A
timer may be used so that
students can take breaks at
planned intervals. Students may
be allowed to take brief breaks
in the testing room during a
test session.
|
|
Utah
|
Extended Time
- On the CRTís, subtest sessions
must be completed on the same
day they are started. On the
UBSCT, subtests must be given on
the assigned day and completed
within the school day. There are
no time restrictions on
statewide assessments or on the
Iowa Tests.
With Breaks - On the
CRTís, subtest sessions must be
completed on the same day they
are started. On the UBSCT,
subtests must be given on the
assigned day and completed
within the school day.
Time Beneficial to Student
- On the CRTís, subtest sessions
must be completed on the same
day they are started. On the
UBSCT, subtests must be given on
the assigned day and completed
within the school day.
|
|
Vermont
|
Extended Time
- Allow extended time, beyond
what is recommended, until in
the administratorís judgment,
the student can no longer
sustain the activity.
With Breaks - Allow
short, supervised breaks during
testing.
Time Beneficial to Student
- Administer the test at the
time of day that takes into
account the studentís medical
needs or learning style.
|
|
Washington
|
With Breaks
- Breaks of 15 minutes of less
may be given at predetermined
intervals or after completion of
assignments, test, or
activities. Individual breaks
when needed.
Time Beneficial to Student
- Assessment for students in
grades 3-8 occurs at a time of
day best suited for the student.
Over Multiple Days -
Assessment may be administered
across the entire three-week
WASL window. Decision to provide
accommodation must be made on an
individual basis and must not be
used for the first time on state
tests. Students with an IEP or
504 Plan may continue to work on
each subtest for more than one
day as long as they are
productively engaged as
specified on the IEP or Section
504 plan as an accommodation
allowed during regular classroom
and state testing.
Other - Allow students to
complete only one test section
each day. This accommodation is
available at high school,
however, all tests must be
administered within the testing
window.
|
|
West Virginia
|
Extended Time
- Students requiring additional
time must be provided the time
needed to complete the test
within the confines of the test
day. If a student requiring
additional time stops working
for more than 10 minutes, it is
recommended that the testing
session be ended.
With Breaks
- Provide more breaks than are
scheduled as long as the breaks
do not allow an opportunity for
the student to study information
on a test already started.
Schedule breaks according to
studentís needs.
Time Beneficial to Student
- Determine the testing schedule
that provides optimum testing
conditions for individual
students on the APTA.
Over Multiple
Days - If either a medical
or behavioral crisis precludes
the student from completing the
section within the school day,
the student, once the crisis has
passed, may complete the
unfinished items on another day
within the testing window. Only
allowed for all students taking
the APTA.
Flexible
Scheduling - Have flexible
scheduling that allows for
students who may not complete
the testing before a scheduled
meal break.
|
|
Wisconsin
|
Extended Time
- Extra time for any timed test,
as long as a test session is
completed within the same day
the student started the session.
Over Multiple Days -
Allow student to test across
multiple days, as long as a test
session is completed within the
same day the student started the
session.
|
|
Wyoming
|
Extended Time
- Provide extended time to
complete assessment as long as
the student is working and
making progress.
With Breaks - Allow
multiple and/or frequent breaks
during testing. Page 19 of
accommodations manual.
Time Beneficial to Student
- Test during time of day when
student is most responsive.
|
Table B.26A: Setting
Accommodations (1 out of 2)
A = Allowed, AC
= Allowed in Certain Circumstances, AI =
Allowed with Implications for Scoring, P
= Prohibited
AS = All Subjects, R = Reading/Language
Arts, M = Math, S = Science, W =
Writing, SS = Social Studies
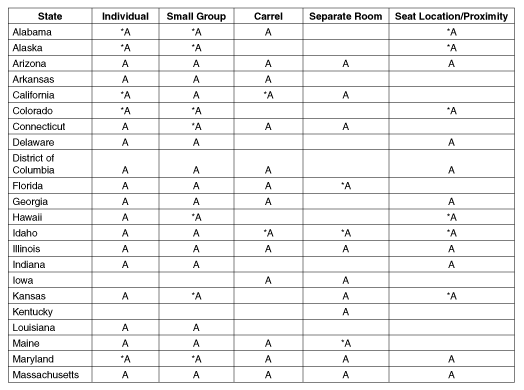
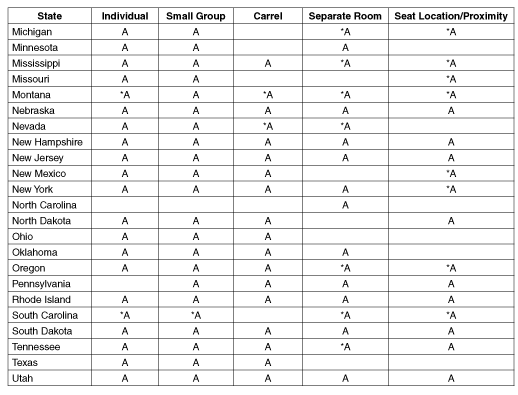
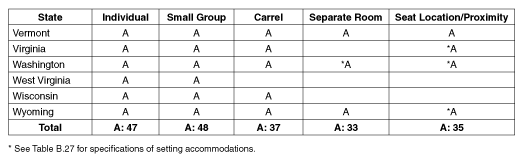
Table B.26B: Setting
Accommodations (2 out of 2)
A = Allowed, AC
= Allowed in Certain Circumstances, AI =
Allowed with Implications for Scoring, P
= Prohibited
AS = All Subjects, R = Reading/Language
Arts, M = Math, S = Science, W =
Writing, SS = Social Studies
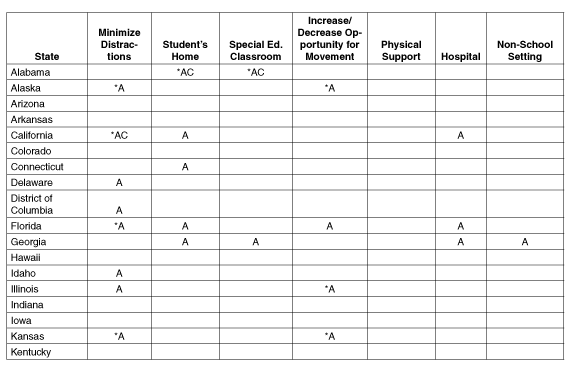
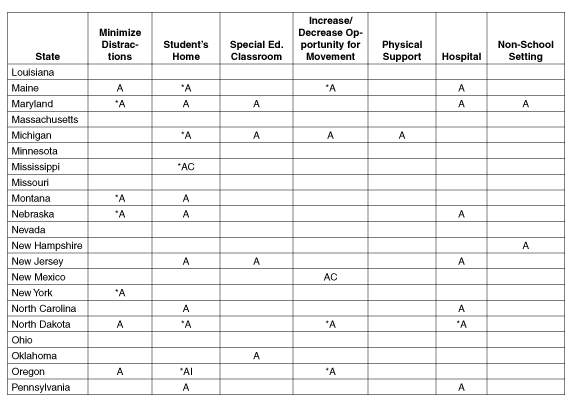
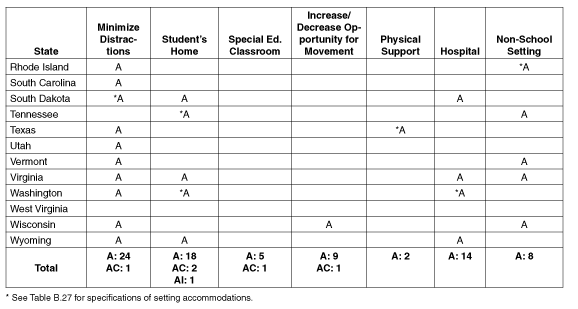
Table B.27: Specifications
and Descriptions of ďCertain
Circumstances,Ē ďImplications for
Scoring,Ē ďUnique Aggregated,Ē and
ďOtherĒ Setting Accommodations
|
Alabama
|
Individual -
Not applicable on the Dynamic
Indicators of Basic Early
Literacy Skills (DIBELS),
allowed on all other tests.
Small Group - Not
applicable on the Dynamic
Indicators of Basic Early
Literacy Skills (DIBELS),
allowed on all other tests.
Seat Location/Proximity -
Not applicable on the Dynamic
Indicators of Basic Early
Literacy Skills (DIBELS),
allowed on all other tests
Studentís Home - For
homebound students only
Special Ed.
Classroom - Allowed for IEP
and 504 on the Alabama Science
Assessment (ASA). Prohibited on
the Alabama Alternate Assessment
(AAA). Allowed for IEP but not
504 for all other assessments.
Other - With teacher
facing student.
|
|
Alaska
|
Individual -
Administering test individually
in a separate location.
Small Group -
Administering test to a small
group in a separate location.
Seat
Location/Proximity - Using
preferential seating.
Minimize Distractions -
Administering test in locations
with minimal distractions (e.g.,
small group, study carrel, or
individually).
Increase/Decrease Opportunity
for Movement - Support of
physical position of student by
increasing or decreasing
opportunity for movement.
|
|
California
|
Individual -
Test individual student
separately, provided that a test
examiner directly supervises the
student.
Carrel - All students may
have these testing variations if
regularly used in the classroom.
Minimize Distractions -
Structure the testing
environment to eliminate
distractions for students who
are particularly distractible;
available only on the CAPA
(alternate assessment); from
CAPA core adaptations.
|
|
Colorado
|
Individual -
Implied. Required for other
accommodations (interpreter
Small Group - Grouping
students to provide other
accommodations.
Seat
Location/Proximity - Change
of location.
|
|
Connecticut
|
Small Group
- For students getting a read
aloud accommodation, the limit
for size of small group was five
students.
|
|
Florida
|
Separate Room
- Separate room allowed for
students with an IEP or 504
Plan. Testing in a separate room
with the English for speakers of
other languages (ESOL) or
heritage language teacher acting
as test administrator for ELL
students with disabilities.
Minimize Distractions -
With white noise (sound
machines) to reduce auditory
distractions.
|
|
Hawaii
|
Small Group
Ė The number of students should
not exceed 12 to maintain the
intent and benefits of a
small-group setting.
Seat Location/Proximity -
Being seated near the Test
Administrator.
|
|
Idaho
|
Carrel -
Location to reduce distractions
such as a study carrel.
Separate Room - Separate
but familiar setting.
Seat Location/Proximity -
Location to provide assistive
technology devices or special
equipment.
|
|
Illinois
|
Increase/Decrease Opportunity
for Movement - Provide
opportunities for a student to
stand, move, and/or pace during
the test session (student must
be tested separately so as not
to disturb other test takers).
Other - Familiar room.
Other - Special setting.
|
|
Kansas
|
Small Group
- If student received read-aloud
accommodation in a group for the
assessment items and answer
choices.
Seat Location/Proximity -
Proper seating, sit in front of
room, change location to access
special equipment.
Minimize Distractions -
Change location so student does
not distract others. Change
location to reduce distractions,
reduce visual distractions
Increase/Decrease Opportunity
for Movement - Change
location to increase physical
access.
Other - Access to a
computer lab
|
|
Maine
|
Separate Room
- School site other than regular
classroom; alternative site.
Studentís Home -
Out-of-school setting by school
personnel
Increase/Decrease Opportunity
for Movement - Opportunity
for student to move, stand,
and/or pace during assessment.
Hospital - Out-of-school
setting by school personnel;
out-of-school testing may be
used for students who are
hospitalized.
|
|
Maryland
|
Individual -
A setting accommodation to
reduce distractions would allow
a student to do individual work
or take tests in a different
location, usually in a place
with few or no other students.
Small Group - A setting
accommodation to reduce
distractions would allow a
student to do individual work or
take tests in a different
location, usually in a place
with few or no other students.
Minimize Distractions -
Reduce distractions to student
and surrounding students (in the
case of a distracting
accommodation such as a scribe.)
|
|
Michigan
|
Separate Room
- Administration of the
assessment in a
Bilingual/English as a Second
Language, special education
setting or a distraction free
space or alternate location.
Provision for assessment
administration to student in an
interim alternative education
setting with appropriate
supervision of a school district
professional.
Seat Location/Proximity
-"Placement of student where
he/she is most comfortable
(e.g., front of the room, back
of the room). Placement of
teacher/proctor near student.
Studentís Home -
Provision for assessment
administration at home when
student is homebound or in a
care facility when medically
necessary, with appropriate
supervision by a school district
professional.
|
|
Mississippi
|
Separate Room
- In a familiar room.
Seat Location/Proximity Ė
At the front of the room.
Studentís Home Ė At home
(only for homebound students).
Other - Facing the test
administrator while directions
are given.
|
|
Missouri
|
Seat
Location/Proximity - Testing
with teacher facing the student.
|
|
Montana
|
Individual -
Individual Administration: Test
was administered in a one to one
situation.
Carrel - Reduce
distractors: student is seated
in a carrel or other physical
arrangement that reduces visual
distraction
Separate Room
- Alternative setting: test is
administered to the student in a
different setting.
Seat Location/Proximity -
Front Row Seating: A student is
seated in the front of the
classroom when taking the test.
Minimize
Distractions - Reduce
distractors: student is seated
in a carrel or other physical
arrangement that reduces visual
distraction.
|
|
Nebraska
|
Minimize
Distractions - Reduce
distractions to other students.
Some students use accommodations
that may distract other
students, such as having a
reader or scribe...Distractions
to other students are reduced by
using these accommodations in
individual settings.
|
|
Nevada
|
Carrel -
Provide for test administration
in a study carrel or reasonable
substitute
Separate Room -
Administration in an alternative
setting will be allowed.
|
|
New Mexico
|
Seat
Location/Proximity -
Location appropriate to the
testing needs of students.
Preferential
Increase/Decrease Opportunity
for Movement - Increased or
decreased opportunity for
movement provided.
|
|
New York
|
Seat
Location/Proximity -
Preferential seating.
Minimize Distractions -
Location with minimal
distractions
|
|
North Dakota
|
Studentís Home
- Administration at home for
homebound student, or in a care
facility when medically
necessary with appropriate
supervision by school district
professional.
Increase/Decrease Opportunity
for Movement - Location so
student is able to move, stand,
or pace during test in manner
where othersí work cannot be
seen and student is not
distracting to others.
Hospital - Administration
at home for homebound student,
or in a care facility when
medically necessary with
appropriate supervision by
school district professional.
Other - General education
classroom with adjusted
grouping.
Other - General education
classroom with additional school
support (instructional
assistant, special education or
other teacher) that does not
help student read or respond to
items.
|
|
Oregon
|
Separate Room
- Test an individual student in
a separate location or test a
small group of students in a
separate but familiar location
Seat
Location/Proximity -
Preferential seating.
Studentís Home
- Administering the test at a
studentís home is considered a
modification. Modifications
change the content and/or
performance standards of what is
being measured by the test.
Increase/Decrease Opportunity
for Movement - Support
physical position of student,
e.g. increase/decrease
opportunity for movement, and
provide position assistance.
|
|
Rhode Island
|
Non-School
Setting - Administer the
test with school personnel at a
non-school setting.
|
|
South Carolina
|
Individual -
Individual administration in a
separate location.
Small Group - Small group
administration in a separate
location.
Separate Room - Separate
location.
Seat Location/Proximity -
Preferential seating.
|
|
South Dakota
|
Minimize
Distractions - Location with
minimal distractions.
|
|
Tennessee
|
Separate Room
- Another classroom setting.
Studentís Home -
Homebound students may take the
test at home.
|
|
Texas
|
Physical Support
- Manipulating test materials
for students...such as test
booklet pages, rulers, etc.
|
|
Virginia
|
Seat
Location/Proximity -
Preferential seating
|
|
Washington
|
Separate Room
- Provide a separate testing
location if the student has a
human reader, plays
audio-recordings without
headphones, reads directions and
items aloud, uses speech-to-text
software without headphones.
Seat Location/Proximity -
Change a studentís location
within a room.
Studentís Home - Separate
testing location: home based,
hospital or other (available for
all students submitting a
Medical Exemption request).
Hospital -
Separate testing location: home
based, hospital or other
(available for all students
submitting a Medical Exemption
request).
Other -
Provide architecturally
accessible testing sites.
Other - Assess students
in their instructional setting
(with appropriate test security
procedures).
|
|
West Virginia
|
Other -
Provide physical support for a
student by an aide if this
support is provided routinely
and if the aide has been trained
as an examiner.
|
|
Wyoming
|
Seat
Location/Proximity - Some
students may need equipment that
requires specific locations
(i.e., a deaf student might
benefit from sitting in close
proximity to the interpreter;
another student may need space
for a guide dog).
|
Top of page |



































